Organic or BIOCHEMISTRY - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Organic or BIOCHEMISTRY
Description:
Unique Properties of Carbon Forms 4 covalent bonds Long Carbon chains are formed. CARBOHYDRATES Chemical Structure Common Monosaccharides Glucose Galactose ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:69
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Organic or BIOCHEMISTRY
1
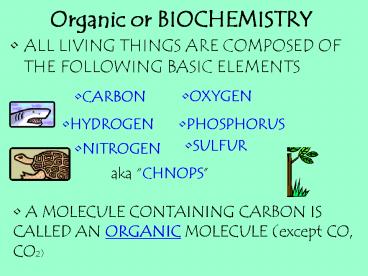
Organic or BIOCHEMISTRY
- ALL LIVING THINGS ARE COMPOSED OF THE FOLLOWING
BASIC ELEMENTS
- CARBON
- OXYGEN
- HYDROGEN
- PHOSPHORUS
- SULFUR
- NITROGEN
aka CHNOPS
- A MOLECULE CONTAINING CARBON IS
- CALLED AN ORGANIC MOLECULE (except CO, CO2)
2
Unique Properties of Carbon
- Forms 4 covalent bonds
- Long Carbon chains are formed.
3
THERE ARE 4 Major CARBON COMPOUNDS IN ALL LIVING
THINGS
1. CARBOHYDRATES
2. LIPIDS
3. PROTEINS
4. NUCLEIC ACIDS
4
CARBOHYDRATES
- Chemical Structure
Saccharide (monomer/subunit) One saccharide or
Monosaccharide
5
Common Monosaccharides
- Glucose
- Galactose
- Fructose
ose sugar
Common Disaccharides
- Glucose Galactose Lactose
- Glucose Fructose Sucrose
- Glucose Glucose Maltose
6
Common Polysaccharides
Starch
..
Cellulose
..
Glycogen
..
Starch Sugar
Cellulose is undigestible sugar (cotton, paper,
wood, stems)
Glycogen quick sugar because of branching
7
CARBOHYDRATES
- INCLUDE SUGARS, STARCHES, CELLULOSE
- PROVIDES ENERGY FOR ORGANISMS
8
- Glucose C6H12O6.
- Main product of photosynthesis
- Starting material for Cellular Respiration
- fuel in living things
- transported by body fluids to all cells, where is
it METABOLIZED to release energy.
9
- Polysaccharides complex carbs
- Formed by linking many monosaccharides
- Starches hundreds of glucose units linked
together - Storage for carbohydrates in PLANTS
- Glycogen stored in human liver
- Thousands of glucose units
- Cellulose structural carbohydrate (for SUPPORT)
- Glucose units, but cannot be released from one
another except for a few species of organisms - Wood
- Cell walls of plants
- Humans CANNOT digest cellulose!
10
Lipids
- Chemical Structure
Fatty Acid (monomer/subunit)
11
Lipids
12
Lipids
13
LIPIDS
INCLUDE FATS, OILS,, PHOSPHOLIPIDS, STEROIDS,.
- CARBOHYDRATES MAY BE CONVERTED INTO LIPIDS
- FOR LONG-TERM ENERGY STORAGE FAT
- PHOSPHOLIPIDS MAIN COMPONENT OF CELL
- MEMBRANE
- Nonpolar Polar portions
14
Cell Membrane LipidsPhospholipid bilayer
15
Lipids
Unsaturated C-C-CC-C-C-C-C
Saturated C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C
16
PROTEIN
- Chemical Structure
Amino Acid (monomer/subunit)
17
PROTEIN
18
PROTEINS
- Most complex organic molecules
- COMPOSED OF SMALLER MOLECULES/SUBUNITS CALLED
AMINO ACIDS - There are 20 Amino Acids (or AAs)
Protein Functions
- enzymes, muscles, skin, hair
19
NUCLEIC ACIDS (DNA/RNA)
- Nucleotide
- (monomer/subunit)
- Nitrogen Base
- Sugar
- Phosphate
20
NUCLEIC ACIDS
21
NUCLEIC ACIDS
- LARGE COMPLEX MOLECULES
- CONTAINING HEREDITY MATERIAL
- Made of Nucleotides (sugar, phosphate group,
nitrogen base)
- DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID -D N A
- (deoxyribose sugar)
2. RIBONUCLEIC ACID- R N A (ribose sugar)
- D N A CARRIES INSTRUCTIONS THAT
- REGULATE CELL ACTIVITIES
22
(No Transcript)
23
Carbon Cycle