Bonding in Solids
Title: Bonding in Solids
1
Bonding in Solids
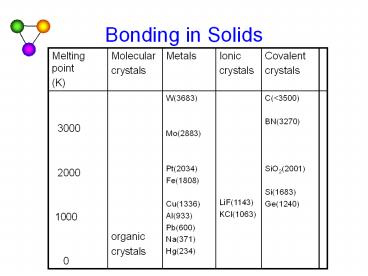
Melting point (K) Molecular crystals Metals Ionic crystals Covalent crystals
3000 2000 1000 0 organic crystals W(3683) Mo(2883) Pt(2034) Fe(1808) Cu(1336) Al(933) Pb(600) Na(371) Hg(234) LiF(1143) KCl(1063) C(lt3500) BN(3270) SiO2(2001) Si(1683) Ge(1240)
2
Crystallography
Crystals can possess point group symmetry
rotation (x,0,z) (xcosj,xsinj,z) j360/n,
n1,2,3,4,6
reflexion (x,y,z) (x,y,-z)
inversion (x,y,z) (-x,-y,-z)
z
(x,y,z)
O
m
y
x
(x,y,-z)
3
Symmetry
Symmetry symbols
2 (360o/2)
2mm (360o/2 two reflexion)
4mm
square
a
60o
120o
6mm
triequiangular net
a
4
Symmetry
z
Symmetry symbols
y
x
Symmetry of a cube
m planes parallel to the faces (3)
m diagonal planes (6)
4 tetrad axes (3)
2 diad axes (6)
3 triad axes (4)
5
Symmetry
There are 32 crystal classes and 230 space groups
(see Practical Crystallography).
Crystal systems
System Axes Min sym
Triclinic (1) a¹b¹c, a¹b¹g¹90o 1,1
Monoclinic (2) a¹b¹c, ab90o¹g 2,m,2/m
Orthrhombic (4) a¹b¹c, abg90o mm,22
Trigonal (1) abc, abg¹90o 3
Tetragonal (2) ab¹c, abg90o 4
Hexagonal (1) ab¹c, ab90o g120o 6
Cubic (3) abc, abg90o Four-3
6
Sterographic projection
The points are projected to the equatorial plane
N
Normals cut the sphere of at some points
Steno law face normals are the same for all
specimens
P
Q
S
Symmetry 4/m
7
Crystal structurelattice basis
Lattice is a regular periodic array of points in
space defined by
Basis is atom or group of atoms attached to every
lattice point
basis
8
Miller Indices
2,3,3
2
Indices of the plane (Miller) (2,3,3)
2
Indices of the direction 2,3,3
3
9
Miller Indices
100
(100)
Set of dirctions- set of similar directions
resulting from symmetry operation lt100gt Þ 100,
010, 001 lt110gt Þ 6 members lt111gt Þ 4 members
10
Screw axis and glide plane
N-fold screw axes C - combination of rotation
360o/n around C
and translation by integer of C/n
11
Screw axis and glide plane
Glide plane - translation parallel to the glide
plane by a/2
b
g
c
a
a/2
a/2