Vocabulary - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
Vocabulary
Description:
Title: First Global Age Author: Christensen Family Created Date: 2/6/2005 3:08:05 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Company. Other titles – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:144
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Vocabulary
1
Vocabulary
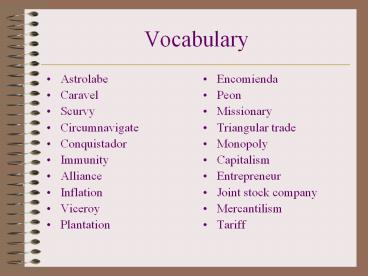
- Astrolabe
- Caravel
- Scurvy
- Circumnavigate
- Conquistador
- Immunity
- Alliance
- Inflation
- Viceroy
- Plantation
- Encomienda
- Peon
- Missionary
- Triangular trade
- Monopoly
- Capitalism
- Entrepreneur
- Joint stock company
- Mercantilism
- Tariff
2
First Global Age
- Chapters 15 16
27
3
The Search for Spices
- Sought a new sea route to Asia
- Wanted to convert others to Christianity
4
Advances in technology
- Improved ships Caravel
- Triangular sails
- Rudder
- Smooth bottom
- Navigational tools
- Improved Magnetic compass (1000 to 1500)
- Astrolabe (1400's)
- Sextant (1730)
5
Portuguese Explorers
- Henry the Navigator mapped the African coast
Bartholomeu Dias rounded the Cape of Good Hope
(1488)
Vasco de Gama reached Calicut in India (1497)
6
Spanish Explorers
- Columbus (1492)
- Oct. 12th landed in Bahamas
- Sailed four times
- Claimed area for the Spanish crown
Vasco Nunez de Balboa (1513) Walked over Panama
and saw the Pacific
Ferdinand Magellan (1519 to 1521) Circumnavigat
ed the globe
7
Treaty of Tordesillas
- Drew a line down the Atlantic
- West is Spains
- East is Portugal
8
Northwest Passage
- English Sent John Cabot Newfoundland
French sent Jacques Cartier St. Lawrence River
Dutch sent Henry Hudson Explored the Hudson
River
9
Summary
- Summarize your notes using at least four
sentences.
10
European Footholds in Southeast Asia and India
- Portuguese controlled the spice trade for most
of the 1500s - Thanks to superior military power
- Dutch replaced the Portuguese
- By the late 1500s
- Built Cape Town as a repair and a resupply depot
11
Mughal IndiaThe world leader in textile
manufacturing
- Ackbar allowed European trading post to be set up
- Successors ended religious tolerance
- Caused a civil war in the 1700s
- European nations were able to extend their
influence into India. - The English and French vied for dominance
- By 1756 they were at war
- Locked in a global power struggle
- By the end of the 1700's Englands British East
India Company ruled India
12
Europeans in East Asia
- The Ming Dynasty
- Had little use for foreigners
- Demanded payment in gold
- Portuguese got a trading post at Macao
- The Qing dynasty (Manchu1680s)
- Restricted foreign contact and trade.
- Chinese territory expanded
- New crops, potatoes and corn
- Population grew 140 million in 1740 to 300
million in 1800 - Rejected British offer of trade
13
Feudal Japan
- Welcomed western traders and missionaries in
1543 - Many Japanese converted to Christianity scaring
Tokugawa shoguns - Loyal to a foreign power the Pope
- Philippines taken over by Spain
- Embarked on a policy of strict isolation that
lasted more than 200 years.
Oda Nobunaga pounded the rice,Hideyoshi baked
the cake,And Tokugawa Ieyasu ate it.
14
Summary
- Summarize your notes using at least four
sentences.
