HEART - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 65
Title: HEART
1
HEART
2
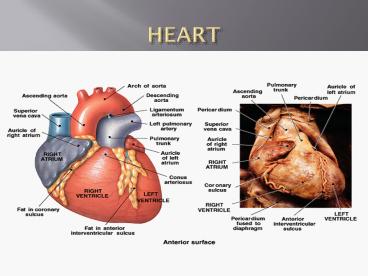
HEART
- Hollow, muscular organ.
- 300 grams.
- 4 chambers.
- found in chest between lungs .
- surrounded by membrane called Pericardium.
- Pericardial space is fluid-filled to nourish and
protect the heart.
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
HEART ANATOMY
- The heart is a complex muscular pump that
maintains blood pressure and flow through the
lungs and the rest of the body. - The heart pumps about 100,000 times and moves
7200 liters of blood every day.
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
- Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart via the
superior and inferior vena cava, enters the right
atrium, passes into the right ventricle, and from
here it is ejected to the pulmonary artery. - Oxygenated blood returning from the lungs enters
the left atrium via the pulmonary veins, passes
into the left ventricle, and is then ejected to
the aorta.
11
Blood Vessels
12
Functions of the Heart
- Generates blood pressure.
- The role of the heart is to pump oxygen-rich
blood to every living cell in the body and
deoxygenated blood to the liver. - Routes blood
- Heart separates pulmonary and systemic
circulation.
13
Functions of the Heart
- The heart pumps the blood, which carries all the
vital materials which help our bodies function
and removes the waste products that we do not
need. - Heart failure is the inability of the heart to
provide enough blood flow to maintain normal
metabolism
14
QUIZ
- The right ventricle is the chamber of the heart
that pumps blood for the pulmonary circulation.
Based on this information, blood from the right
ventricle is on its way to the ----- - Which of the following is also known as the
mitral valve? - How much does your heart weigh?
15
- Which of these are a part of your circulatory
system? - Arteries, veins
- capillaries
- all of the above
- Where in your body is your heart located?
- Blood transported by the pulmonary veins returns
to the - The bulk of the heart consists of
- Blood vessels that carry blood away from the
heart are called
16
What is Heart Disease?
- Coronary heart disease- arteries that
- supply the heart with blood and oxygen
- are narrowed by a build-up of plaque,
- and less blood gets through.
17
Angina-pain or pressure that occurs because blood
flow and oxygen to the heart is reduced. Is a
symptom of heart disease. Heart Attack-blood
flow to part of the heart is completely blocked
and cells begin to die from lack of oxygen.
18
Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary artery disease is one of the most common
and serious effects of aging. Fatty deposits
build up in blood vessel walls and narrow the
passage way for the movement of blood. The
resulting condition, called atherosclerosis often
leads to blockage of the coronary arteries and a
heart attack.
19
(No Transcript)
20
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
- Atherosclerosis is in which the walls of the
blood vessels become thickened and hardened by
"plaques." The plaques are composed of
cholesterol and other lipids, inflammatory cells,
and calcium deposits.
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
Development of Atherosclerotic Plaques
Fatty streak
Normal
Lipid-rich plaque
Foam cells
Fibrous cap
Lipid core
Thrombus
Ross R. Nature. 1993362801-809.
24
Atherosclerotic Plaque Rupture and Thrombus
Formation
Growth of thrombus
Intraluminal thrombus
Blood Flow
Lipid pool
Intraplaque thrombus
25
ATHEROSCLEROSIS SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
- Heart
- Brain
- Legs, pelvis, or arms
- Kidneys.
26
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis in the Heart
- Chest pain or chest discomfort (angina).
- Pain in one or both arms, the left shoulder,
neck, jaw, or back. - Shortness of breath.
- Dizziness.
- Faster heartbeats.
- Nausea .
- Abnormal heartbeats.
- Feeling very tired.
27
Symptoms in the Brain
- Sudden numbness or weakness of face, arm, or leg,
especially on one side of the body. - Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or
understanding speech. - Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of
balance or coordination. - Sudden severe headache with no known cause.
28
Symptoms in the Legs, Pelvis, or Arms
- Ache, or cramping in the muscles that occurs
during exercise but improves with rest. - Cold or numb feeling in the feet or toes,
especially at night.
29
Atherosclerosis Symptoms and the Kidneys
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Nausea.
30
Causes
- High blood cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Improper dietary pattern.
31
Risk Factors
- Uncontrollable
Controllable
- Sex
- Hereditary
- Race
- Age
- High blood pressure
- High blood cholesterol
- Smoking
- Physical activity
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Stress and anger
32
DIAGNOSIS
- Blood Tests
- Blood tests that may be ordered as part of making
anatherosclerosis diagnosis include - A fasting glucose test that checks your blood
sugar level to screen for diabetes. - A fasting lipid panel to check your cholesterol an
dtriglyceride levels.
33
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
- An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that
records your heart's electrical activity and can
show certain problems, such as abnormal
heartbeats or damage to the heart.
34
CHEST X-RAY
- A chest x-ray provides a picture of the lungs,
heart, large arteries, ribs, and the diaphragm.
35
Stress Tests
- During stress testing, a patient exercises or is
given medicine to make the heart work harder and
beat faster while tests are performed. In an
exercise stress test, your heart, breathing,
and blood pressure are monitored while you
exercise using a treadmill or a stationary
bicycle.
