KNR 445 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
KNR 445
Description:
2. KNR 445. Statistics. Hyp-tests. Slide . Stage 5: The test statistic! So, we insert that threshold value, and now we are asked for some more values The sample mean – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:61
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: KNR 445
1
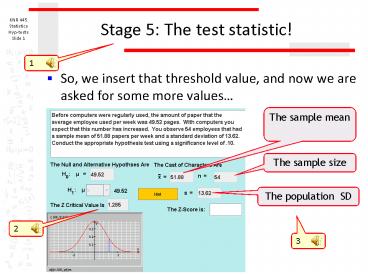
Stage 5 The test statistic!
1
- So, we insert that threshold value, and now we
are asked for some more values
The sample mean
The sample size
The population SD
2
3
2
Stage 5 The test statistic!
- Why do we need these three? Because now we have
to convert our difference score to a score on the
distribution of sample means - Remember this?
The purpose of this statistic was to convert a
raw score difference (from the mean) by scaling
it according to the spread of raw scores in the
distribution of raw scores
1
3
Stage 5 The test statistic!
The purpose of this statistic is the same, but it
converts a sample mean difference (from µ) by
scaling it according to the spread of all sample
means in the distribution of sample means
1
2
3
4
Stage 5 The test statistic!
- Understanding influences on the distribution of
sample meanswell use the applet again
1
Note sample size
note spread of sample means
5
Stage 5 The test statistic!
- Understanding influences on the distribution of
sample meanswell use the applet again
1
As sample size goes up
Spread of sample means goes down
6
Stage 5 The test statistic!
- Understanding influences on the distribution of
sample means - That means that the test statistic has to take
sample size into account - Other influences are mean difference (sample
population) and variability in the population - How do you think each of these things influence
the test statistic? - This will help you understand why the test
statistic looks like it does
1
2
3
4
7
Stage 5 The test statistic!
A closer look to understand how the mean
difference, population variance, and sample size
affect the test statistic, we need to look at the
SEM in more detail
1
8
Stage 5 The test statistic!
1
Population standard deviation
Socan you see the influences?
2
3
4
Sample size
9
Stage 5 The test statistic!
- To calculate, then
- First the standard error of the mean
- Now the test statistic itself
1
10
Stage 5 The test statistic!
- For you to practice, Ive provided a simple excel
file that does the calculation bit for you
1
11
Stage 6 The comparison decision
- Do we fail to reject the null? Or reject the null?
1
12
3 ways of phrasing the decision
- What is the probability of obtaining a Zobs
1.273 if the difference is attributable only to
random sampling error? - Is the observed probability (p) less than or
equal to the ?-level set? - Is p ? ? ?
1
13
Reporting the Results
- The observed mean of our treatment group was
51.88 (? 13.62) pages per employee per week. The
z-test for one sample indicates that the
difference between the observed mean of 51.88 and
the population average of 49.52 was not
statistically significant (Zobs 1.27, p gt 0.1).
Our sample of employees did not use significantly
more paper than the norm.
1
14
Do not reject H0 vs. Accept H0
- Accept infers that we are sure Ho is valid
- Do not reject implies that this time we are
unable to say with a high enough degree of
confidence that the difference observed is
attributable to anything other than sampling
error.
2
1