Digital Modulation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Digital Modulation
Digital Modulation The discontinuity between analog and digital modulation is that in analog modulation, there are theoretically an infinite number of possible states ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Title: Digital Modulation
1
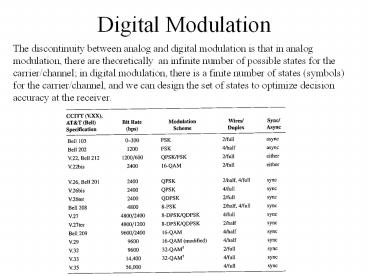
Digital Modulation
The discontinuity between analog and digital
modulation is that in analog modulation, there
are theoretically an infinite number of possible
states for the carrier/channel in digital
modulation, there is a finite number of states
(symbols) for the carrier/channel, and we can
design the set of states to optimize decision
accuracy at the receiver.
2
Phase Shift Keying (PSK)
Bit 1
Bit 0
0
Oscillator
BPSK
0
QPSK
180o
1
1
90o
180o
01
0
1
00
10
11
3
Phase Shift Keying (PSK)
0
Oscillator
Bit 1
180o
1
QPSK
90o
0
Bit 0
180o
1
10
00
01
11
4
Differential Binary Phase Shift Keying(DBPSK)
e.g., A zero causes a 180 degree phase change, a
one causes no phase change.
p
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
Mixer
Rx
LPF
Data
Data
To Phase Modulator
delay
delay
5
Carrier Recovery
BP _at_ fIF
BPF _at_ 2 fIF
Loop Filter
BPSK _at_ fIF
X 2
PD
VCO
X 2
PD
LPF
Data
6
Quiz
- A 3 kHz BW analog signal of 5v p-p is quantized
a resolution of DQ 0.020 volts. - What is the transmitted bit rate (/- 5)?
7
Differential QPSK
Phase Reference Previous Carrier Phase
10
00
01
11
8
Quadrature Demodulation
Q-bit
Carrier Recovery (x4)
00
10
I-bit
QPSK
01
11
90o
LPF
Q-data
LPF
I-data
9
Bit Clock Recovery
T
RZ Signal
I or Q Data
Narrowband PLL fc 1/T
Recovered Bit Clock
T/2 Delay
10
Other Quadrature Modulations
8-PSK
8-QAM (8 Phase)
16-QAM
8-QAM (4 Phase)
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.