Epistemological Framework for Reuse - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
Epistemological Framework for Reuse
Description:
Title: Progress Report - OU Author: Enrico Motta Last modified by: Enrico Motta Created Date: 5/16/2000 3:18:35 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:59
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Epistemological Framework for Reuse
1
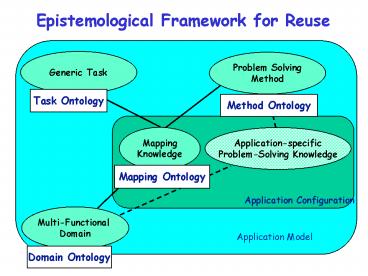
Epistemological Framework for Reuse
Generic Task
Problem Solving Method
Task Ontology
Method Ontology
Mapping Knowledge
Application-specific Problem-Solving Knowledge
Mapping Ontology
Application Configuration
Multi-Functional Domain
Application Model
Domain Ontology
2
A Library of Components for Classification
Problem Solving
3
Main Goals
- To carry out a knowledge-level analysis of
classification - To develop a practical resource to support the
development of classification applications - To provide a concrete set of components to act as
a test case for IBROW brokering system and IRS
4
Classification
- Classification can be seen as the problem of
finding the solution (class), which best explains
a set of known facts (observables), according to
some criterion
Observables
Candidate Sols.
Classification
Solution
Solution Criterion
5
Example
Observables
backgroundgreen areachina...
chinese-granny, dutch-granny, etc..
Classification
Candidate Sols.
Solution
chinese-granny
Criterion
Complete-coverage-criterion (every observable has
to be explained)
6
Observables
- Observables set_of (Observable)
- Observable feature, value.
- Well defined Observables (obs)
- (f1, v1 ? obs ? f1, v2 ? obs) -gt v1 v2
- (f1, v1 ? obs) -gt legal_feature_value (f1, v1 )
7
Solutions
- Solution set_of (Feature_Spec)
- Feature_Spec Feature, Feature_value_spec
- Feature_value_spec Unary_Relation
- Well defined Solution (sol)
- f1, s1 ? sol ? holds (s1, v1 ) -gt
legal_feature_value (f1, v1 )
8
Matching
- Observablef1, v1 matches Solutionsol iff
- f1, c ? sol ? holds (c, v1 )
9
Matching Sets of Obs to a Solution
- Sol fsol1, c1...fsolm, cm Obs fob1,
v1...fobn, vn - Four possible cases
- fj, cj ? sol ? fj, vj ? obs ? holds (cj, vj)
-gt Explained (fj) - fj, cj ? sol ? fj, vj ? obs ? not holds (cj,
vj) -gt Inconsistent(fj) - fj, vj ? obs ? fj, cj ? sol -gt Unexplained
(fj) - fj, vj ? obs ? fj, cj ? sol -gt Missing (fj)
10
Default Match Criterion
- Match Score
- Vector ltI, E, U, Mgt
- Match Comparison Relation
- S1 (i1, e1, u1, m1) S2 (i2, e2, u2, m2)
- S1 better_score than S2 iff
- (i1 lt i2) ?
- (i2 i1 ? e2 lt e1) ?
- (i2 i1 ? e2 e1 ? u1 lt u2) ?
- (i2 i1 ? e2 e1 ? u2 u1 ? m1 lt m2)
11
Other Match Criteria
- SUBSET-BASED-MATCH-CRITERION
- Uses subset instead of lt to determine best match
- ABSTRACTION-AWARE-MATCH-CRITERION
- Matching mechanism able to handle both
observables and abstracted data - EXPLANATION-CENTRED-MATCH-CRITERION
- Focuses on explanation power
- EQUAL-RATING-MATCH-CRITERION
- Very stupid one, which gives every solution the
same score
12
Possible Solution Criteria
- Positive Coverage
- Some feature is explained and none is
inconsistent - Complete Coverage
- All features are explained and none is
inconsistent - No missing features
- No inconsistent features and no missing features
13
Hierarchy of Criteria
Match Criterion
Match Score Mechanism
Match Score Comparison Rel
Macro Score Mechanism
Feature Score Mechanism
14
Observables
- (def-class observables (set) ?obs
- "This is simply a set of observables.
