Potency - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 86
Title: Potency
1
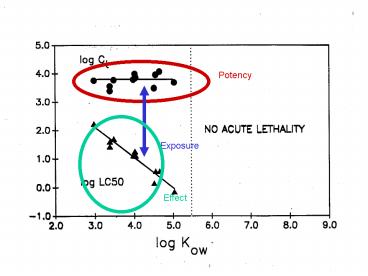
Potency
Exposure
Effect
2
- Recipe for a Toxic Effect
- Ingredients
- Exposure
- Relationship between external concentration and
the concentration at the active site - Potency
- concentration at the active site required to
trigger the effect - Directions
- concentration at the active site gt concentration
at the active site required to trigger the effect
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
Criteria for Inherently toxic (iT) in CEPA, UNEP
- Proposed iT criteria for non-human organisms
- aquatic acute effects levels of lt 1 mg/L
- above 1 mg/L professional judgment considering
other factors (e.g. molecular weight,
metabolism...) - log Kow gt 6 (consideration of effects to
wildlife)
6
1 mg/L
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Non-Polar Narcosis similarity with anesthetics
chloroform Lethality at an internal
concentration 3 to 6 mmol/kg All chemicals all
organisms mechanism unknown likely affect
membranes swells membranes causing a physical
effect affects membrane proteins Narcosis is the
most basic mode of toxic action. Chemicals will
have at least this toxicity or they may have a
greater toxicity.
12
(No Transcript)
13
Acute vs. Chronic Toxicity
Water Concentration pg/L
1 0.5 0.1
Lethal Body burden
14
Mixtures of Chemicals For chemicals that share
Non-Polar Narcosis Mode of Toxic
Action If Scinternal gt 5 mmol/kg Then 50
lethality
15
For Chemicals Acting by Non-Polar
Narcosis Mixture Toxicity Scinternal gt 5
mmol/kg)
16
Ferguson cut-off Chemical concentration in the
water that is required to produce the internal
concentration in the organism that is needed to
trigger the effect exceeds the chemicals water
solubility.
17
(No Transcript)
18
Dioxin Toxicity in Lake Trout
19
Dose-Response Curve for TCDD
20
Substances with Dioxin-like Toxicity
21
Dioxin Toxicity
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
4 Angstrom
10 Angstrom
22
Mechanism of Toxic Action
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
Cytochrome P450 Cycle
27
Phase I Reaction
28
Phase II Reaction
29
Role of Cytochrome P450 in Bioactivation
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
For Chemicals with Dioxin like mode of toxic
action Dioxin-like Mixture Toxicity Toxic
Equivalent Concentration (ng/kg) ? (CPCDDi
TEFi) ? (CPCDFi TEFi) ? (CPCBi TEFi)
34
(No Transcript)
35
- Recipe for a Toxic Effect
- Ingredients
- Exposure
- Relationship between external concentration and
the concentration at the active site - Potency
- concentration at the active site required to
trigger the effect - Directions
- concentration at the active site gt concentration
at the active site required to trigger the effect
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
FISH 1 FISH 2 Volume Total
(m3) 1 1 Volume Water (m3) 0.9 0.5 Volume
Lipid (m3) 0.1 0.5 Concentration in
water 1.10-6 1.10-6 (mol/m3) ZW 1 1 fW
1.10-6 1.10-6 fL 1.10-6 1.10-6 ZL 104
104 Cw 1.10-6 1.10-6 CL 1.10-2 1.10-2 VW
.CW 0.9 . 10-6 0.5 . 10-6 VL.CL 0.1 .
10-2 0.5 . 10-2 ?Vi.Ci 0.1 . 10-2 0.5 .
10-2 Ci 0.1 . 10-2 0.5 . 10-2
39
- Recipe for a Toxic Effect
- Ingredients
- Exposure
- Relationship between external fugacity and the
fugacity at the active site - Potency
- fugacity at the active site required to trigger
the effect - Directions
- fugacity at the active site gt fugacity at the
active site required to trigger the effect
40
So what?? You want to protect all aquatic life
by setting a water quality criterion for chemical
X, i.e. a water concentration that should not be
exceeded. So, what do you do?
