Evolutionary Computing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Evolutionary Computing
Description:
Evolutionary Computing Genetic Algorithms Primary Features / Concepts of Evolutionary Computing Genetic Algorithms: Population set of solutions for a ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:133
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Evolutionary Computing
1
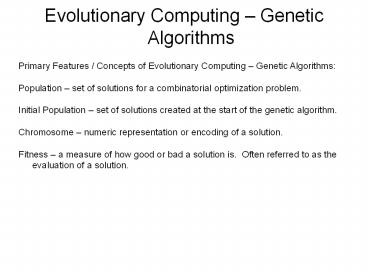
Evolutionary Computing Genetic Algorithms
- Primary Features / Concepts of Evolutionary
Computing Genetic Algorithms - Population set of solutions for a combinatorial
optimization problem. - Initial Population set of solutions created at
the start of the genetic algorithm. - Chromosome numeric representation or encoding
of a solution. - Fitness a measure of how good or bad a solution
is. Often referred to as the evaluation of a
solution.
2
Evolutionary Computing Genetic Algorithms
- Basic Algorithmic Features
- Generate an initial population.
- Evaluate or determine the fitness of individuals.
- Select individuals from the population for the
next generation based on their fitness. - Alter the population through crossovers and
mutations. - Population evolves to become more fit over many
generations.
3
Genetic Algorithms
Set t 0 Generate an initial population P(1) of
size N
Set t t 1
Evaluate the fitness of Individuals within
population P(t)
Select subset of individuals from P(t) to be part
of population P(t1).
Alter the population through crossovers and
mutations, maintaining population size N.
Yes
No
Is t lt T?
Stop
4
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example 10 items available to be
loaded into knapsack of capacity 16. Let 1
represent item loaded into sack, 0 if item not
loaded. Item 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
9 10 Weight 3 4 2 1 3 4 1 2
4 3 Value 3 2 5 4 2 4 3 2 3
4 Example 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 Chromosome
5
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example Let N 6 (usually
larger) Initial Population P(1)
Weight Value Fitness p(1) 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 13
18 16 p(2) 1 1 1 0 1
1 0 1 0 0 18 18
13 p(3) 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
1 16 18 18 p(4) 1
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 15
18 18 p(5) 0 1 1 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 15 20
20 p(6) 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
9 15 15
100 5 point
penalty for being over capacity.
6
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example As a function of the fitness,
randomly select 4 individuals to
remain. Population
Weight Value Fitness p(1)
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 13
16 16 p(3) 0 1 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 16 18
18 p(4) 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0
0 15 18 18 p(5) 0
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 15
20 20
7
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example Crossover (type 1) to create
children
Weight Value
Fitness p(1) 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
1 0 0 13 16 16 p(3)
0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1
16 18 18 p(13) 0 1
1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 21
23 18 p(13) 0 1 0 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 11 11
11 Mutate
Weight Value Fitness p(4)
1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 15
18 18 p(4) 1 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 0 0 17 23
18
8
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example Population P(2)
Weight Value Fitness p(1) gt p(1)
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 13
16 16 p(3) gt p(2) 0 1 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 16 18
18 p(13) gt p(3) 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 21 23 18 p(13) gt
p(4) 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
11 11 11 p(4) gt p(5) 1 1 1
1 0 1 1 1 0 0 17 23
18 p(5) gt p(6) 0 1 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 15 20 20
101
9
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example Randomly select 4 individuals
to remain.
Weight Value
Fitness p(1) 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 13 16 16 p(2) 0
1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 16
18 18 p(3) 0 1 1 0 0 1
1 1 1 1 21 23
18 p(6) 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1
15 20 20
10
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example Crossover (type 2) to create
children
Weight Value
Fitness p(1) 0 1 1 0 0 1 1
1 0 0 13 16 16 p(6)
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1
15 20 20 p(16) 0 1
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 12
16 16 p(16) 0 1 1 0 0 1
1 1 0 1 16 20
20 Mutate
Weight Value Fitness p(1)
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 13
16 16 p(1) 0 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 0 0 14 20
20
11
Genetic Algorithms
Knapsack Example Population P(3)
Weight Value Fitness p(1) gt p(1)
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 14
20 20 p(2) gt p(2) 0 1 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 16 18
18 p(3) gt p(3) 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 21 23 18 p(6) gt p(4)
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 15
20 20 p(16) gt p(5) 0 1 1
1 0 0 1 1 0 0 12 16
16 p(16) gt p(6) 0 1 1 0 0 1
1 1 0 1 16 20 20
112
12
Genetic Algorithms
Issue 1 What is a mutation? A minor
perturbation of a chromosome. Issue 2 How do
you perform a mutation? Example Knapsack
Generate a U0,1 random number for each bit
within the chromosome. 0 1
1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
Chromosome r .37 .46 .03 .78 .25 .92
.56 .43 .21 .37 If r lt pm then flip the bit.
If pm .05 0 1 0 0
0 1 1 1 0 0 Note pm should be
very small. Some claim .01 or .001.
13
Genetic Algorithms
Issue 3 What is a crossover? Parents
producing offspring. Issue 4 How do you perform
a crossover? Example Knapsack generate a
random number r between 2 and the number of bits
in the chromosome. Select 2 parents and r
4 p(1) 0 1 1 0 0
1 1 1 0 0 p(2) 1 0
1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
child (1) 0 1 1 0 1 1 0
0 0 0 child (2) 1 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 0
14
Genetic Algorithms
- Issue 5 How do you perform survival of the
fittest? - Roulette wheel approach
- Calculate fitness value eval(p) for each
chromosome. - Calculate the total fitness value
- Calculate a selection probability for each
chromosome. - Calculate a cumulative probability for each
chromosome. - Generate N-d random numbers r U0,1. Find i
such that qi-1 lt r lt qi . Note, OK to
select same chromosome more than once (identical
twins). d is the number of chromosomes not
selected to move to next generation.
15
Genetic Algorithms
- Issue 6 What is a good population size?
- Not too small (limits search space). Not too
large (computation speed impact and number of
generations produced). - Problem specific.
- Set N 20-100?
- Issue 7 Termination conditions?
- number of generations
- little change in total population value for
successive generations - computation time