- An important constraint is that there cannot
be two values for the same feature - in a set of observables"
- iff-def (every ?obs observable)
- constraint (not (exists (?ob1 ?ob2)
- (and (member ?ob1
?obs) - (member ?ob2
?obs) -
(has-observable-feature ?ob1 ?f) -
(has-observable-feature ?ob2 ?f) -
(has-observable-value ?ob1 ?v1) -
(has-observable-value ?ob2 ?v2) - (not ( ?v1
?v2))))))
15
Solutions
- (def-class solution () ?x
- "A solution is a set of feature definitions"
- iff-def (every ?x feature-definition))
- (def-class feature-definition () ?x
- ((has-feature-name type feature)
- (has-feature-value-spec type unary-relation))
- constraint (gt (and (has-feature-name ?x ?f)
- (has-feature-value-spec ?x
?spec)) - (gt (holds ?spec ?v)
- (legal-feature-value ?f
?v))))
16
Solution Criterion
- (def-class solution-admissibility-criterion () ?c
- ((applies-to-match-score-type type
match-score-type) - (has-solution-admissibility-relation type
unary-relation)) - constraint (gt (and (solution-admissibility-crit
erion ?c) - (has-solution-admissibility-
relation ?c ?r) - (domain ?r ?d))
- (subclass-of ?d match-score)))
17
Monotonicity of Admissibile Solutions
- (def-axiom admissibility-is-monotonic
- "This axiom states that the admissibility
criterion is monotonic. That is, if a solution,
?sol, is admissible, then any solution which is
better than ?sol will also be admissible" - (forall (?sol1 ?sol2 ?obs ?criterion)
- (gt (and (admissible-solution
- ?sol1 (apply-match-criterion
?criterion ?obs ?sol1)
?criterion) - (better-match-than ?sol2 ?sol1
?obs ?criterion)) - (admissible-solution
- ?sol2 (apply-match-criterion
?criterion ?obs ?sol2)
?criterion))))
18
Complete Coverage
- (def-instance complete-coverage-admissibility-crit
erion - solution-admissibility-criterion
- ((applies-to-match-score-type default-match-score
) - (has-solution-admissibility-relation
- complete-coverage-admissibility-relation)))
- (def-relation complete-coverage-admissibility-rela
tion (?score) - "a solution should be consistent and explain
all features" - constraint (default-match-score ?score)
- iff-def (and ( (length (first ?score)) 0)
no inconsistency - ( (length (third ?score)) 0)))
no unexplained
19
Classification Task Ontology
- 70 Definitions
- Provides both a theory of classification and a
vocabulary to describe classification problems - Ontology is separated from task specifications
20
Generic Classification Task
- Input roles
- Candidate Solutions, Match Criterion, Solution
Criterion, Observables - Precondition
- Both observables and candidate solutions have to
be provided - Goal
- To find a solution from the candidate solutions
which is admissible with respect to the given
observables, solution criterion and match
criterion
21
- (def-class classification-task (goal-specification
-task) ?task - "Classification is defined here as finding one
or more admissible solutions - out of a predefined solution space, which
explain the features of a - given set of observables, in accordance with a
given match criterion and - solution admissibility criterion.
- Because different variants of the goal can be
formulated, the goal - of the task is given here only as a default"
- ((has-input-role value has-candidate-solutions
- value has-observables
- value has-match-criterion
- value has-solution-admissibili
ty-criterion) - (has-output-role value has-solutions)
- (has-candidate-solutions type solution-space)
- (has-observables type observables)
- (has-match-criterion type match-criterion
- default-value
default-match-criterion) - (has-solution-admissibility-criterion
- type solution-admissibility-criterion
- default-value default-solution-admissibility-
criterion)
22
- (has-precondition
- value (kappa (?task)
- (exists (?x ?y)
- (and (member ?x
(role-value ?task 'has-observables)) - (member ?y
(role-value
?task 'has-candidate-solutions)))))) - (has-goal-expression
- default-value
- (kappa (?task ?sols)
- (forall ?sol
- (gt (member
- ?sol
- (role-value ?task
'has-solutions)) - (admissible-solution
- ?sol
- (apply-match-criterion
- (role-value ?task
'has-match-criterion) - (role-value ?task
'has-observables) - ?sol)
- (role-value
23
Specific Classification Tasks
- Single-Solution Classification Task
- Single-solution assumption
- Optimal Classification Tasks
- Goal requires optimality
