Work - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Work
Description:
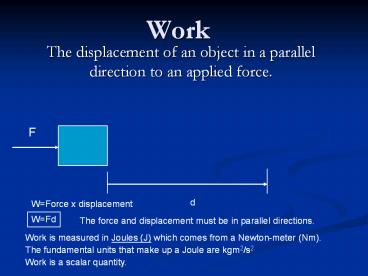
Work The displacement of an object in a parallel direction to an applied force. F d W=Force x displacement W=Fd The force and displacement must be in parallel directions. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:268
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Work
1
Work
- The displacement of an object in a parallel
direction to an applied force.
F
d
WForce x displacement
WFd
The force and displacement must be in parallel
directions.
Work is measured in Joules (J) which comes from a
Newton-meter (Nm).
The fundamental units that make up a Joule are
kgm2/s2
Work is a scalar quantity.
2
Vertical Work
hf
F
FW for a mass lifted at constant velocity
d
dchange in heightfinal height initial height
hi
Vertical Work Work(weight)(?h)
W
3
d
F
No work is accomplished by force F in this
situation.
4
Work
- Also defined as a transfer of energy.
- Whenever work is accomplished, energy of some
type is transferred.
5
Work by various components
f
F
d
WFFd Work accomplished by force, F moving a
distance d Wf -fd Work accomplished by
friction through a distance, d.
Constant velocity Net work is zero WnetFnet(d)(F
-f)dFd-fdWF-Wf0
Acceleration WnetFnet(d)mad(F-f)dWF-Wf
6
Work is positive when the force and
displacement are in the same direction.
F
d
F
Work is negative when the force and displacement
are in opposite directions.
d
- Positive work
- Work is accomplished by the force.
- Energy in transferred into the system
- Negative work
- Work is accomplished on the force.
- Energy is transferred out of the system
7
- Work is the area under a force-displacement graph.
8
Power
- Power is the rate of doing work.
- Power is the rate of energy transfer.
- Power Work/time ? P W/t
- Power (F)(d)/t F(d/t)
- Power Force x velocity ? PFv
- v average velocity (vfvi)/2
- P ? (N)(m)/s (J)/(s)(kgm2/s3) Watt
- Power is measured in Watts, abbreviated W.
- 1 horsepower 746 Watts (1 hp 746 W)
9
Work in Various Directions
d
10
Situation 1
An object pulled at an angle on a level
horizontal surface.
F
The applied force F and d are not in a parallel
direction.
WFxd
Fx
FxFcos?
W(Fcos?)d
d
11
Situation 2
h
W
?
x
Given W, x, ?
hxtan?
WorkWhWxtan?
12
Situation 3
d
F
?
x
Given F, x, ?
dx/cos?
WFd
13
Situation 4
F
d
?
?
x
F
Given F, d, ?
xdcos?
or
F!!Fcos?
WFx WFdcos?
WFdFdcos?