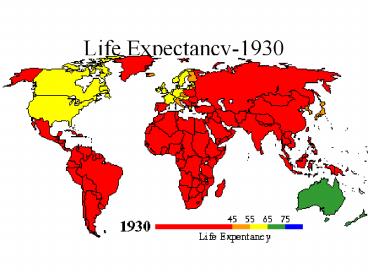
Life Expectancy-1930 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Life Expectancy-1930
Description:
Life Expectancy-1930 – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:109
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Life Expectancy-1930
1
Life Expectancy-1930
2
Life Expectancy-1960
3
Life Expectancy-1990
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
Factors Affecting Human Population Size
8
Current Status
- World Population Size 6.8 billion
- World Growth Rate 1.4, 84 million/year
- U.S. Population Size 273.6 million
6.1 billion people are breeding exponentially.
The process of fulfilling their needs and wants
is stripping Earth of its biotic capacity to
produce life.
9
Birth Death Rates
Birth and death rates are coming down, but death
rates have fallen more sharply than birth rates.
Hence more birth than death occur.
10
Population Growth
Worlds population will double in 52 years
11
Population projections by regions (1999 2025)
Over 95 of this increase will take place in
Developing Countries
12
Total fertility rates in 2000
13
Total fertility rates for the US
14
Infant Mortality Rates
15
3. Human Carrying Capacity
Can the world/biosphere provide an adequate
standard for the increasing population or are we
at the limit?
16
Computer Models
- The Limits to Growth (1972) predicted economic
environmental collapse
17
U.S. 278 million people
- fertility near replacement rate
- continued population increase because of
immigration.
18
India 1 billion1/5 of worlds population
- 1952 first national family planning program
- program disappointing
- fertility still 3.5.
19
China 1.3 billion people 1/5 of worlds
population
- since 1970 efforts to better feed people
control population growth - strict population control measures prevent
couples from having more than one child - although considered coercive, the policy is
significantly slowing population growth.
20
How to Reduce Population Growth?
- improve access to family planning reproductive
health care - improve heath care for infants, children,
pregnant women - improve equality between men women
- increase access to education, especially for
girls - increase the involvement of men in child rearing
family planning - reduce poverty
- reduce eliminate unsustainable patterns of
production consumption.
21
Current Situation
- Each year nearly 11 million children die before
the age of five,30,000 every day,largely from
preventable causes. - 50 of these deaths occur in only six countries
90 of these deaths occur in 42 of 192 countries. - 41 of these deaths occur in Africa, which has
only 10 of the worlds under-five population. - 33 of all child deaths occur in the first month
of life.
22
11 Million Children Die/year (70 From 5 Major
Causes)
Malnutrition 56
Birth Trauma Neonatal Deaths Tetanus Fever Low
Birth Weight
23
Causes of Death in the World Agelt5 yrs
of Deaths
24
Main Causes of Death
Disease or Condition Proportion of Under-five Deaths
Neonatal Illnesses 33
Diarrhea 22
Pneumonia 21
Malaria 9
AIDS 3
Measles 1
Other 9
Malnutrition is an underlying cause of 53 of all child deaths Malnutrition is an underlying cause of 53 of all child deaths
Source The Lancet. Vol.361, June 28, 2003
25
Under-Five Mortality Rate Regional and Global
Averages
Deaths per 1,000 Live Births
Source UNICEF Times Series Estimates, 2000
Year
26
(No Transcript)
27
Neonatal Mortality Relative to Infant Mortality
Deaths per 1,000 Live Births
Source Demographic Health Surveys
Country
28
Infectious Diseases
- Tuberculosis prevention, control treatment
- Malaria prevention, control treatment
- Anti-microbial resistance
- Local capacity for surveillance and response
29
Gaps in Child Survival
- Gaps in child mortality are increasing between
rich and poor countries. - Mortality rates in sub-Saharan Africa average 175
per 1,000, compared to 6 per 1000 in
industrialized countries. - Within countries, gaps in mortality rates between
rich and poor children are also increasing.
30
Urban/Rural Under-five Mortality Rates by Country
Deaths per 1,000 Live Births
Source Demographic Health Surveys
Country
31
We Know What Works
- Six million children each year could be saved
with basic, cost-effective measures such as
vaccines, antibiotics, insecticide-treated bed
nets, breastfeeding, micronutrients, and health
and nutrition education. - We know what it takes to improve child health but
increased resources are needed to ensure all
children have access to these proven measures.
32
Child deaths from HIV/AIDS during 1997
33
Estimated impact of AIDS on under-5 child
mortality rates
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
DALYs
- Disability Adjusted Life Years
- QALY Quality Adjusted Life-Years
- Both are attempts to express burden of disease in
a single number
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
(No Transcript)
48
(No Transcript)
49
(No Transcript)
50
(No Transcript)
51
(No Transcript)
52
Most significant public health achievements in
the U.S. in the 20th Century
- Vaccination
- Motor-vehicle safety
- Safer workplaces
- Control of infectious diseases
- Decline in deaths from coronary heart disease and
stroke - Healthier mothers and babies
- Recognition of tobacco as the major killer and
cause of disease
53
20th Century Environmental Health Events
- 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act
- 1918 Flu Epidemic
- 1948 Donora PA. Air Pollution Episode
- 1952 London England Air Poll. Episode
- 1958 Mercury Poisoning Minamata Bay
- 1962 Rachel Carsons Silent Spring
- 1970 Earth Day-Sen. Gaylord Nelson
54
20th Century Environmental Health Events Cont.
- 1970 U.S. Clean Air Act, EPA, OSHA Created
- 1972 Federal Water Pollution Control Act,
Consumer Product Safety Act - 1974 Superfund Act
- 1975 Safe Drinking Water Act
- 1976 Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
- Toxic Substances Control Act
- 1979 Three Mile Island
- 1984 Bhopal India
- 1986 Chernobyl