Numeriska ber
1 / 33
Title: Numeriska ber
1
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
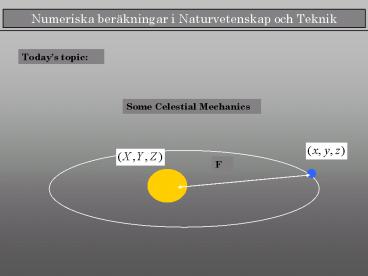
Todays topic
Some Celestial Mechanics
F
2
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Coordinate systems
Cartesian coordinates
Unit vectors are Orthogonal with norm 1
3
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Cylindrical coordinates
4
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Vector- och scalar product in cylindrical
coordinates
Orthogonal
Right hand system
5
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Spherical coordinates
6
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Introductory mechanics
Force law
Torque
Angular momentum
gives
7
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
The angular momentum is constant...
8
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
r x p is orthogonal to r, i.e. r is orthogonal to
L which is constant.
Central force
1 Angular momentum is a constant of motion 2.
Motion is in a plane
9
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
To write down the equations of motion we need the
acceleration in cylindrical coordinates
10
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Velocity in cylindrical coordinates
Motion in the plane due to central force
Radial velocity
Angular velocity
11
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Acceleration in cylindrical coordinates
12
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Acceleration in cylindrical coordinates
13
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Acceleration in cylindrical coordinates
Ins. from above
14
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Equations of motion in the central force system
with the acceleration in the plane
this can also be written as
15
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Equations of motion in the plane in cylindrical
coordinates
Depends explicitly on the force
Can be integrated without defining F
Now, use the following trick...
i.e.
Which gives
16
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Sector velocity
Keplers second law
17
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Rho direction Equations of motion in the plane
in cylindrical coordinates
We want only one variable. So eliminate phi
Now use
since
We have
i.e
18
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
The energy is a second constant of motion...
19
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
A second constant of motion
For a conservative force, i.e. a force with
potential
Multiply by
new trick...
These are equal
20
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Continue by looking at the left hand side
in the eq. below
l.h can be written
We now have time derivatives on both sides of
this equation!
i.e.
21
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
The velocity is
From L constant we have (still)
22
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Solving the equations of motion
One can now either try to integrate with respect
to the time, t, or, one can solve with respect
to the angle. We start with the latter case and
transform the time derivative to a derivative
with respect to the angle phi
23
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Solving the equations of motion
At this point we have
but
Binet!
24
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Solving the equations of motion
Binets equation for the kepler case (1/r2 )
Second order diff equation. (solve with secular
equation!)
25
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Different orbits
Reference direction when a is zero
26
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Different orbits
Investigate in the project!
27
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Orbial motion?(t)
28
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Orbital motion?(t)
This integral can in principle be solved t(?) but
its invertion ?(t) is not possible in simple
functions. The same is true for the angle as a
funtion of time.
What to do?
29
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Variable substitution...
Half major axis
Eccentric anomaly
Mean anomaly (ohmega constant, if e0) Actual
angle true anomaly)
30
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
After this substitution...
Keplers third law (can also be found from
geometical considerations)
31
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Generally at time t
Keplers equation
How find ?(t)?
Only numerical solution
Gives ? for this t!
32
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Two body problem
For two interacting bodies the mass above is
substituted by the so-called reduced mass
Three body problem...
Many tried to solve it (Poincare and other) but
no solution exists in simple analytical form.
Power series expansions exist. The problem has a
very interesting backgroun story. As an example,
find and read on your own the story behind the
Mittag-Leffler prize.
33
Numeriska beräkningar i Naturvetenskap och Teknik
Notera att volymelementet i cylinderkoordinater
är