41
So what?? You want to protect all aquatic life
by setting a water quality criterion for chemical
X, i.e. a water concentration that should not be
exceeded. So, what do you do? This WQC is
derived from a study of LC50 or NOAEC derived in
the lab, and you take the lowest LC50 divide it
by a safety factor (e.g. 10), and this becomes
your criterion.
42
So what?? You want to protect all aquatic life
by setting a water quality criterion for chemical
X, i.e. a water concentration that should not be
exceeded. So, what do you do? This WQC is
derived from a study of LC50 or NOAEC derived in
the lab, and you take the lowest LC50 divide it
by a safety factor (e.g. 10), and this becomes
your criterion. Then you manage environmental
quality by a monitoring program that measures
water concentrations compares them with the
WQC.
43
- Tissue Residue Approach for Characterizing
Toxicity - Merits
- eliminates transport/bioaccumulation from the
external environment (Exposure), including - bioavailability
- dietary uptake and biomagnification
- metabolism
- accumulation kinetics
44
Limitations Applies to Threshold Effects Only
45
- Fundamental Modes of Toxic Action
- Threshold Effects
- Carcinogenic Effects
- Endocrine Disruption (maybe)
46
Dose - Response Relationship
47
(No Transcript)
48
(No Transcript)
49
Application of Toxicity Data to conduct Hazard
and Risk Assessment General Problem The
ingested dose of Trichlorobenzene by (humans or
sea otters) in food items is 5.10-2
mg/kg/day LD50 in rats (14 days) 50
mg/kg/day LOAEL 5 mg/kg/day What is the hazard
and/or risk to humans or sea otters?
50
Hazard Potential for a toxicological effect
occurring
51
Assessment of Hazard
52
Reference Dose Is an estimate of the daily dose
to a population that is unlikely to produce an
appreciable risk of adverse effect during a life
time. Similar to an acceptable daily
intake. Reference Concentration Is an estimate
of the concentrations to a population that is
unlikely to produce an appreciable risk of
adverse effect during a life time. Similar to an
acceptable concentration.
53
(No Transcript)
54
Hazard Index H dose / Rfd lt 1.0 There is no
hazard gt 1.0 There is a hazard
55
Hazard Index Rfd 5 mg/kg/day(LOAEL)/1000
5.10-3 H 5.10-2 / 5.10-3 10 There is a
hazard gt 1.0 There is a hazard
56
Risk Probability of a toxicological effect
occuring
57
Single-Point Exposure and Effects Comparison
58
(No Transcript)
59
- Quotient-Method
- Cexposure / Ceffect
- Ceffects can be LC50, LD50, EC50, NOAEL, LOAEL,
LC5 etc. - Sometimes combined with a safety-factor
60
Example LC5 50 ng/L Exposure Concentration
30 ng/L Cexposure/LC5 60
61
Example LC5 50 ng/L Exposure Concentration
30 ? 15 ng/L (normal)
8.3
62
Example LC5 50 ng/L Exposure Concentration
30 ? 15 ng/L (log-normal)
22
63
Toxicity and the Law
64
- CEPA - toxicity
- A substance is toxic if it is entering or may
enter the - environment in a quantity or concentration or
under conditions - (a) having or that may have an immediate or
long-term harmful - effect on the environment
- (b) constituting or that may constitute a danger
to the - environment on which human life depends
- (c) constituting or that may constitute a danger
in Canada to - human life or health
65
(No Transcript)
66
Inherently toxic (iT) in CEPA 99
- No agreed upon definition exists
- CEPA 99 requires categorization of substances
against inherently toxic (hazard) - Proposed iT criteria for non-human organisms
(Environment Canada) - aquatic acute effects levels of lt 1 mg/L
- above 1 mg/L professional judgment considering
other factors (e.g. molecular weight,
metabolism...) - log Kow gt 6 (consideration of effects to
wildlife)
67
(No Transcript)
68
(No Transcript)
69
Fisheries Act 36 (3) no person shall deposit or
permit the deposit of a deleterious substance of
any type in water frequented by fish or in any
place under any conditions where the deleterious
substance or any other deleterious substance that
results from the deposit of the deleterious
substance may enter any such water.
