Unit 1 : Macroeconomics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Unit 1 : Macroeconomics
Description:
Production Possibilities Curve Production Possibilities Curve Absolute Advantage and Comparative Advantage ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE One individual or nation can produce ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:36
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Unit 1 : Macroeconomics
1
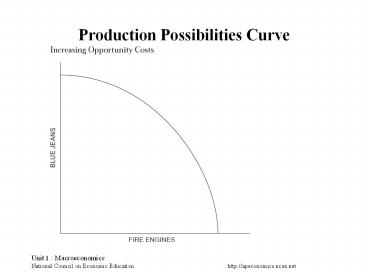
Production Possibilities Curve
2
Production Possibilities Curve
Constant Opportunity Cost
Decreasing Opportunity Cost
3
Absolute Advantage andComparative Advantage
- ABSOLUTE ADVANTAGE
- One individual or nation can produce more
output with the same resources as another
individual or nation. - COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
- One individual or nation can produce a good at
a lower opportunity cost than another - EXAMPLES OF COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE
- Economics professor and secretary
- Auto mechanic and medical doctor
4
Determining ComparativeAdvantage (Output Method)
- Which nation has an absolute advantage in
producing corn? - Which nation has an absolute advantage in
producing sunscreen? - Which nation has a comparative advantage in
producing corn? - Which nation has a comparative advantage in
producing sunscreen? - Should Mexico specialize in corn or sunscreen?
- Should France specialize in corn or sunscreen?
5
Movement Along a Demand Curve
As the price declines from P to P1, the quantity
increases from Q to Q1
6
Shift in Demand
- Factors that Shift Demand
- Number of Consumers
- Price of complementary good
- Price of substitute good
- Consumer income
- Expectations about income or prices
Increase in demand from D to D1 shows that at the
same price (P), the quantity increased from Q to
Q1
7
Movement Along a Supply Curve
As the price declines from P1 to P, the quantity
decreases from Q1 to Q.
8
Shift in Supply
- Factors that Shift supply
- Number of suppliers
- Prices of resources used to produce good
- Prices of related goods produced
- Technology
- Expectations about future prices
Increase in supply from S to S1 shows that at the
same price (P), the quantity increased from Q to
Q1.
9
Equilibrium Quantity and Price
What happens if the price is 10? What happens if
the price is 6? What happens if the price is 8?
10
Calculation of Price Elasticity of Demand
11
Price Elasticity along a Demand Curve
12
Effects of Different Demand Elasticities
Which demand curve is more inelastic? What
happens to the equilibrium price and quantity
with an elastic demand curve if supply
increases? What happens to the equilibrium price
and quantity with an inelastic demand curve if
supply increases?