Classification of Simulation Models - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Classification of Simulation Models
Description:
Classification of Simulation Models Static vs. Dynamic Simulation Model ... a Departure of a customer from a queuing model Simulation clock 0 There are 2 approaches ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:181
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Classification of Simulation Models
1
Classification of Simulation Models
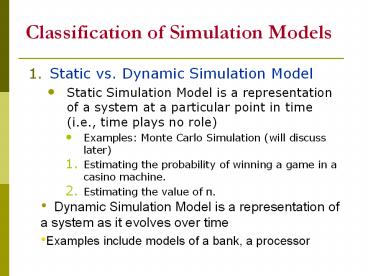
- Static vs. Dynamic Simulation Model
- Static Simulation Model is a representation of a
system at a particular point in time (i.e., time
plays no role) - Examples Monte Carlo Simulation (will discuss
later) - Estimating the probability of winning a game in a
casino machine. - Estimating the value of p.
- Dynamic Simulation Model is a representation of
a system as it evolves over time - Examples include models of a bank, a processor
2
- Deterministic vs. Stochastic Simulation Models
- Deterministic Simulation Model does not
contain any probabilistic components. - Example a system of differential equations
representing a chemical reaction. - Output are also deterministic
- Stochastic Simulation models those having at
least some random input components. - Examples include Queuing models (Interarrival
times between two consecutive customers and
service times are usually random) - They produce output that are also random.
3
- Continuous vs. Discrete Simulation Models.
- Discrete Simulation models those representing
systems whose state changes at discrete points of
time. - Changes of the system occur continuously as the
time evolves
4
Discrete-event Simulation Model
- Simulation models we consider in this course are
discrete, dynamic, and stochastic. Such models
are called Discrete-Event Simulation Models - Changes occur at a separate points of time
- i.e., The system can change only at a countable
number of points in time. - What does it change the system state? Events
- Event is an instantaneous occurrence that
changes the state of the system Examples Arrival
of a new customer, a Departure of a customer from
a queuing model
5
Time-Advance Mechanism
- Simulation Clock is a variable in the simulation
model that keeps track of the current simulation
time (does not depend on the computer time)
0
Simulation clock
- There are 2 approaches for advancing the
simulation clock - Next-event time advance
- Fixed-increment time advance
0
Dt
2 Dt
3 Dt
4 Dt
6
Next-Event Time Advance
- The most common used approach
- The simulation clock is initialized to zero.
- Time of occurrence of future events are
determined. - The simulation clock is then advanced to the time
of the occurrence of the next event (the event
that is scheduled to occur first). - The system is updated taking in account that the
event has occurred. - Update the time of the occurrence of the next
events. - Go to step 3.
- Repeat until a stopping criterion is satisfied.
7
Example A single server Queuing system
- e.g., one-operator barbershop, a cashier in a
supermarket, etc. - Define
- ti time of arrival of the ith customer.
- Ai ti ti-1 the interarrival time between
the (i-1)st and the ith customer. - Si the service time of the ith customer
- Di the delay time in queue of the ith
customer. - ci ti Di Si departure time of the ith
customer. - ei The time of the occurrence of the ith event.
8
The next-event time-advance approach illustrated
for the single-server queuing system.