Chapter 8: Major Elements - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Chapter 8: Major Elements
Description:
Lithology and thickness of a typical ophiolite sequence, based on the Samial Ophiolite in Oman. After Boudier and Nicolas (1985) Earth Planet. Sci. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:139
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 8: Major Elements
1
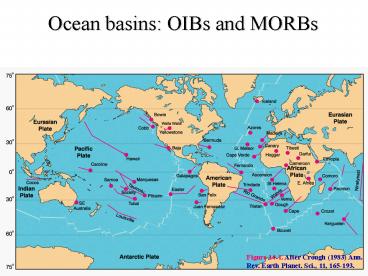
Ocean basins OIBs and MORBs
Figure 14-1. After Crough (1983) Ann. Rev. Earth
Planet. Sci., 11, 165-193.
2
Updates/questions
- Next Wednesday review, midterm on April 2nd
- Lab next week
- Topics
- Systematics for
- Mid ocean ridge basalts (oceanic plate)
- Ocean island basalts (hotspots)
3
Figure 13-3. Lithology and thickness of a typical
ophiolite sequence, based on the Samial Ophiolite
in Oman. After Boudier and Nicolas (1985) Earth
Planet. Sci. Lett., 76, 84-92.
4
Oceanic Crust and Upper Mantle Structure
- Layer 1 sediment
- Layer 2 ab pillows
- c sheeted dikes
- Layer 3 a transitional gabbros
- b layered gabbros -- magma chamber
- Layer 4 ultramafics
- -- cumulates, then mantle
Figure 13-4. Modified after Brown and Mussett
(1993) The Inaccessible Earth An Integrated View
of Its Structure and Composition. Chapman Hall.
London.
5
Petrography and Major Element Chemistry
6
Crystallization Sequence
Constant composition
Constant pressure
Figure 7-2. After Bowen (1915), A. J. Sci., and
Morse (1994), Basalts and Phase Diagrams. Krieger
Publishers.
7
- The major element chemistry of MORBs
8
Major elements
- MgO ?and FeO ? by olivine
- Al2O3 ? and CaO ? by cpx
- SiO2 ? less in crystals
- Na2O, K2O, TiO2, P2O5 all ? not in crystals
Figure 13-5. Fenner-type variation diagrams for
basaltic glasses from the Afar region of the MAR.
Note different ordinate scales. From Stakes et
al. (1984) J. Geophys. Res., 89, 6995-7028.
9
Trace Element Chemistry
Figure 13-10. Data from Schilling et al. (1983)
Amer. J. Sci., 283, 510-586.
10
Trace Element Chemistry
11
Conclusions about MORBs
- Range in MORB composition due to fractional
crystallization - Modeling suggests 60 fractional
crystallization - MORBs have gt 1 source type
- N-MORB
- E-MORB
- Transition between them (T-MORB)
12
OIBs ocean islands and seamounts
13
Types of OIB Magmas
14
Hawaiian Stages-eruptive cycle
- 1. Pre-shield stage variable alkaline/tholeiitic
- 2. Shield-building stage tholeiitic, 98 of the
volcano - 3. Post-shield stage more alkaline, more
differentiated - 4. After 1Ma break, post-erosional stage highly
- alkaline and
- silica-undersaturated
- magmas
15
Evolution in the Series
Figure 14-2. After Wilson (1989) Igneous
Petrogenesis. Kluwer.
16
Trace Elements REEs
Enriched
Depleted
Figure 14-2. After Wilson (1989) Igneous
Petrogenesis. Kluwer.
17
MORB-normalized Spider Diagrams
Figure 14-3. Winter (2001) An Introduction to
Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology. Prentice Hall.
Data from Sun and McDonough (1989).
18
Trace Elements
19
Isotope Geochemistry
- Isotopes do not fractionate during partial
melting of fractional melting processes, so will
reflect the characteristics of the source - OIBs only cross oceanic plate, limiting
contamination (lt-gt continent) good estimate of
mantle
20
Sr Isotope Evolution
Figure 9-13. After Wilson (1989). Igneous
Petrogenesis. Unwin Hyman/Kluwer.
21
Sm-Nd Evolution opposite to Rb - Sr Ctl Crust
(enriched) hi 87Sr/86Sr, lo 143Nd/144Nd
147Sm?143Nd by alpha decay half life 106
Ga Daughter more incompatible
- 143Nd/144Nd (143Nd/144Nd)o
- (147Sm/144Nd)(elt-1)
22
MORB Sr - Nd Isotopes
Figure 13-12. Data from Ito et al. (1987)
Chemical Geology, 62, 157-176 and LeRoex et al.
(1983) J. Petrol., 24, 267-318.
23
MORBOIB Sr - Nd Isotopes
Range in compositions mantle array Every
composition by mixing end-members DM -depleted
mantle EM 12 - enriched mantle HIMU - high m
238U/204Pb 238U -gt 206Pb So high 206Pb/204Pb
DM
MORB
OIB (colors)
HIMU
BSE
EM2
EM1
24
A Model for Oceanic Magmatism
Continental Reservoirs
DM
OIB
EM and HIMU from crustal sources (subducted OC
CC seds)
Figure 14-10. Nomenclature from Zindler and Hart
(1986). After Wilson (1989) and Rollinson (1993).