24
Problem Solving Library
- Based on heuristic classification model
- Includes both data-directed and solution-directed
methods - Supported by a method ontology
25
Method Ontology Main Concepts
- Abstractors
- Mechanism for performing abstraction on
observables - Abstractor Obs -gt Obs
- Refiners
- Mechanism for specialising a solution
- Refiner Sol -gt Sol
- Candidate Exclusion Criterion
- A criterion which is used to decide when a search
path is a dead-end - Default criterion rules out inconsistent solutions
26
Monotonicity of Exclusion Criterion
- (def-axiom exclusion-is-monotonic
- (forall (?sol1 ?sol2 ?obs ?criterion)
- (gt (and (ruled-out-solution
- ?sol1 (the-match-score ?sol1)
?criterion) - (not (better-match-than ?sol2
?sol1 ?obs -
?criterion))) - (ruled-out-solution
- ?sol2 (the-match-score
?sol2)?criterion))))
27
Axiom of Congruence
- (def-axiom CONGRUENT-ADMISSIBILITY-AND-EXCLUSION-C
RITERIA - (forall (?sol ?task)
- (gt (member ?sol (the-solution-space
?task)) - (not (and (admissible-solution
- ?sol
- (the-match-score ?sol)
- (role-value
- ?task
- 'has-solution-admissibil
ity-criterion)) - (ruled-out-solution
- ?sol
- (the-match-score ?sol)
- (role-value
- ?psm
'has-solution-exclusion-criterion)))))))
28
Three Heuristic Classification PSMs
- Two Data-directed
- Admissible Solution Classifier
- Finds one admissible solution according to the
given criteria - Uses backtracking hill climbing
- Optimal Classifier
- Performs complete search looking for optimal
solution - Uses best-first strategy
- Uses candidate exclusion criterion to prune
search space - One Solution-directed
- Goes down the solution hierarchy, acquiring
observables as needed - Ask for observables with max discrimination power
29
Four Assumptions in Main PSMs
- No cycles in abstraction hierarchy
- No cycles in refinement hierarchy
- At least one class in the solution space is an
admissible solution - The solution refinement hierarchy is consistent
with the candidate exclusion criterion. That is
if sol is ruled out, all refinements of sol can
also be ruled out
30
Task-Method Hierarchy
31
Example
- Apple Domain
- Originally developed in Amsterdam
- Solutions Apple Types granny, noble,
delicious... - Hierarchy of Apple Types
- Features bkg-colour, fg-colour, rusty....
- Pretty trivial really!
32
(No Transcript)
33
Mapping Solutions and Obs to Apples
- (def-relation-mapping solution up
- ((solution ?x)
- if
- (or ( ?x apple)
- (subclass-of ?x apple))))
- (def-relation-mapping observable up
- ((observable ?x)
- if
- (or ( ?X (?f ?v ?obs))
- ( ?x (?f ?v)))))
34
More Relation Mappings
- (def-relation-mapping has-observable-feature up
- ((has-observable-feature ?x ?f)
- if
- (or ( ?X (?f ?v ?obs)) ( ?x (?f ?v)))))
- (def-relation-mapping has-observable-value up
- ((has-observable-value ?x ?v)
- if
- (or ( ?X (?f ?v ?obs)) ( ?x (?f ?v)))))
- (def-relation-mapping directly-abstracts-from up
- ((directly-abstracts-from ?ob ?obs)
- if
- ( ?ob (?f ?v ?obs))))
35
Sample Abstractor
- (def-instance sugar-abstractor abstractor
- ((has-body '(lambda (?obs)
- (in-environment
- ((?v . (observables-feature-value
?obs 'sugar))) - (cond ((gt ?v 70)
- (list-of 'sweet-level
'high - (list-of
(list-of 'sugar ?v)))) - ((and (lt ?v 70) (gt ?v 40))
- (list-of 'sweet-level
'medium - (list-of
(list-of 'sugar ?v)))) - ((lt ?v 40)
- (list-of 'sweet-level
'low - (list-of
(list-of 'sugar ?v)))))))) - (applicability-condition
- (kappa (?obs) (member 'sugar
- (all-features-in-observa
bles - ?obs))))))
36
Generic (reusable) Refiner
- (def-instance refinement-through-subclass-of-links
refiner - "If the solution space is specified by means of
classes arranged in a subclass-of hierarchy, then
this is a good refiner to use" - ((has-body '(lambda (?sol)
- (setofall ?sub (direct-subclass-of
- ?sub ?sol))))
- (applicability-condition
- (kappa (?sol) (and (class ?sol)
- (exists ?sub
- (direct-subclass-of ?sub
?sol)))))))
37
Evaluation/Results
- Library provides an analytical tool to understand
classification problem solving - Library tested on a number of domains
- ECAI Paper classification
- Paleontology
- Medical Diagnosis
- No changes the organization of library needed
- Only adding new components, e.g. new match
criteria - Used by van Harmelen and Ten Teije to study
automatic PSM adaptation
38
(No Transcript)