The Nervous System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
The Nervous System
Description:
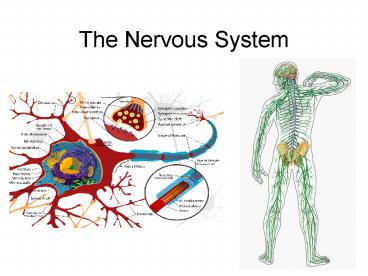
The Nervous System Nervous System Nervous System: Collects information, processes, and responds to internal and external environment Overview of Nervous System ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:84
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Nervous System
1
The Nervous System
2
Nervous System
- Nervous System Collects information, processes,
and responds to internal and external environment
3
Overview of Nervous System
- Stimulus Something in environment causes a
response - Neuron Cell that receive, conduct, and transmit
impulses - Response Reaction to environmental conditions
synapse
RESPONSE!
4
The Neuron
- Neurons build into nerves!
5
Parts of the Neuron
- Dendrites
- Receive messages from previous neurons
- Send message to cell body
- Cell Body
- Contains nucleus and cytoplasm
6
Parts of the Neuron Contd
- Axon
- Long fiber that carries messages away from the
cell body - Myelin Sheath
- Insulating membrane helps send the signal down
the axon - Nodes of Ranvier
- Gaps between Schwann Cells
- Impulse jumps from one node to next
- Schwann Cells
- Supporting cells that wrap around the myelin
sheath
7
Parts of the Neuron Contd
- Axon Terminals
- Branches at the end of an axon
- Contain synapses where neurotransmitters are
released
8
Synapses
- Synapse
- Space between neurons
- Carry messages or impulses from one nerve to the
next - Neurotransmitters
- Chemical messages sent between neurons
- Diffuse to next neuron
9
How does a neuron work? Summary
- Neurotransmitter received from another neuron in
dendrites through cell body - Impulse travels down the axon
- Neurotransmitter released into synapse
- Neurotransmitter received by protein receptors in
dendrites of next neuron
10
A closer look at how an impulse travels down the
axon
- Polarization- differences in charge ( or -)
- Electrical charges are different inside a neuron
compared to outside - Caused by K and Na
- K and Na can move through channels within the
axon membrane
11
A closer look at how an impulse travels down the
axon
- Impulse is carried down the axon
- Resting
- Negative inside (-70 mV)
- Active- Impulse in progress
- Positive inside (40 mV)
12
How does a neuron work?
- http//outreach.mcb.harvard.edu/animations/actionp
otential.swf
13
Types of Neurons
Motor Neuron (Spinal Cord and Brain ? Muscles and
Glands)
Receptor Sensory Neurons (Sensory Organs
?Spinal Cord and Brain)
Interneurons Sends Messages between Nerves
(Sensory, Receptor, Motor, and other Interneurons)
14
Reflex Arc
No brain involved!
Receptor
Afferent Neurons
Sensory Neuron
Spinal Cord
Interneuron
Efferent Neurons
Motor Neuron
Effector (Muscle)
15
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Consists of the brain and spinal column
16
Spinal Cord
- Gray Matter
- Consists of cell bodies
- White Matter
- Consists of axons
17
Parts of the Brain
Meninges- protective covering of the brain/spinal
cord
Corpus Collasum
Occipital
18
Brain Area Function
Meninges Protection of spinal cord and brain
Cerebrum Memory center
Cerebellum Coordination and balance
Medulla Involuntary processes
Spinal Cord Nerves from brain
Thalamus Relay center between brain and spinal cord
Occipital Vision Hearing
Hypothalamus Homeostasis- hunger, thirst, hormones Links endocrine to nervous system
Corpus Collasum Connects left and right brain
19
Peripheral Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System- connects the central
nervous system to the rest of the body - Somatic- voluntary
- Autonomic- involuntary
- Parasympathetic- at rest
- Sympathetic- fight or flight
20
Malfunctions
- Meningitis- swelling of meninges
- Cerebral Palsy- birth defect, affects muscle
coordination - Stroke- blood clot to the brain
- Polio- viral illness
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)- break down of myelin
sheath- impairs movement
21
Malfunctions
- Drug Addictions
- Stimulants
- Increase the number of neurotransmitters
- Depressants
- Decrease the number of neurotransmitters