NOTES: 2.1 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
NOTES: 2.1
Description:
The Nature of Matter ... H2O Salt NaCl Methane ... Life the time it takes for half the nuclei in a radioactive isotope sample to decay Energy Level of Electrons ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:46
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: NOTES: 2.1
1
NOTES 2.1 The Nature of Matter
2
Key Questions
- Identify the three subatomic particles found in
atoms. - Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are
similar and how they are different. - Explain how compounds are different from their
component elements. - Describe the two main types of chemical bonds
3
What makes up all matter?
- A chemical element is a pure substance that
consists of just one type of atom. - Atoms are the basic unit of matter.
- The atom is the smallest unit which retains all
of the physical and chemical properties of its
element.
4
(No Transcript)
5
- Chemical Compound - A substance formed by the
chemical combination of two or more elements in a
fixed proportion. - The properties of the compound are usually very
different from the elements that make up the
compound.
6
Examples of Compounds
- Water - H2O
- Salt NaCl
- Methane CH4
- Titanium Dioxide TiO2
7
Examples of Compounds
8
Properties of Elements
9
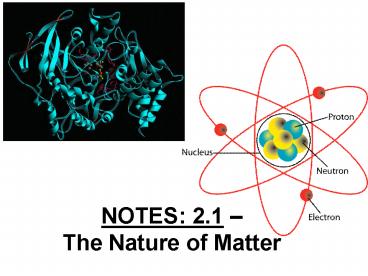
Three Subatomic Particles
Particle Charge Location Mass
Proton () Nucleus 1.0007 amu
Neutron Neutral Nucleus 1.0008 amu
Electron (-) Orbiting nucleus 0.0005 amu
10
- Atomic Number
- -the number of protons in an atom of an element
- all atoms of an element have the same atomic
- written as a subscript next to the elements
symbol - in a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal
to the number of electrons (balanced charges).
11
- Mass Number
- -the number of protons and neutrons in an
atom of - an element.
- The number of neutrons may vary, but the proton
number remains constant. - Written as a subscript next to the elements
symbol
12
Isotopes-
- -Atoms of an element that have more or fewer
neutrons.
13
Isotopes-
- in nature, elements occur as mixtures of
isotopes. - some are radioactive unstable isotope where
nucleus decays emitting sub-atomic particles
and/or energy
14
Half-Life
- the time it takes for half the nuclei in a
radioactive isotope sample to decay
15
Energy Level of Electrons
16
Chemical Bonding
Covalent Bond strong chemical bond between
atoms formed by electrons being shared by the
atoms.
17
- Ionic Bond
- bond formed by the attraction of a positive ion
to a negative ion - Anion positive ion
- Cation negative ion
18
Chemical Reactions bonds between atoms are
formed or broken, causing substances to combine
and recombine as different molecules
CH4 O2 CO2 H2O
19
Chemical Reactions
- All of the chemical reactions that occur within
an organism are referred to as that organisms
metabolism
20
Chemical Reactions
- Reactants
- the substance(s) at the beginning of a reaction
shown on the left side of the equation - Products
- the substance(s) at the end of a reaction shown
on the right side of the equation.
CH4 O2 CO2 H2O