70
"deleterious substance" means (a) any substance
that, if added to any water, would degrade or
alter or form part of a process of degradation or
alteration of the quality of that water so that
it is rendered or is likely to be rendered
deleterious to fish or fish habitat or to the use
by man of fish that frequent that water, or (b)
any water that contains a substance in such
quantity or concentration, or that has been so
treated, processed or changed, by heat or other
means, from a natural state that it would, if
added to any other water, degrade or alter
or form part of a process of degradation or
alteration of the quality of that water so that
it is rendered or is likely to be rendered
deleterious to fish or fish habitat or to the use
by man of fish that frequent that water,and
without limiting the generality of the foregoing
includes
71
(c) any substance or class of substances
prescribed pursuant to paragraph (2)(a), (d) any
water that contains any substance or class of
substances in a quantity or concentration that is
equal to or in excess of a quantity or
concentration prescribed in respect of that
substance or class of substances pursuant to
paragraph (2)(b), and (e) any water that has
been subjected to a treatment, process or change
prescribed pursuant to paragraph (2)(c)
72
Pharmacokinetics / Toxicokinetics
Cwater
GILL UPTAKE
GILL ELIMINATION
73
(No Transcript)
74
Compartmental Kinetics The one-compartment model
GILL UPTAKE
Cwater
GILL ELIMINATION
75
GILL UPTAKE
Cwater
GILL ELIMINATION
Set up the mass balance equation
76
GILL UPTAKE
Cwater
GILL ELIMINATION
MF Mass in Fish MW Mass in Water CF
Concentration in Fish CW Concentration in
Water kWF Uptake rate constant kFW
Elimination rate constant VW Volume of Water VF
Volume of Fish k1 Uptake clearance rate k2
Elimination rate constant
Set up the mass balance equation dMF / dt
kWF.MW - kFW.MF dCF / dt kWF.MW / VF -
kFW.CF dCF / dt kWF.VW.CW / VF - kFW.CF dCF /
dt k1.CW k2.CF
77
Solve Mass Balance Equation 1. Steady-State CF
CW.k1/k2 2. Integration CF CW.k1/k2.(1 -
exp(-k2.t)) 3. Numerical Integration
78
(No Transcript)
79
CF Concentration in Fish CW Concentration in
Water k1 Uptake clearance rate k2 Elimination
rate constant t time ? Error
80
CF 0 at t0 CW 1 ng/L k1 100 L/kg.day k2
0.01 1/day
CF Concentration in Fish CW Concentration in
Water k1 Uptake clearance rate k2 Elimination
rate constant t time ? Error
81
CF Concentration in Fish CW Concentration in
Water k1 Uptake clearance rate k2 Elimination
rate constant t time ? Error
82
(No Transcript)
83
M1 Mass in Compartment 1 M2 Mass in
Compartment 2 R Dose k12 Rate constant for 1
to 2 k21 Rate constant for 2 to 1 k10 Rate
constant for 1 to outside X1 , X2, X3, X4
Constants ? Constant ? Constant
84
(No Transcript)
85
Q
Q
Mi Mass in Compartment i Cbl Concentration in
arterial blood Cv Concentration in venuous
blood Q Blood Flow K Partition Coefficient
venuous blood/organ
86
Application of Toxicity Data to conduct Hazard
and Risk Assessment General Problem The
Concentration of Trichlorobenzene in River Water
is 5.10-6 mmol/L LC50 in guppies (48 hr)
5.10-4 mmol/L What is the hazard and/or risk to
rainbow trout?