Nervous System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 57
Title:
Nervous System
Description:
Neurons. Structures: Axon: long-stem that extends to dendrite of another neuron. Axon hillock: where the axon meets the cell body. Dendrite: receiving node of the neuron – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:89
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Nervous System
1
Nervous System
2
Introduction
- Neurons Nerve cells
- Nerve Impulses transmitted information.
- Nerves are bundles of axons
- Neuroglial cells cells that support the neurons.
- Central Nervous System (CNS) brain and spinal
cord - Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Connects the
CNS to the rest of the body.
3
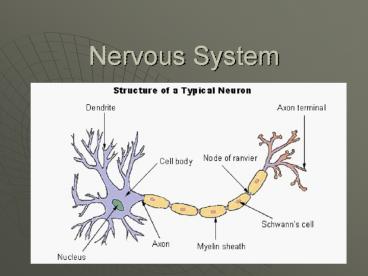
Anatomy of a Neuron
- 4 Parts
- Cell Body
- Rounded area
- Dendrites
- Receive electrochemical messages
- Axons
- Extensions that send information
- Terminal
- - Contains neurotransmitters
4
Functions of the Nervous System
- Receive sensory information from sensory
receptors. - Convert environmental information into nerve
impulses. - Once received, send messages to effectors, which
are responsive structures (i.e. muscles)
5
Functions of the Nervous System
- 2 types of motor functions
- Somatic Nervous System are consciously
controlled - Autonomic Nervous System Involuntary control
6
Types of Neuroglial Cells
- Microglial cells phagocytize bacteria and other
debris - Oligodenmdrocytes provide layers of insulation
(myelin) around axons of the CNS.
7
Types of Neuroglial Cells
- Astrocytes found b/t neurons and blood vessels.
- Help regulate concentrations of ions and
nutrients - Form scar tissue in the CNS
- 4. Ependymal cells cover specialized parts of
the brain. (i.e. choroid plexuses)
8
Classification of Neurons
- Bipolar Neurons
- 2 processes one from each end. 1 is the axon and
1 is the dendrite. - Found in the eyes, nose, and ears.
9
Classification of Neurons
- Unipolar Neurons
- 1 single process extending from the cell body.
- Process will divide into 2 shortly after leaving
the cell body. - Dendrite branches into the PNS. Axon into the
CNS. - Cell bodies can group together to form ganglia
outside the CNS.
10
Classification of Neurons
- Multipolar Neurons
- Have many processes arising from the cell
bodies. - Most neurons in the brain and spinal cord.
11
Classification of Neurons
- Sensory Neurons
- Carry impulses from the peripheral body parts to
the brain and spinal cord. - Either have receptor ends at tips of dendrites or
they are near receptor cells. - Most are unipolar, while some are bipolar.
- Neurons also have functional differences.
- Motor Neurons
- Multipolar
- Carry impulses out of brain and spinal cord to
effectors. - Stimulate muscles to contract and glands to
secrete.
12
Classification of Neurons
13
Classification of Neurons
- Interneurons
- Found in brain and spinal cord.
- Multipolar and link to other neurons.
- Link parts of the brain and spinal cord together
for processing and interpreting.
14
Cell Membrane Potential
- Cell membrane is usually polarized
- Why????
- Distribution of Ions
- Determined by pores or channels in the cell
membrane. - Some are always open, while others open and
close. - K moves easiest, while Ca is slowest.
- Na is medium
15
Cell Membrane Potential
- Resting Potential
- K concentration is usually greater inside the
cell and Na outside. - Always have negative ions inside that cannot
leave. - Difference in charges b/t the 2 regions is called
potential difference. - In a resting cell potential difference is called
resting potential. - Na/K pump
16
Cell Membrane Potential
17
Cell Membrane Potential
18
(No Transcript)
19
Cell Membrane Potential
- A stimulus will affect the resting potential of a
neuron by depolarizing the cell (more on the
inside). - Changes are graded (proportional to stimuli).
- Once the threshold stimulus has been met. The
action potential occurs
20
Cell Membrane Potential
- Action Potential
- Once depolarization occurs it causes the Na
channels to open up. - This causes repolarization.
21
Cell Membrane Potential
22
Nerve Impulse
- Is caused by a wave of action potentials moving
down through the axon.
23
Impulse Conduction
- Conduction is much faster when the axon is
myelinated. - Impulse jumps from schwann cell to schwann cell.
- Action potential is met at the nodes of ranvier.
- All impulses are All-or-None.
24
Synaptic Transmission
- Synapse is the junction between communicating
neurons. - Terminal releases neurotransmitters across the
membrane
25
Neurotransmitters
- Impulses that increase membrane permeability are
said to be excitatory. - If they decrease called inhibitory
- Terminals from many neurons may communicate with
the dendrites of other neurons.
26
Neurotransmitters
- About 50 types.
- Common
- Acetycholine muscles
- Norepinephirne makes you feel good.
- Dopamine feeling good. Low levels assoc. with
Parkinsons - Serotonin- leads to sleepiness,mood, emotion, and
aggression - Histamine Promotes alertness
27
Nerve Pathways
- Reflex Arc Simplest path with few neurons.
- Reflex- Automatic subconscious response to a
change in stimuli.
28
Meningges
- Surround the CNS.
