Homework: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Homework:
Description:
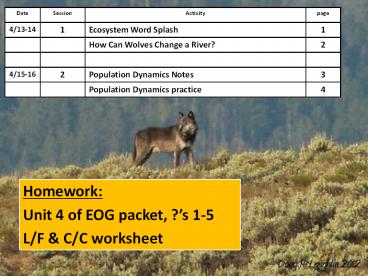
Date Session Activity page 4/13-14 1 Ecosystem Word Splash 1 How Can Wolves Change a River? 2 4/15-16 2 Population Dynamics Notes 3 Population Dynamics practice – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Homework:
1
Date Session Activity page
4/13-14 1 Ecosystem Word Splash 1
How Can Wolves Change a River? 2
4/15-16 2 Population Dynamics Notes 3
Population Dynamics practice 4
- Homework
- Unit 4 of EOG packet, ?s 1-5
- L/F C/C worksheet
2
- 8.L.3 Understand how organisms interact with and
respond to the biotic and abiotic components of
their environment - 8.L.3.1 Explain how factors such as food, water,
shelter, and space affect populations in an
ecosystem. - 8.L.3.2 Summarize the relationships between
producers, consumers and decomposers including
the positive and negative consequences of such
interactions including - Coexistence and cooperation
- Competition (predator/prey)
- Parasitism
- Mutualism
- 8.3.3 Explain how the flow of energy within food
webs is interconnected with the cycling of matter
(including water, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and
oxygen)
3
- TLW describe how various factors affect
populations in an ecosystem by - brainstorming
- Taking notes
- Analyzing graphs
4
Ecosystem Levels of Organization(Hierarchy)
Organism a single member of a species
Population all the organisms of one
species that live in the
same place at the same time. They can
be described
based on their size, distribution or density.
Community all the
different populations that live in an
area
at the same time. This includes plants,
animals, bacteria, etc. All BIOTIC FACTORS
5
Ecosystem Levels of Organization(Hierarchy)
A system formed by the interaction of a
community of organisms with their environment.
This includes biotic and abiotic factors in the
environment
6
Find examples of the different levels of
organization in these two environments.
A B
7
Population Dynamics
- http//www.bbc.com/future/story/20140128-how-wolve
s-saved-a-famous-park - Why do populations look like this
- Instead of this?
8
Why cant we have 1,000,000 students at CHMS?
- Space
- Teachers
- Supplies
- Student behavior
These resources are limiting factors
9
(No Transcript)
10
2 Types of Limiting Factors
- Density Dependent
- These increase their affect on a population as
the population density increases - They are a type of negative feedback that help to
stabilize a population - These are usually biotic
- Density Independent
- These affect a population regardless of its
density/size - They do not act as feedback to slow growth or
stabilize a population. - These are usually abiotic
- Try and sort your list into these two categories
11
Make a list of some of the factors that limit
populations in Yellowstone.
12
- Density Dependent Density
Independent - Food Weather
- Predators Natural Disasters
- Disease
13
Carrying Capacity
- An environment can only support as many organisms
as there is available food, shelter, water and
space. - Carrying capacity maximum number of organisms
that can live in an ecosystem - Limiting factors determine carrying capacity.
14
Imagine Your Fridge
Your fridge is like all of the resources (food,
water, shelter, space) in an ecosystem. What if
we want to throw a party?
15
Imagine Your Fridge
We can keep inviting people, as long as theres
enough food in the fridge.
But with each new guest, theres less to go
around.
16
Imagine Your Fridge
- The fridge wont replenish magically, and I dont
have the money to keep putting food in the fridge
forever. - So too many guests means that
- So too many animals means that
- Someone goes hungry
- Not enough food/water/free space
- And leaves the party. ?
- And organisms die. ?
17
Carrying Capacity
When a population is BELOW its carrying capacity,
it will INCREASE in size Birth rate exceeds death
rates When a population is ABOVE its carrying
capacity, it will DECREASE in size Birth rate
exceeds death rates Until eventually, the
population size BECOMES STABLE AT THE CARRYING
CAPACITY Birth rate death rate http//study.com/
academy/lesson/populations-growth-density-and-carr
ying-capacity.html
18
- What are three
- factors that limit
- deer population
- size?
- Why does
- population size
- decrease in the highlighted portion of the
graph? - At which point does birth rate exceed death rate
the most? - What is the carrying capacity of deer on
WallaWalla Island? - At which point do deer exceed their carrying
capacity?
19
- In what three
- years does
- population size
- most exceed
- carrying capacity?
- Why does the population
- decrease after 1850?
- Why does population size rise again after each
big drop? - Identify three periods of time where birth rate
exceeds death rate - What is the relationship between population size
and carrying capacity between 1800-1840?
20
Within an ecosystem, each species has a
- Habitat the place where an organism lives. It
supplies all the biotic and abiotic factors the
organism needs to survive. - Niche an organisms role/job.
- what it eats, how it eats and what it eats
- If the niche of one organism overlaps the niche
of another organism, you have competition! - http//study.com/academy/lesson/ecosystems-habitat
s-and-ecological-niches.html - Reginald http//www.youtube.com/watch?v2L6N2diE
8jc
21
- What is Reginalds habitat?
- What is Reginalds niche?
22
Ticket Out
- CHOOSE ONE, PART A
- CHOOSE ONE, PART B
- Describe the habitat and niche of the Yellowstone
Park wolves. - Describe the habitat and niche of the Yellowstone
Park Elk - (remember, habitat is NOT A SPECIFIC PLACE)
- Bears eat salmon. If a disease causes massive
amounts of salmon to die, what will likely happen
to the bears? Explain why. - If a population has exceeded its carrying
capacity, what will happen to it? Explain why.
23
(No Transcript)