Mitosis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Mitosis
Description:
Mitosis & Cell Division Why Divide? Cell Cycle Mitosis The process in which a cell divides to produce two daughter cells. Both daughter cells are genetically ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:327
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Mitosis
1
Mitosis Cell Division
2
Why Divide?
3
Cell Cycle
4
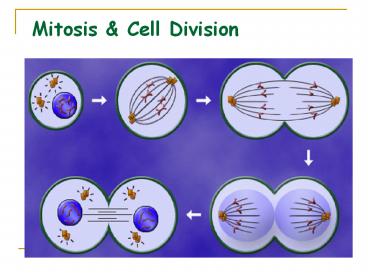
Mitosis
- The process in which a cell divides to produce
two daughter cells. - Both daughter cells are genetically identical
copies of the parent cell and have the same
number of chromosomes. - Focuses on what chromosomes do during cell
division. During mitosis, chromosomes occur in
like-pairs and are referred to as homologous.
5
Figure 12.3 Chromosome duplication and
distribution during mitosis
6
Interphase
- resting phase
- Cell is going through normal activities, but is
resting from division. - When ready to begin dividing the chromosomes
duplicate and DNA is replicated.
7
Prophase
- mitosis begins
- chromosomal material condenses into thread-like
chromosomes - nuclear membrane and nucleolus break up
- in animal cells centrioles divide and begin to
move to the poles (no centrioles in plant cells) - spindles appear
8
Metaphase
- Chromosome pairs move towards the center and line
up on the equator of the cell - A spindle fiber attaches to each of the
centromeres of the chromosomes
9
Anaphase
- paired chromatids separate and are pulled apart
by the spindle fibers to the poles - daughter chromosomes are created (division of
genetic material)
10
Telophase
- clean up stage
- a nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear
- chromosomes unwind
- Spindle fibers disappear
11
Cytokinesis
- Once mitosis is completed (in the animal cell),
the cytoplasm splits - Two genetically identical daughter cells are
produced - Next, the two new cells each begin the cell cycle
12
Cell Division
Plant cell
Animal cell
13
(No Transcript)