1: Levels of Abstraction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
1: Levels of Abstraction
Description:
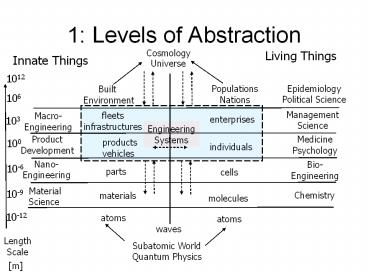
1: Levels of Abstraction Cosmology Living Things Innate Things Universe 1012 Epidemiology Political Science Populations Nations Built Environment 106 Management Science – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 1: Levels of Abstraction
1
1 Levels of Abstraction
1012
106
103
100
Nano- Engineering
Bio- Engineering
10-6
parts
cells
10-9
10-12
Length Scale
m
2
Need for Reconfigurability
Uncertainty Management
Resource Efficiency
System Evolution
Graceful Degradation
3
Stage of Occurence
4
Definitions Reconfiguration Objects
- Modules (in the context of reconfigurability) are
basic units that can be either added, removed, or
transformed during a reconfiguration process, or
in other words, that can be subject to
modification1 - Interfaces are what establish interactive links
between a module and entities that are external
to the module. Each interface can be described in
terms of its nature, extent, timing, and
sensitivity characteristics - Effectors are the elements that are necessary for
carrying out the reconfiguration processes. They
can be internal or external to the
modules/system.
Examples
1 A. Urbani, S.P. Negri,Example of Measure of
the Degree of Reconfigurability of a Modular
Parallel Kinematic Machine
5
Classification
Modules Modules-Nature Interfaces Interface - Nature Processes LC Stage
Iso-Modular (FPGA, satellite cluster, polybot etc.) Physical Common (sectional-modularity systems etc.) Material Transformation (space radar etc) Production (automobiles, aircraft etc)
Iso-Modular (FPGA, satellite cluster, polybot etc.) Physical Common (sectional-modularity systems etc.) Informational Transformation (space radar etc) Production (automobiles, aircraft etc)
Iso-Modular (FPGA, satellite cluster, polybot etc.) Physical Common (sectional-modularity systems etc.) Informational Substitution (for upgrades/repair) Active Operation (morphing UAVs etc)
Poly-Modular (LEGO, RMS etc.) Informational Specific (PSV, morphing UAV) Energy Addition (ISS, buildings etc.) Passive Operation (SR cell phones, FPGAs etc.)
Poly-Modular (LEGO, RMS etc.) Hybrid Specific (PSV, morphing UAV) Hybrid Hybrid Passive Operation (SR cell phones, FPGAs etc.)