Review of the Periodic Table and its Trends - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title: Review of the Periodic Table and its Trends
1
Review of the Periodic Table and its Trends
2
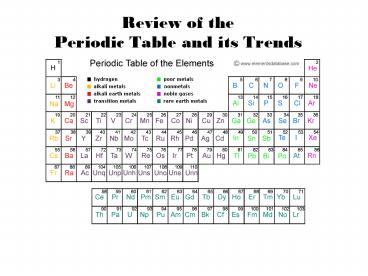
You must be able to read the table!
3
I II
III IV V VI
VII VIII
4
- The Periods and Valence Orbitals
5
- The Groups with a Roman Numeral represent the
Primary or A elements - The others are the Transition Elements or B
elements - The Lathinides and Actinides are the Inner
Transition Elements - The Roman Numeral equals the Number of Valence e-
for that Group - Valence e- are those in the last Energy level (n)
6
(No Transcript)
7
- Dmitri Mendeleev is given credit for developing
the first periodic table based on atomic weight
it allowed him to predict new elements. - However, it was Henry Moseley who set it up using
the atomic number (Z).
8
The First Periodic Trend
- Atomic Radius This varies according to the
distance of the valence e- to the nucleus - Two factors affect atomic radius the valence
shells n (energy level) and the
attractions/repulsions that occur in the atom
9
- Atomic Radius (and Ionic Radius) is measured in
Angstroms or pm or nm - 1 A 10-10 m 0.1 nm 100 pm
- Atomic Radius Decreases
- I
- n
- c
- r
- e
- a
- s
- e
- s
10
- Atomic Radii are measured using
- rcov which measures from the nuclei
- rvdw van der Waals which is used for non-bonding
noble (inert) gases - See the charts handed out for actual radii
11
Metal molecules form lattice structures cube
shaped crystals with an atom at each corner.
12
2. Ionic Radius
- This measures the size of an ion in a crystal
lattice structure - rion increases if a negative ion (anion)
- and decreases with a positive ion
- (cation)
- This is easy to explain a cation has lost e-
and an anion has gained them changing the radius
13
3. Ionization Energy (EI)
- This is the energy needed to remove an e- from an
atom and create a cation - The 1st Ionization Energy is the lowest since it
is removing an e- from the valence shell - EI increases as you get closer to the nucleus due
to an increase in the attraction (EMF) - Measured in eV or KJ/mol
- 1 eV is the charge of one e-
- 1 eV 1.60217653 x 10-19 J 96.48538 KJ/mol
14
- EI Increases
- D
- e
- c
- r
- e
- a
- s
- e
- s
15
(No Transcript)
16
- EI decreases due to distance from the nucleus
and due to the shielding or screening effect - The Shielding Effect is due to the interference
of inner e-s disrupting the forces of nuclear
attraction on an outer e- - This effect, the Z or Zeff measures the amount
of nuclear attraction on any particular electron - Z Z - s
17
4. Electron Affinity (EA)
- EA is the measure of how capable an atom is in
gaining an e- and becoming an anion (negative
ion) - When an e- is gained, a quanta of energy is
released as a photon or gamma particle - This trend really centers on Group VI and VII
- Only Group VI has a 2nd EA
- Measured in kJ/mol or - eV
18
(No Transcript)
19
- E A Increases
- D
- e
- c
- r
- e
- a
- s
- e
- s
20
- 5. Electronegativity (?) or (EN)
- This is the power of an atom to attract e- and
thus, form bonds - There are several scales used to determine
- EN
- 1. The Pauling Scale ranges from 0.7 to 4.0
- The difference in EN between two atoms will
determine what type of bond has been formed
(see the scale handed out in class)
21
- 2. The Mullikan Scale
- Also called the Absolute EN Scale
- Uses the mean of the 1st EI and EA to measure
bond attraction - EN in eV 0.187 (EI EA / 2) 0.17
- EN in kJ./mol (1.97 x 10-3)(Mean) 0.19
- 3. Allred-Rochow EN Scale
- EN is related to charge experienced on surface of
atom
22
- Uses Slaters Rules to find Z
- EN 0.359 (Z / rcov2 ) .744
- 4. Allen EN Scale
- EN nsEs npEp
- ns np
- Es and Ep are an e- energies of the s and p
orbitals in the valence shell - Ns and np are the number of e- in these orbitals
- kJ/mol _____ x (1.75 x 10-3)
- eV _____ x (0.169)
23
- EN Using the Pauling Scale
24
- E N Increases
- D
- e
- c
- r
- e
- a
- s
- e
- s
25
The End. . .
26
(No Transcript)