Unit 7: Cellular Reproduction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
Title:
Unit 7: Cellular Reproduction
Description:
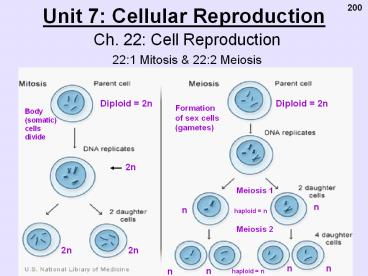
Unit 7: Cellular Reproduction 200 Ch. 22: Cell Reproduction 22:1 Mitosis & 22:2 Meiosis Diploid = 2n Diploid = 2n Formation of sex cells (gametes) Body (somatic ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:243
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Unit 7: Cellular Reproduction
1
Unit 7 Cellular Reproduction
200
- Ch. 22 Cell Reproduction
- 221 Mitosis 222 Meiosis
2
Recall
- Why are cells small?
- to keep surface area to volume ratio high
- How do cells stay small?
- by dividing
- What must happen before a cell divides? Why?
- DNA is replicated so each new cell gets a copy
- Why else do cells divide?
- growth (increase of cells)
- repair damage
- replace old/worn out cells
3
Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes
- Prokaryotes have a single, circular chromosome.
- Cell reproduction is by binary fission.
- chromosome duplicates
- cell divides in ½.
- Each daughter cell is genetically identical to
each other as well as parent cell.
4
What are the 2 Types of Cellular Reproduction in
Eukaryotes?
- mitosis
- meiosis
- occurs in all body (somatic) cells
- cell divides once
- results in
- 2 diploid cells
- with same of chromosomes (as parent cell)
- 46 (23 pairs) (humans)
- function
- growth
- repair
- occurs in (germ) cells of reproductive organs
- ovaries testes
- cell divides twice
- results in
- 4 haploid cells
- with ½ of chromosomes (as parent cell)
- 23 (humans)
- function
- makes gametes (sperm eggs) for sex. reprod.
- promotes variation
5
Diploid Haploid Cells
- What does it mean when a cell is diploid?
- cell contains two of each (type of) chromosome
- thus 2 sets of genes
- 1 from each parent
- How do we indicate that a cell is diploid?
- represented by 2n
- ex. humans ? 2n 46
- What types of cells are diploid?
- ex. somatic (body) cells
6
Diploid Haploid Cells
- What does it mean when a cell is haploid?
- cell contains one of each (type of) chromosome
- thus 1 set of genes
- ½ the original number
- How do we indicate that a cell is haploid?
- represented by n
- ex. humans ? n 23
- What types of cells are haploid?
- ex. gametes (sperm/eggs)
7
Cellular Reproduction Mitosis Meiosis
2n 4 (double stranded)
n 2 (double stranded)
(single stranded)
2n 4 (single stranded)
n 2
n 2
n 2
8
Mitosis (Ch. 221)
9
The Cell Cycle Has 3 Main Phases
- Interphase
- Mitosis
- has 4 parts
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
- Cytokinesis
- I Pee MATt, C?
Which takes longer, interphase or mitosis?
10
A. Before Mitosis Interphase
- What is happening in the cell?
- life functions are being carried out
- DNA is in the form of...?
- chromatin
- What happens before mitosis begins?
- DNA replicates
- forming 2 strands called sister chromatids
- held together by centromere
- centrioles duplicate (in animal cells only)
11
B. Mitosis (ProphaseStep 1)
spindle fibers
centrioles
- What happens during prophase?
- Double-stranded chromosomes become clearly
visible. - Nucleolus nuclear membrane disintegrate.
- (In animals) centrioles move to opposite poles
(ends). - Spindle fibers form connecting centrioles.
12
B. Mitosis (MetaphaseStep 2)
- What happens during metaphase?
- Chromosomes line up single-file at middle
(equator) of cell. - Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers by
centromeres.
13
B. Mitosis (AnaphaseStep 3)
- What happens during anaphase?
- Centromeres divide.