15
The New World America
- First encounters
- Christopher Columbus landed in the West Indies in
1492 - Indians were friendly
- Chris thought they could be converted
- Spanish conquistadors
- Seized the Indians land and enslaved those who
did not convert
Quetzalcoatl.was the Aztex god who was suppose
to return from the East to reclaim his power
16
Hernan Cortez 1519
- Landed with 600 men and a few cannons
- Moctezuma thought he was Quetzalcoatl
- Sent gifts of silver and gold
- Welcomed Cortez into the city
- He drove them out a short time later
- Cortez rebuilt his army with Indians and
destroyed Tenchtitlan - Built Mexico City on the site
17
Inca and Pizarro1532
- Atahualpa won civil war
- Through deception, took Atahualpa hostage
- Incas paid 20 tons of gold and silver
- Pizarro tied him to a stake and strangled him
- By the end of 1500 Incas endangered
18
Spanish Victory
- Military Technology
- Division and discontent among Indians
- Disease
- Attitude toward war
19
Life in Spanish America
- Strict control
- Needed labor imported Africans
- Rigid social structure
- Peninsulares
- Natives
- Slaves
- Blended European, Native and African culture
20
English/French Colonies
William III and Mary II
1689-1702
Louis XIV, The Great King of France, 1638-1715
21
French in America
- Between Verrazanos visit to the Atlantic
coastline in 1524 and the end of the Seven Years
War in 1763, the French colonized or visited
nearly every corner of North America. - Due to a harsh climate its population grew slowly
- Economy based on fur trapping
- Louis XIV sent wives
22
English In America
- Set up 13 Colonies
- Enjoyed a large degree of self government
- Cultural differences
- North.Religious
- South.Money
23
Native Americans and the Europeans
- Encounters with Europeans often led to disaster
for Native Americans - disease killing many
- clashes over settlers taking their land
- The Indian way of life helped shape the emerging
culture of North America. - learned to grow corn, beans, squash and tomatoes
- adopted their clothing style
- used their trails through the wilderness
24
Summary
- Summarize your notes using at least four
sentences.
25
Turbulent Centuries in Africa
- In the 1400s, Europeans established
trading outposts in Africa. - Never penetrating into the interior
- Harsh treatment reduced trade
- The Atlantic slave trade begins 1500s
- Plantations in the new world needed labor
- Over the next 300 years, 13 million slaves were
imported from Africa - Slave traders
- Africans rounded up slaves from the interior and
brought them to the coast - Europeans bought them and shipped them to America
26
Slave Trade begins in 1500s
Middle passage The middle leg of the trade
network Manufactured goods from Europe, raw
materials from America and slaves from Africa The
passage was brutal 2 million slaves died during
the voyage
27
The Columbian Exchange
- Migration of people and their stuff
- New plants
- New animals
- Technology
- Disease
Old World Horses, Cattle, Pigs, Sheep, Goats,
Chickens Rice, Wheat, Barley, Oats,
Coffee,Sugarcane, Bananas, Melons, Olives,
Dandelions Smallpox, Measles, Chicken
Pox,Malaria,Yellow Fever,Influenza,The Common
Cold
New World Dogs, llamas, guinea pigs, Turkeys
Corn, Potatoes, Beans, Tobacco, Peanuts, Squash,
Peppers, Tomatoes, Pumpkins, Pineapples, Cacao,
Chicle, Papayas, Tapioca, Guavas, Avocados
Syphilis
28
Effects of the Exchange
- By 1700's new foods and technologies had spread
worldwide - At the same time the world experienced a
population explosion - The rise of capitalism (buy low, sell high)
- Entrepreneurs took the risks necessary to make a
profit - Adopted Arab bookkeeping to show profit and lost
- Joint stock companies pooled funds from many
investors - Began to use put out systems (cottage industry)
- Which led to the industrial revolution
- The fierce competition for trade and empire,
created a policy of mercantilism - Colonies existed to enrich the parent nation
- Supply the raw material
- Buy the manufactured goods
- Leads to Imperialism
29
Stay TunedThe Age of Absolutismis coming
30
Summary
- Summarize your notes using at least four
sentences.