Home Health Care and Assisted Living - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Home Health Care and Assisted Living
Description:
Home Health Care and Assisted Living John Stankovic, Sang Son, Kamin Whitehouse Wood, Z. He, Y. Wu, T. Hnat, S. Lin, V. Srinivasan Department of Computer Science ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:124
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Home Health Care and Assisted Living
1
Home Health Care and Assisted Living
- John Stankovic, Sang Son, Kamin Whitehouse
- Wood, Z. He, Y. Wu, T. Hnat, S. Lin, V. Srinivasan
Department of Computer Science, University of
Virginia
AlarmNet is a wireless sensor network (WSN)
system for smart health-care that opens up new
opportunities for continuous health monitoring in
assisted-living or residential facilities. It
provides real-time (24/7) access to physiological
and environmental data, tracks long-term changes
in behavioral patterns, and allows ad hoc
deployment in existing structures. Results
demonstrate a strong potential for improved
quality of medical care.
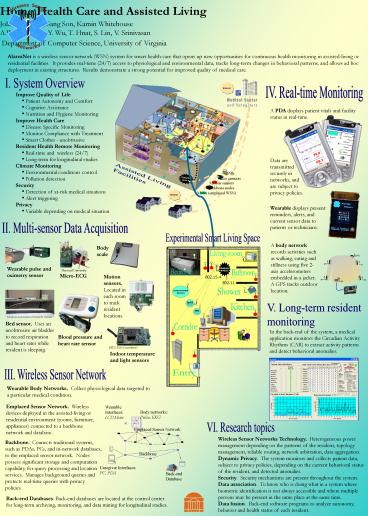
I. System Overview
IV. Real-time Monitoring
- Improve Quality of Life
- Patient Autonomy and Comfort
- Cognitive Assistance
- Nutrition and Hygiene Monitoring
- Improve Health Care
- Disease Specific Monitoring
- Monitor Compliance with Treatment
- Smart Clothes - unobtrusive
- Resident Health Remote Monitoring
- Real-time and wireless (24/7)
- Long-term for longitudinal studies
- Climate Monitoring
- Environmental conditions control
- Pollution detection
- Security
- Detection of at-risk medical situations
- Alert triggering
- Privacy
- Variable depending on medical situation
A PDA displays patient vitals and facility status
in real-time.
Data are transmitted securely in networks, and
are subject to privacy policies.
Pills
Assisted Living Facilities
Video cameras
Motion sensors
Backbone nodes
Motes (emplaced WSN)
Wearable displays present reminders, alerts, and
current sensor data to patients or technicians.
II. Multi-sensor Data Acquisition
Experimental Smart Living Space
A body network records activities such as
walking, eating and stillness using five 2-axis
accelerometers embedded in a jacket. A GPS tracks
outdoor location.
V. Long-term resident monitoring
In the back-end of the system, a medical
application monitors the Circadian Activity
Rhythms (CAR) to extract activity patterns and
detect behavioral anomalies.
III. Wireless Sensor Network
Wearable Body Networks. Collect physiological
data targeted to a particular medical condition.
Emplaced Sensor Network. Wireless devices
deployed in the assisted-living or residential
environment (rooms, furniture, appliances)
connected to a backbone network and database.
VI. Research topics
Wireless Sensor Networks Technology.
Heterogeneous power management depending on the
patterns of the resident, topology management,
reliable routing, network arbitration, data
aggregation. Dynamic Privacy. The system
monitors and collects patient data, subject to
privacy policies, depending on the current
behavioral status of the resident, and detected
anomalies. Security. Security mechanisms are
present throughout the system. Data
association. To know who is doing what in a
system where biometric identification is not
always accessible and where multiple persons may
be present in the same place at the same
time. Data fusion. Back-end software programs
to analyze autonomy, behavior and health status
of each resident.
Backbone. Connects traditional systems, such as
PDAs, PCs, and in-network databases, to the
emplaced sensor network. Nodes possess
significant storage and computation capability,
for query processing and location services.
Manages background queries and protects real-time
queries with privacy policies.
Back-end Databases. Back-end databases are
located at the control center for long-term
archiving, monitoring, and data mining for
longitudinal studies.