- Sister chromatids are pulled apart (_at_ centromere)
- forming single-stranded chromosomes
- Chromosomes move toward opposite poles (away from
middle).
14
B. Mitosis (TelophaseStep 4)
- What happens during telophase?
- Chromosomes gather at opposite ends of cells.
- Nuclear membrane reforms
- forming 2 new nuclei
- Chromosomes unravel back into chromatin form.
- Nucleoli reappear
- Cytokinesis begins
- cleavage furrow forms (animal)
- cell plate forms (plant)
15
C. After Mitosis Cytokinesis
- When does cytokinesis start?
- during telophase (but cytokinesis is not a phase
of mitosis) - What happens during cytokinesis?
- Cytoplasm is divided
- by cleavage furrow in animal cells
- by cell plate in plant cells
- which becomes new cell wall
- 2 new diploid cells are formed
- have 2 of each chromosome
16
So, What is the End Result of Mitosis?
- The DNA that was duplicated during interphase is
equally divided into 2 new diploid daughter cells - same DNA as parent cell each other
17
Mitosis Animations http//www.sumanasinc.com/webco
ntent/animations/content/mitosis.html http//highe
red.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0
/chapter2/animation__mitosis_and_cytokinesis.html
http//www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/
celldivision/crome3.swf http//www.teachersdomain.
org/asset/tdc02_vid_dnadivide/
18
(No Transcript)
19
What are the 2 Types of Cellular Reproduction in
Eukaryotes?
- mitosis
- meiosis
- occurs in all body (somatic) cells
- cell divides once
- results in
- 2 diploid cells
- with same of chromosomes (as parent cell)
- 46 (23 pairs) (humans)
- function
- growth
- repair
- occurs in (germ) cells of reproductive organs
- ovaries testes
- cell divides twice
- results in
- 4 haploid cells
- with ½ of chromosomes (as parent cell)
- 23 (humans)
- function
- makes gametes (sperm eggs) for sex. reprod.
- promotes variation
20
Cellular Reproduction Mitosis Meiosis
2n 4 (double stranded)
n 2 (double stranded)
(single stranded)
2n 4 (single stranded)
n 2
n 2
n 2
21
Meiosis The Production of Gametes (222)
- What would happen if the of chromosomes wasnt
reduced by ½ during meiosis? - After fertilization there would be 2x the of
chromosomes - How does meiosis promote genetic variation?
- mixing DNA from 2 different parents
22
Meiosis
- Interphase
- Meiosis 1 (separation of homologous chromosomes)
- has 4 parts
- Prophase 1
- Metaphase 1
- Anaphase 1
- Telophase 1
- Cytokinesis 1
- Meiosis 2 (separation of sister chromatids
essentially mitosis) - has 4 parts
- Prophase 2
- Metaphase 2
- Anaphase 2
- Telophase 2
- Cytokinesis 2
23
(No Transcript)
24
A. Before Meiosis Interphase
- What happens during interphase?
- Cell is diploid (has 2 of each chromosome)
- DNA replicates forming double-stranded
chromosomes. - But, the cell is still diploid (2n).
25
B. Meiosis 1 (Prophase 1Step 1)
- What happens during prophase 1?
- Nucleolus nuclear membrane disintegrates.
- (In animals) centrioles move to opposite poles.
- Spindle fibers form, connecting centrioles.
- Homologous chromosomes join (synapsis), forming
tetrads (4 chromatids). - genes may swap (crossing over)
2n
26
B. Meiosis 1 (Metaphase 1Step 2)
- What happens during metaphase 1?
- Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes.
- Tetrads line up (double file) _at_ the middle
(equator). - Can have different arrangements (due to
independent assortment). - What does this cause?
- genetic variability
2n
27
B. Meiosis 1 (Anaphase 1Step 3)
- What happens during anaphase 1?
- Tetrads (pairs of double-stranded homologous
chromosomes) separate. - move towards opposite poles
2n
28
B. Meiosis 1 (Telophase 1Step 4)
- What happens during telophase 1?
- Chromosomes gather at opposite ends.
