1. The Solar System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 42
Title:
1. The Solar System
Description:
Title: Planets of Our Solar System Author: Goulburn Last modified by: McGonigle, Jennifer Created Date: 4/23/2004 1:10:57 AM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:109
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 1. The Solar System
1
1. The Solar System
2
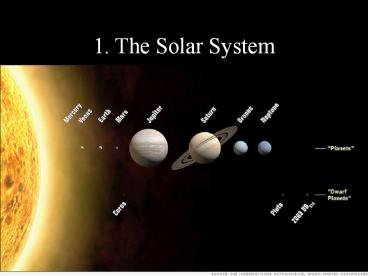
Solar System to Scale (size)
3
2. The Sun is the center of our solar system.
First proposed by Copernicus in 1543.
4
People used to think the solar system was
Geocentric (Earth Centered)
- Early Greeks created this model
- Problems with it included retrograde motion of
planets (a figure 8 path) - http//www.lasalle.edu/smithsc/Astronomy/retrogra
d.html - http//www.youtube.com/watch?v72FrZz_zJFU
5
Later observations confirmed the Heliocentric
Model (Sun Centered)
- Described in 1543 by Copernicus
- Confirmed by Galileo using his telescope to
observe Venus
6
(No Transcript)
7
The Sun contains 99.86 of all the Solar Systems
mass.
8
- The force of gravity from the sun holds our solar
system together. - The larger an objects mass, the greater its
gravitational force.
9
4. Planets closer to the Sun orbit the Sun
FASTER than planets farther from the Sun.
- http//janus.astro.umd.edu/javadir/orbits/ssv.html
- http//www.kidsastronomy.com/solar_system.htm
10
5. Which planet takes longer to orbit the Sun?
- Neptune or Jupiter?
- Mars or Earth?
- Venus or Mercury?
- Uranus or Saturn?
- Pluto takes 248 years to complete one orbit!
11
Why doesnt Mercury have an atmosphere?
- No atmosphere due to
- low gravitational pull (its the smallest planet)
- high daytime temperatures (2nd hottest planet)
- solar winds blast away any remaining gasses
12
What causes Venus to be so warm?
- Heat is trapped due to the intense greenhouse
effect due to the thick atmosphere. - Temperatures average 460 degrees C on Venus
13
Greenhouse Effect
14
Image of Maat Mons- the highest volcano on Venus.
Taken with radar since the temperature and
pressure destroy any probes that land on the
surface.
15
8. What makes Earth different from all other
planets?
- It has liquid water (not just frozen or gas
forms) - Life is found here.
16
9. Identify all the features found near/on Mars
- Ice caps (on N and S poles)
- Volcanoes (largest in the solar system taller
than 3 Mt Everests and wider than Hawaiian island
chain)
17
- No Oceans (may have lots of frozen water or even
salt water below the surface) http//www.google.co
m/mars/ - No life
- A thin atmosphere of mostly carbon dioxide
- Seasons (it has a tilted axis like Earth)
- 2 moons
- No hot temperatures (range is -125C to 35C)
18
10. What elements are primarily found in
Jupiters atmosphere?
- Hydrogen and helium
- If Jupiter were a little larger, it may have
turned into a small star
19
11. Why do we study Jupiters moons?
- Studying these moons add to the knowledge about
the origin of Earth and the rest of the solar
system
20
Saturns rings are made out of particles of
- Ice and rocks
21
13. Uranus is tipped on its side, how did this
probably happen?
- A collision with another object probably tipped
it over.
22
14. When was Neptune discovered and what gases
are found in its atmosphere?
- Discovered in 1846
- Methane gases give Neptune its blue-green color
23
15. Identify reasons why Pluto is different from
the other outer planets
- Only has a thin atmosphere, other outer planets
have thick atmospheres. - Only outer planet with a solid, icy-rock surface
24
Orbit of Pluto
25
The Inner Planets
26
The Inner Planets
- Small in size
- Solid/rocky
27
The Outer Planets
28
Outer Planets
- Large in size
- Made of gas
- Have rings
- Have many moons
29
Dwarf Planetshttp//www.youtube.com/watch?vFqX2Y
dnwtRcfeaturerelated
- Orbit the sun, but have not cleared the
neighborhood- no clean path around Sun - Be spherical in shape, but small
30
What can I see in the sky this Autumn?
- http//www.astronomy.com/asy/default.aspx?caid1
0184
31
Out of this World Lab
- What would be different about life on another
planet? Life on a star? - You will be calculating weight, jumping ability,
and age if you lived on different planets.
http//www.youtube.com/watch?vbDpwtnGS6ucfeature
BFalistPL68BB0B53B47E8190lfresults_main Jumpi
ng http//www.youtube.com/watch?vckHQy84ml4A Fal
ling
32
Vocabulary
- Mass-The amount of matter (stuff) in an object.
- Stays the same from planet to planet
- Weight-A measurement of the gravitational force
acting on an object. - Changes as you move from planet to planet.
33
- Gravitational Force-The force of attraction
between any two objects. - The more massive the object is and the closer it
is, the greater its gravitational force.
34
- Planetary Year-the length of time it takes a
planet to revolve around the sun.
35
Predictions (Hypothesis)
- Weight Possible locations
- Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn,
Uranus, Neptune, Pluto, Sun, White Dwarf - Jumping locations
- Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn,
Uranus, Neptune, Pluto, Sun, White Dwarf - Age Possible locations
- Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
Neptune, Pluto
36
Weight on other planets- MULTIPLY your weight on
Earth by the gravity factor to calculate your
weight on another planet.
Location Weight on Earth Gravity Factor Weight (lbs)-round to the nearest whole number
Mercury 110 0.38
Venus 110 0.91
Mars 110 0.38
Jupiter 110 2.36
Saturn 110 1.06
Uranus 110 0.89
Neptune 110 1.13
Pluto 110 0.07
The Moon 110 0.17
The Sun 110 27.1
A White Dwarf Star 110 1,300,000.00
37
Jump on another planet- DIVIDE the distance of
your jump (in inches) on Earth by the gravity
factor to calculate your jump distance on another
planets.
Location Jump on Earth Gravity Factor Inches jumped (round to the nearest whole number)
Mercury 45 inches 0.38
Venus 0.91
Mars 0.38
Jupiter 2.36
Saturn 1.06
Uranus 0.89
Neptune 1.13
Pluto 0.07
The Moon 0.17
The Sun 27.1
A White Dwarf Star 1,300,000.00
38
Age on another planet- MULTIPLY your age by the
planetary year factor to calculate your age on
other planets.
Location Age on Earth Planetary Year Factor Age (years)
Mercury 12 4.15
Venus 12 1.63
Earth 12 1
Mars 0.53
Jupiter 0.08
Saturn 0.03
Uranus 0.012
Neptune 0.006
Pluto 0.004
39
Conclusions
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vEDab4e6L0c0
- Magic school bus Gains Weight
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vTsXUmiLRroo
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vxICEt51A-Ac
40
Larger objects (more massive) have more gravity
41
Orbiting the Sun
Planet Day Length Day Length Year Length Year Length
Mercury 58.65 0.24 0.24
Venus 243.01 0.61 0.61
Earth 1.00 1.00 1.00
Mars 1.03 1.88 1.88
Jupiter 0.41 11.86 11.86
Saturn 0.44 29.46 29.46
Uranus 0.65 84.07 84.07
Neptune 0.77 164.82 164.82
42
Planet Names
- http//planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/append7.html
- Scale sizes of solar system
- http//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_System_model
- http//joshworth.com/dev/pixelspace/pixelspace_sol
arsystem.html - Scroll to the right