Atomic Theory - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Atomic Theory
Description:
Atomic Theory Ancient Greeks believed that elements must be made up of small indivisible particles they called atomos, meaning indivisible where the word atom ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:66
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Atomic Theory
1
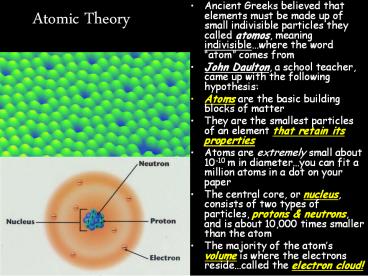
Atomic Theory
- Ancient Greeks believed that elements must be
made up of small indivisible particles they
called atomos, meaning indivisiblewhere the word
atom comes from - John Daulton, a school teacher, came up with the
following hypothesis - Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter
- They are the smallest particles of an element
that retain its properties - Atoms are extremely small about 10-10 m in
diameteryou can fit a million atoms in a dot on
your paper - The central core, or nucleus, consists of two
types of particles, protons neutrons, and is
about 10,000 times smaller than the atom - The majority of the atoms volume is where the
electrons residecalled the electron cloud!
2
Atoms
- Protons have a positive electrical charge
- Neutrons, have no electrical chargethey are
neutral - Both Protons and Neutrons are located in the
NUCLEUS, which is located at the center of the
atomthe nucleus moves! - Most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in
the nucleusthe nucleus is held together by
strong nuclear force - In an atom with no charge, the number of
positively charged protons is balanced by an
equal number of small, negatively charged
particles called electrons. - Electrons have a high kinetic energy but little
massthey are about 2,000 times smaller than a
proton - Remember, an atom that has an equal number of
protons electrons will have no overall charge - Electrons move around in a cloud outside the
nucleus at different energy levels - Each energy level holds a certain number of
electronsThe first energy level can hold 2
electronsThe second energy level can hold up to
8 (atoms like to have a filled outer shell!!) - Electrons do not orbit the nucleus in a defined
path, it is impossible to know exactly where an
electron is at any given time - Electrons, which take up most volume of the atom,
play a major role in chemical reactions
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
Atomic Number Atomic Mass
- All atoms of the same element will have the same
amount of protonsthe amount of protons is the
atomic number of that particular element - The atomic mass of an atom is the number of
protons PLUS the number of neutronsan electrons
mass is so small it is not included in the mass - Atomic Mass Atomic Number (Protons) Neutrons
- Atomic Mass Neutrons Atomic Number (protons)
- Atomic weight (average atomic mass) is the
average of the atomic masses of the isotopes of
each elementit is listed for each element of the
periodic table
7
Elements
- Elements are pure substances that cannot be
broken down chemically into simpler kinds of
matter EACH HAVE THEIR OWN PROPERTIES
(CHARACTERISTCS) - They are made of only one type of atom each
element is made of a different atom. - There are over 100 known elements they are to
molecules as the alphabet is to words All are
located on The Periodic Table of the Elements
which is in order of increasing atomic number - Each element has a different chemical symbol that
is composed of one or two letters - Some of the words are abbreviations of their
Latin names
8
Isotopes
- Atoms of the same element with different numbers
of - neutrons are called isotopes
9
Ions
- Electrons, which take up most volume of the atom,
play a major role in chemical reactions and
bonding - Electrons move around in a cloud outside the
nucleus at different energy levels, or distances
from the nucleus - Each energy level holds a certain number of
electronsThe first energy level can hold 2
electronsThe second energy level can hold up to
8 (atoms like to have a filled outer shell!!) - Electrons like to have a valence (outer) shell
with 8 electrons! - An Ion is an atom or a molecule where the total
number of electrons does not equal the total
number of protons, giving it an overall charge - Ions form when an atom gains or loses one or more
electrons, giving them an overall charge() ions
are called cations, while (-) ions are called
anions - In general, metal atoms tend to lose electrons or
form cations nonmetal atoms tend to gain
electrons or form anions
10
Common Ions
11
Chemical Formulas and Chemical Reactions
- Chemical formulas show the proportion of each
element in each compound (H2O) for example 2
Hydrogen 1 oxygen atom - Properties of a compound differ from the
properties of the elements that compose
itdepends on the type of bond - Most elements undergo chemical reactions to
become stablebonds break, form, and reform - In nature, almost all elements do not exist by
themselves as illustrated on the periodic table - The same elements can make different
compoundsthey have different chemical formulas
(CO, CO2) (H2O, H2O2)look at the elements
involved! - In a chemical formula coefficients show how many
molecules are present - Subscripts show how many of each element are
presentdont write 1 - In a chemical reaction, the molecules or elements
to the left of the arrow are reactants, or what
is present before the reactionto the right of
the arrow are products, or what is formed from
the reaction
NH3
Subscripts
12
Bonding
- In nature, most elements do not exist by
themselves - They are reactive, so they combine with other
elements to form molecules and compounds - A pure substance that is made up of atoms of two
or more different elements is called a compound - An elements ability to form compounds depends on
the amount and arrangement of electrons in their
outer energy levels - An atoms outer energy level electrons are called
valence electrons - Atoms are stable when their outer energy level is
filled!! They bond with each other to make them
filled
13
BondIonic Bond Taken not shared
- Electrons move around in a cloud outside the
nucleus at different energy levels - Each energy level holds a certain number of
electronsThe first energy level can hold 2
electronsThe second energy level can hold up to
8 (atoms like to have a filled outer shell!!) - Sodium has one electron in its outer shell
- Chlorine has seven
- What needs to be done for each to become stable?
- Sodium becomes a positive ion, because it gives
up an electron, while chlorine becomes a negative
ion because it accepts an electronopposite
charges attract, resulting in an ionic bondforms
sodium chloride (table salt) - Common between metals and non metals
- Ionic compounds are electrically neutral, so the
charges will predict the ratio of atoms
14
COVALENT Bond
- Forms by the sharing of electrons between
atomsbetween two nonmetals!! - In the bond, no atom gains or loses electronsno
ions are formed! - Water, for example has one oxygen atom and two
hydrogen atoms held together by covalent bonds - If you recall, hydrogen needs two electrons to
become stable in the outer energy level, and
oxygen needs two (because it has six electrons in
the outer shell) - Therefore, in the presence of one another, they
share electrons - Compounds that dont share the electrons equally
form POLAR COVALENT BONDS in which the electrons
spend more time around one element, creating a
polarized molecule
15
Metallic Bonds
- Metal atoms share electrons equally in all
directions - They are basically a nucleus in a sea of
electrons - This allows metals to be good conductors of
electric current and heat - This also gives them their high melting points
- What are some other characteristic properties of
metals?