Molecular Basis for - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Molecular Basis for
Description:
Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype DNA genotype DNA sequence transcription RNA translation amino acid sequence protein function – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:80
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Molecular Basis for
1
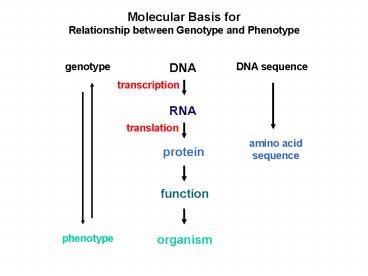
Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype
and Phenotype
DNA
genotype
DNA sequence
transcription
RNA
translation
amino acid sequence
protein
function
organism
phenotype
2
(No Transcript)
3
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation - Transcription
Expression of genes can be - constitutively on
(housekeeping genes ... 15,000 in humans) -
regulated (temporally or spatially ... up to
2000 unique proteins in differentiated cell)
Differentiation is a manifestation of genes
being selectively turned off. Regulation of
gene expression involves - cis-acting
regulatory elements - trans-acting transcription
factors
4
Cis-acting Regulatory Elements
Promoter - located near transcription-initiation
site - binds RNA polymerase II
Promoter-proximal Elements - located near
promoter - binds proteins that assist RNA
polymerase binding Distance-independent
Elements - enhancers increase transcription
rates - silencers decrease transcription rates
5
Promoter and Promoter-proximal Elements
In all cells, constitutive expression of
transcription factors that bind to upstream
promoter elements ensures active transcription at
all times.
6
Promoter and Promoter-proximal Elements
Effect of point mutations on transcription rate
of b-globin gene. In general, transcription rate
is reduced when base sequence is changed in the
core promoter and promoter-proximal elements.
7
Distance-independent Cis-acting Elements
Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription
rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the
binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer
sequences contain multiple binding sites for
trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers
could be located upstream from the promoter,
downstream from the gene, or even within an
intron of a gene.
8
Distance-independent Cis-acting Elements
Interaction between regulatory proteins that bind
to enhancer elements and promoter-proximal
elements with RNA polymerase initiates
transcription at appropriate levels. Architectura
l proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all
components together, both spatially and
functionally.
9
Regulatory Proteins that Modulate Transcription
- These proteins contain one or more functional
domains - Recognize DNA regulatory sequence
- Interact with transcriptional apparatus proteins
(RNA polymerase, proteins associated with RNA
polymerase) - Interact cooperatively with other regulatory
proteins bound to DNA sequence - Influence chromatin condensation
- Act as sensor of intracellular physiological
conditions
10
Transcription Factors
- Transcription factors have
- DNA binding domain (interact with
promoter-proximal elements or enhancers/silencers)
- Transactivation domain (activate or repress
transcription, involved in protein/protein
interaction)
11
Structural Families of Transcription Factors and
Regulatory Proteins
Helix-Turn-Helix Zinc-Finger
Leucine Zipper Helix-Loop-Helix
Many homeotic genes code for TF's of this
class. Many steroid hormone receptor
protein TF's belong to this class.
Proto-oncogenes such as c-jun and c-fos are
genes that encode TF's of this class. Certain
proto-oncogenes and genes involved in
differentiation encode TF's of this class.
12
Structural Families of Transcription Factors and
Regulatory Proteins
Zinc-Finger
Leucine Zipper
Helix-Loop-Helix