- Nuclear membrane reforms around each cluster of
chromosomes - forming 2 new haploid (n) nuclei
- with 1 of each double-stranded chromosome.
- Chromosomes unravel back into chromatin form.
- Nucleoli reappear.
- Cytokinesis 1 starts.
n
n
29
C. After Meiosis 1 Cytokinesis 1
- When does cytokinesis 1 start?
- during telophase 1 (but is not a phase of
meiosis) - What happens during cytokinesis 1?
- Cytoplasm is divided
- by cleavage furrow in animal cells.
- by cell plate in plant cells
- which becomes new cell wall.
- 2 new haploid cells are formed
- with 1 of each chromosome.
30
Moving From Meiosis 1 to Meiosis 2
- Replication does NOT occur again before meiosis
2. - Daughter cells from meiosis 1 stay haploid.
- Meiosis 2 happens in both daughter cells.
31
D. Meiosis 2 (Prophase 2Step 1)
- What happens during prophase 2?
- Nucleolus nuclear membrane disintegrate.
- (In animals) centrioles move to opposite poles.
- Spindle fibers form, connecting centrioles.
n
n
32
D. Meiosis 2 (Metaphase 2Step 2)
- What happens during metaphase 2?
- Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes at
centromere. - Double-stranded chromosomes line up (single file)
_at_ equator - so 1 sister chromatid is on each side of equator.
n
n
33
D. Meiosis 2 (Anaphase 2Step 3)
- What happens during anaphase 2?
- Sister chromatids separate (at centromere)
- forming single-stranded chromosomes.
- move towards opposite poles
n
n
34
D. Meiosis 2 (Telophase 2Step 4)
- What happens during telophase 2?
- Chromosomes gather at opposite ends.
- Nuclear membrane reforms around each cluster of
chromosomes - forming 4 new haploid (n) nuclei
- with 1 of each single-stranded chromosome.
- Chromosomes unravel back into chromatin form.
- Nucleoli reappear.
- Cytokinesis 2 starts.
35
E. After Meiosis 2 Cytokinesis 2
- When does cytokinesis 2 start?
- during telophase 2
- What happens during cytokinesis 2?
- cytoplasm is divided
- by cleavage furrow in animal cells.
- by cell plate in plant cells
- which becomes new cell wall.
- What does each new cell end up with?
- combo of chromosomes from mom dad
- Only one chromosome from each homologous pair
n
n
n
n
36
To summarize
- Meiosis Has 2 Stages (Divisions)
- Meiosis 1
- Homologous chromosomes are separated, but are
still double stranded. - Cells become haploid.
- Meiosis 2
- Sister chromatids are separated.
- Still haploid, but now have single strands.
37
End Result of Meiosis
- What is the result of meiosis in males?
- spermatogenesis (formation of sperm)
- all 4 daughter cells become sperm
- What is the result of meiosis in females?
- Oogenesis (formation of eggs)
- only 1 daughter cell becomes ovum (egg)
- other 3 daughter cells are small, nonfunctional
polar bodies
38
spermatogenesis
39
oogenesis
40
Fertilization
- What is fertilization?
- the fusion of sperm egg
- What is formed by fertilization?
- a zygote (which will develop into a baby)
- What happens to the chromosome after
fertilization? - diploid number restored (zygote has 2 of each
chromosome)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
Review Animations
- mitosis
- http//www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/tutorials/
cell_cycle/cells3.html - http//www.johnkyrk.com/mitosis.html
- http//www.accessexcellence.org/RC/VL/GG/mitosis.p
hp - meiosis
- http//www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/co
ntent/meiosis.html - http//www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/
celldivision/meiosis.swf - http//highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/s
tudent_view0/chapter28/animation__stages_of_meiosi
s.html - http//highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/s
tudent_view0/chapter28/animation__how_meiosis_work
s.html - comparison mitosis meiosis
- http//highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072495855/s
tudent_view0/chapter2/animation__comparison_of_mei
osis_and_mitosis__quiz_1_.html - http//www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/divi_flash.ht
ml