Molecules of Life Biomolecules - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
Molecules of Life Biomolecules
Description:
Title: 6.3 Molecules of Life Last modified by: Williams, Maria Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) Company: mrs User Other titles: Arial Calibri Office ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:163
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Molecules of Life Biomolecules
1
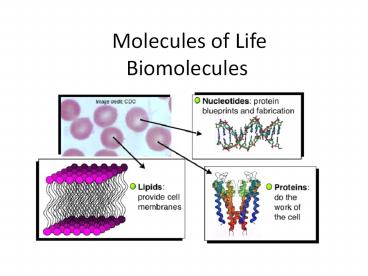
Molecules of LifeBiomolecules
2
- Monomers simplest subunits, building blocks
- Polymers repeating monomers
3
- Monomers join to form polymers through the
process of condensation (removing a water
molecule) - Condensation is also known as polymerization!
4
(No Transcript)
5
- Hydrolysis breaking down polymers (adding a
water molecule)
6
4 classes of Life Substances
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Nucleic Acids
7
Journal 1
- Why might a coach tell an athlete to eat pasta
the night before an athletic event? - What major class of bio-molecules is pasta a part
of?
8
Carbohydrates (Carbs)
- Composed of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
- Used by cells to provide ENERGY
- Fuel for the cell
9
Carbs continued
- Monomer is called a monosaccharide
- Polymer is called a polysaccharide
- Examples
- Monosaccharide glucose
- Polysaccharide starch in plants, glycogen in
animals
10
Journal 2
- List anything that you associate with protein.
- What does your list have in common?
11
Proteins
- Functions
- forms muscle tissue
- transport oxygen in blood
- provide immunity (antibodies)
- carry out chemical reactions (enzymes)
- Receptors
12
Proteins Continued
- Monomer amino acid
- Polymer polypeptide
- (3 or more amino acids)
- Polypeptides are formed by peptide bonds.
13
- Polypeptides are formed by peptide bonds
14
Levels of Protein Structure
15
(No Transcript)
16
- There are about 20 common amino acids that are
the building blocks of 1000s of different
proteins. - Journal 3 How can this be??? Propose an
explanation.
17
- Some amino acids are acidic, others are basic,
and some are neutral. Polar/nonpolar - This causes the amino acids to interact in
different ways to each other. Some attract, some
repel. - Unique
- properties
- unique shapes
- unique functions
18
(No Transcript)
19
- Based on the unique sequence of the amino acids
in a particular polypeptide the protein will
fold in a particular way. - With 20 different amino acids, the variety of
sequences and shapes that will result is
limitless!!!
20
- Enzymes a special class of proteins
- Function Increase the rate of a reaction by
lowering the amount of energy required for the
reaction to take place. - PLEASE CAREFULLY READ AND UNDERSTAND PAGE 162 of
your text book (B) Biology The dynamics of Life
(Whale cover)
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
Lets Review.
- What is a monomer?
- What is a polymer?
- What is the building block of Carbohydrates?
- What is the building block of Proteins?
24
Lipids
- Monomers fatty acids, glycerol
- Polymer trigylcerides, phospholipids, wax
25
(No Transcript)
26
- Used for long term energy storage, insulation,
and protective coverings. - Examples- Fats, oils, waxes
27
Journal
- How is information passed along in cells???
- What codes for everything????
28
Nucleic Acids
- Store hereditary information in a code
- Monomer nucleotide
29
Nucleic Acids
- Polymers DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
- RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
30
- The end of todays lesson.
- Time to Review!!!