- 3 layers
- Dura mater outermost layer
- Arachnoid layer
- Pia mater layer
29
Brain - General
- About 100 billion multipolar neurons
- 3 major portions
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Brain stem
30
Brain - General
- Cerebrum
- Largest
- Centers associated with motor and sensory
functions and higher mental functions. - Memory and reasoning
- Diencephalon processes sensory
31
Brain - General
- Cerebellum
- Coordinates voluntary muscular movements.
- Brain stem
- Connects parts of the nervous system and
regulates some visceral activities.
32
Structures of the Cerebrum
- Cerebral hemispheres
- Divided by the corpus callosum
- Convolutions (gyri) ridges
- Sulcus grooves
- Fissure deep groove
33
Lobes of the Cerebrum
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Temporal
- Occipital
- Cerebral Cortex is the most superficial layer of
the cerebrum made up of gray matter. - Where do you find gray matter?
34
Functions of the Cerebrum
- Motor areas are found in the frontal lobe
- Motor neurons from one hemisphere cross over to
other hemisphere at the brainstem - Controls speech
35
Functions of the Cerebrum
- Sensory areas acquire information from
receptors, produce feelings, and sensations. - Found in parietal along the central sulcus,
posterior occipital lobe, temporal lobe, taste is
along the central sulcus and lateral sulcus. - Like motor neurons they to cross over.
36
(No Transcript)
37
Functions of the Cerebrum
- Association areas are neither sensory or motor.
- They connect the two
- Oversee memory, reasoning, verbalizing, judgment,
and emotion.
38
Hemisphere Dominance
- 90 of population the left side is dominant
- Nerve fibers in the corpus callosum connect the
two hemisphere.
39
Ventricles and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
- Ventricle a space in between the cerebral
hemispheres that contains CSF. - Choroid Plexus is a ventricle that secretes CSF.
- CSF helps protect and maintain homeostasis.
40
Diencephalon
- Located between the cerebral hemispheres and
above the midbrain. - Thalamus main center for sensory impulses such
as pain, touch, and temp. - Hypothalamus maintains visceral activities, by
linking the nervous and endocrine systems.
41
Diencephalon
- Optic tracts and optic chiasm.
- Pituitary gland
- Pineal gland
- Limbic system thalamus, hypothalamus, and basal
nuclei. - Controls emotional experiences
42
Brain Stem
- Connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord.
- Composed of the
- Midbrain reflex center for visual and audio.
- Pons rounded bulge underneath brain stem.
- Help cerebrum and cerebellum communicate.
43
Brain Stem
- Medulla Oblongata controls cardiac, vasomotor,
and respiratory. - Also reflexes such as coughing, sneezing,
swallowing, and vomiting - http//www.exploratorium.edu/memory/braindissectio
n/index.html
44
Cerebellum
- Large mass below the occipital lobe.
- Center for integrating sensory motor responses.
- Damage would result in tremors and inaccurate
movements.
45
Peripheral Nervous System
- Nerves that branch out from the Central Nervous
System. - 2 Types
- Somatic Nervous System oversees conscious
activities - Sensory
- motor
- Autonomic Nervous System Visceral activities
- Parasympathetic
- sympathetic
46
Cranial Nerves
- Olfactory smell
- Optic sight
- Oculomotor eye movt
- Trochlear eyemovt
- Trigeminal sensation to mouth and face, chewing
- Abducers eye movt
- Facial contraction of facial muscles - taste
- Facial contraction of facial muscles taste
- Vestibulochoclear balance and hearing.
- Glosspharyngeal swallowing and taste
- Vagus Autonomic activity of visceral organs
- Accessory head, neck,and shoulder movt
- Hypoglossal tongue movt
47
(No Transcript)
48
Spinal Cord
- Made up of 31 segments that all give rise to
spinal nerves. - Involved with many motor reflexes
- Cervical enlargement gives rise to nerves of
upper limbs - Lumbar enlargement gives rise to nerves of lower
limbs.
49
(No Transcript)
50
Types of Receptors
- Chemoreceptors
- Pain receptors
- tissue damage
- Thermoreceptors
- Mechanoreceptors
- changes in pressure or movement.
- Photoreceptors
51
Somatic Senses
- Touch and Pressure
- Found in epithelial and connective tissue.
- Temperature
- Warm and cold receptors.
- Rapidly adapt.
52
Somatic Senses
- Pain
- Receptors every where except the brain.
- Only receptors in the viscera
- Visceral pain may act as referred pain
53
Special Senses
- Olfactory Receptors
- Smell
- 12 million receptors
- Gustation (taste)
- 10,000 taste buds
- Tastes
- Sweet
- Sour
- Salty
- bitter
54
Special Senseshearing
- Hearing
- External Ear
- Auricle Funnel shaped
- External auditory meatus cannal
- Middle Ear
- Eardrum membrane covered by thin layer of skin
- Auditory ossicles
- Malleus
- Incus
- stapes
55
Special Senseshearing
- Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the
throat. - Inner Ear
- Semicircular canals which provide a sense of
equalibrium. - Cochlea functions for hearing.
56
Special SensesVision
- Cornea transparent bulge forward where light
enters - Sclera white portion of the eye.
- Iris colored portion
- Lens Lies behind Iris
- Pupil opening that allows light to enter.
- Retina contains visual receptors
57
Special SensesVision
- Rods photoreceptor that receives black and
white. - Cones photoreceptor that receives color.
- Fovea sharpest vision.
- Optic nerve is where your blind spot is.