Ecological Relationships - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Ecological Relationships
Description:
Ecological Relationships Important Vocabulary Biotic Factors: living things Abiotic Factors: nonliving, physical things such as: Temperature, sunlight, precipitation ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:884
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Ecological Relationships
1
Ecological Relationships
2
Important Vocabulary
Slide 2
- Biotic Factors living things
- Abiotic Factors nonliving, physical things such
as - Temperature, sunlight, precipitation, soil
- Habitat- The place in which an organism lives.
- Niche An organisms role in the ecosystem
Abiotic Factors
Biotic Factors
COMMUNITY
ECOSYSTEM
3
Five Species of Warblers and Their Niches
Slide 3
- No two species can share the exact same niche in
a habitat. - Shaded areas show where each species feeds (one
factor that defines a niche).
Go to Section
4
Slide 4
Descriptions of a Niche Include
- 1. Its place in the food web
- 2. Conditions Needed for Survival
- a. Temperature Range it has adapted to
- b. Dependance on water
- 3. When and how it reproduces
Top Carnivore
The red legged frog mates from January to March
but the yellow legged frog mates from late March
to May
Yellow Legged frog
Red Legged frog
5
Community Interactions Competition
Slide 5
- Competition occurs when organisms of the same
or different species try to use the same resource
at the same time and place - Resource any necessity for life
- EX water, nutrients, light, food, or living
space
Uniform spacing less competition
Clumped more competition
6
Slide 6
Competition can help define the niche.
Barnacle Species A
Barnacle Species B
7
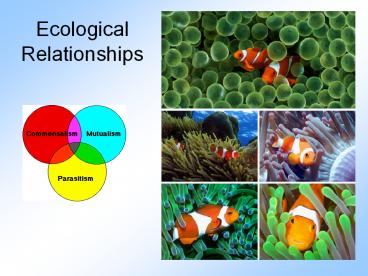
Symbiosis
Slide 7
- Symbiosis close relationship between 2
organisms, in which at least one of the organisms
involved benefits.
8
Symbiosis Parasitism ??
Slide 8
- Parasitism One organism benefits, ? and the
other is harmed (host). ?
Filled with blood
Ticks feed on the blood of the host in which they
live. The closer together organisms live, the
easier these parasites can spread through the
population.
9
Symbiosis Commensalism ??
Slide 9
- Commensalism One organism benefits, ? and the
other is neither helped nor harmed. ?
Barnacles live grow on the bodies of ocean
organisms like whales. However, they do not help
or cause any harm to them.
10
Symbiosis Mutualism ??
Slide 10
- Mutualism Both organisms benefit ?? from the
relationship.
This bird eats insects found on the zebras body.
The bird is high above the ground and has food,
the zebra is removed of pests.
Bees receive food (nectar), while the flowers
pollen is spread for reproduction.
11
Aphids feed on sugary sap from the plant. Aphids
are herded and protected by the ants because the
ants feed on sugary excretions the aphids produce.
Slide 11
-Parasitism
-Mutualism
12
Predator-Prey Relationships
Slide 12
- 1. Predation interaction in which one organism
captures and feeds on another organism - 2. Predator organism that does the killing and
eating - 3. Prey organism that is eaten (food)
Who is the predator?
Lynx
Who is the prey?
Hare
13
Ecological Succession
- 1. Occurs when an area becomes devoid of
vegetation because of a disturbance. - 2. Pioneer species the first to grow in an
area.
Which species is the pioneer species?
Annual grasses
Which community has the greatest biodiversity and
why?
Hardwood forest has the most niches
14
Primary verses Secondary Succession
- Primary succession the initial colonization of
land that has never been colonized before. This
might include areas after a volcanic eruption or
after a glacier recedes. In either case, there
is no starting soil.
Secondary succession is the re-colonization of
areas after a disturbance such as a fire or
abandoned farm land or even when a large tree
falls (such as in the tropical rainforest). Soil
is already in place in the area.