Population Ecology - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Population Ecology
Description:
Population Ecology – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:260
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Population Ecology
1
Population Ecology
2
By the end of this class you should understand
- The language of ecology and how to describe a
population - The different types of growth and survivorship
curves - How to identify limiting factors of a population
3
Ecology
- Ecology is the study of how organisms behave and
interact with each other - Population Ecology is the study of a single
population of animals (all the same species) - Community Ecology is the study of interactions of
populations - Population ecology often closely studies the size
of a population over time - More sex and violence!
4
Key Population Terms
- Population Size
- Number of individuals in a given population
- Population density
- How closely packed these individuals are on
average - Population distribution
- Whether the individuals are evenly spread out or
clumped in some way
5
Population Size
- The number of individuals in a population depends
on how you define population - May be all animals in a particular region
- May be the entire species
- May be more specific, such as all female or all
with a particular gene - Usually a population includes all organisms that
regularly interbreed - Geographically isolated groups are usually
different populations
6
Population Size Change
- A populations numbers can change due to any
number of factors - Death of organisms
- New organisms being born
- Arrival (immigration) and/or leaving (emigration)
of organisms (especially animals) - If a populations numbers do not change over time
it is never because none of these are happening - This is a stable population and almost never
happens
7
Why No Stable Population?
- Remember the struggle for existence!
- Even if a population is isolated, by natural
selection only the horniest of organisms have
reproduced over the years, so they will always be
trying to make babies - Even if there are only limited resources, the
impulse to make babies cannot be denied - Also, there are always predators and disease
- A population will only be stable if the birth and
death rates perfectly cancel out - They might on one given year but not constantly
8
No Predators Or Disease!
- When there is no emigration and no death, a
population will experience exponential growth - This means a population will double in size every
generation - Generation time varies wildly by species
- Bacteria 20 minutes
- Humans 20 years
- All species will have the same curve though
9
Exponential Growth
- Exponential growth cannot be sustained without
unlimited resources - A resource is anything organisms need to survive
- Some resources are in much larger supply than
others and it varies by environment - In the ocean sunlight is a limited resource and
water is a plentiful resource - In the desert sunlight is a plentiful resource
and water is a limited resource
10
Infinite Resources
- It is obviously not possible to have infinite
resources - Eventually space and air would become limited
resources - That means whichever resource runs out first will
become a limiting factor - Normally predators, parasites and natural
disasters are also limiting factors by causing
death
11
Limiting Factors
- The limiting factors of a population create a
certain theoretical maximum of a population size
that would be stable - This limit is called the carrying capacity
- The carrying capacity is dictated by predators,
limited resources, etc. and is not fixed but an
average - Environments can be created or damaged and
carrying capacities can be changed!
12
Environmental Change
- During the time of the bible, the Levant (in the
middle east) was a very fertile region that was
the birthplace of civilization - After centuries of overfarming the plains and
clear-cutting the forests, it is now a desert - NOT due to climate change!
- Elephants also instigate major changes in local
environments, even without climate change
13
Lets make a list!
- What are some limiting factors on populations?
- Note some of these are density-dependent (more
problematic as organisms are more crowded) - Others are density-independent (no change in
danger as population density increases)
14
Carrying Capacity
- When a population hits carrying capacity it can
hit it in one of two ways - It can level out at the carrying capacity
(logistic growth) - It can overshoot the capacity and then crash
(windfall pattern) - If there are many strong limiting factors then
you usually see logistic growth
15
Windfall Pattern
- True story an empty island off the coast of
Alaska had a substantial buildup of moss when
some humans left a few reindeer on this island - No predators or disease lots of babies!
- The population underwent exponential growth until
the moss was all gone, then crashed during a
harsh winter - Eventually all the reindeer died
16
Windfall Population Pattern
17
Why Is This Relevant?
- All populations have carrying capacities
- Including the human population!
- A pre-industrial society has limiting factors
like disease and lack of food - Industrial revolutions are awesome for sanitation
and farming - A post-industrial society has a low birth rate
because babies are expensive
18
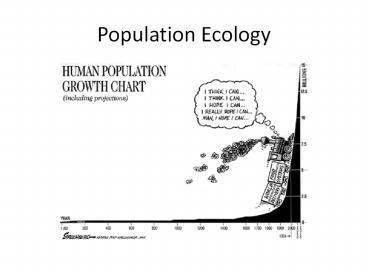
Human Population Growth
- The world didnt hit 1 billion people until
around 1800 - Hit 2 billion around 1927
- 4 billion by 1974
- 7 billion back in 2012
- There are several projections
19
Reproductive Strategies
- Different organisms have different strategies for
survival of the species - Some make tons of babies and hope they survive
- Some put a lot of energy into keeping each
offspring alive - What are some organisms that are on each extreme?
20
Survivorship Curve
- Closely related to the reproductive strategy is
the survivorship curve - Describes the percentage of a group of organisms
that are alive after a given percent of their
maximum lifespan - Organisms that produce many babies have type III
survivorship while organisms that produce few
babies but protect them have type I
21
Survivorship Curves
22
More on Monday!
- See you in lab!