36
NUCLEAR HEART SCAN
- A nuclear heart scan (also known as a thallium
stress test) shows areas of the heart that lack
blood flow and are damaged. - It also can reveal problems with the heart's
pumping action. A small amount
of radioactive material is
injected into a vein,
usually in the arm.
37
ULTRASOUND
- An ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to
create a picture. The picture is more detailed
than an x-ray image.
38
ECHOCARDIOGRAM
- An echocardiogram is an exam of the heart using
sound waves to create a moving picture of the
organ. - An echocardiogram provides information about the
size and shape of your heart and how well your
heart chambers and valves are functioning
39
CT SCAN
- CT, scan provides computer-generated images of
the heart, brain, or other areas of interest.
Some specialized types of CT scans can also be
used to diagnose
40
What is Stroke?
- A stroke occurs when a blood vessel carrying
- oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either
- blocked by a clot or bursts.
- Part of the brain does not get the oxygen it
needs so it starts to die.
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
(No Transcript)
48
(No Transcript)
49
Causes
- If blood flow is stopped for longer than a few
seconds, the brain cannot get blood and oxygen.
Brain cells can die, causing permanent damage.
50
STROKE RISK FACTORS
- High blood pressure is the number one risk factor
for strokes. - Diabetes
- Family history of stroke
- High cholesterol
- Increasing age, especially after age 55
- Race (black people are more likely to die of a
stroke) - People who have heart disease or poor blood flow
in their legs caused by narrowed arteries are
also more likely to have a stroke.
51
- The chance of stroke is higher in people who live
an unhealthy lifestyle by - Being overweight or obese.
- Drinking heavily.
- Eating too much fat or salt.
- Smoking.
- Taking cocaine and other illegal drugs.
52
Symptoms
- Starts suddenly and may be severe.
- Occurs when you are lying flat.
- Wakes you up from sleep.
- Gets worse when you change positions or when you
bend, strain, or cough - Dizziness or abnormal feeling of movement .
- Lack of control over the bladder or bowels.
- Loss of balance.
- Loss of coordination.
53
- Change in alertness (including sleepiness, unconsc
iousness, and coma) - Changes in hearing
- Changes in taste
- Changes that affect touch and the ability to feel
pain, pressure, or different temperatures - Clumsiness
- Confusion or loss of memory
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty writing or reading
54
DIETARY MANAGEMENT
- ENERGY- A hypo caloric diet should be given.
- FAT- Total fat in the diet be reduced to provide
less than 20 of energy for patients with higher
level of serum cholesterol. - Saturated FA- less than 10.
- PUSFA- less than 10 .
- MUSFA-rest of energy.
55
- CHOLESTROL- Less than 200 mg/day
- PROTEIN- Normal protein should be given.
- Animal protein should be avoided as they are rich
source of saturated fats. - CARBOHYDRATES- give complex starches rather than
simple sugar in a diet. - Therefore use of foods containing water soluble
fiber such as whole pulses, legumes, beans, oats,
fruits, and vegetables.
56
- MINERALS AND VITAMINS- These are to be provided
in normal amount in a diet. - As the fat of milk, butter, cream, and fatty
meats are to be avoided. - The diet tend to be in low in vitamin a
especially retinol. - Deep yellow, orange, green vegetables should be
include in the diet. - SODIUM- Reduction of dietary sodium to be
moderate intake between 1.5 to 3 gm per day
57
QUIZ
- Another name for raised lesions seen in
atherosclerosis? - Type of stroke?
- People with a stroke always have numbness,
dizziness and weakness on one side. - Atherosclerosis can affect several parts of the
body and increase your risk of future problems. - The most common form of heart disease is coronary
artery disease caused by atherosclerosis.
58
HEART FAILURE
- It is a condition in which the heart can't pump
enough blood to meet the body's needs. - Some times heart can't fill with enough blood.
- Some time the heart can't pump blood to the rest
of the body with enough force.
59
TWO TYPES OF HEART FAILURE
- Right side Heart failure .
- Lift side Heart failure .
60
RIGHT SIDE HEART FAILURE
- heart failure occurs if the heart can't pump
enough blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
61
LEFT-SIDE HEART FAILURE
- Left-side heart failure occurs if the heart can't
pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the
body.
62
CAUSING SYMPTOMS
- Shortness of breath when you exert yourself or
when you lie down. - Fatigue and weakness.
- Swelling (oedema) in your legs, ankles and feet
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Reduced ability to exercise.
- cough.
- Swelling of your abdomen.
- Sudden weight gain from fluid retention.
- Lack of appetite and nausea.
- Difficulty concentrating or decreased alertness.
63
DIETARY TREATMENT
- ENERGY- The amount of calories should be 1200-
1500 kcals per day. - PROTEIN - the normal intake of protein i.e 1g/kg
body weight. - SODIUM- 2-m3 gm per day is recommended.
64
DIET AND FEEDING PATERN
- To provide adequate nutrition number of feeds
should be increased i.e 5 to 6 a day. - Fixed meal timing and with adequate rest after
meal is important. - Food rich in fat saturated fat and cholesterol
should be avoided. - More fiber should be given.
- Processed food and canned food should be avoided.
65
- FAT-
- FLUID- in sever oedema the intake of fluid is
restricted to match the out put.