Roman Literature - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Roman Literature
Description:
Roman Literature – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:207
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Roman Literature
1
(No Transcript)
2
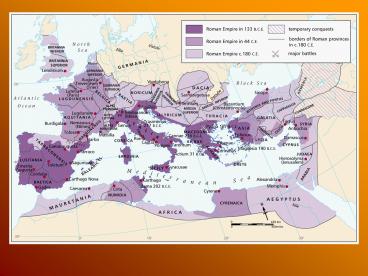
The Roman Empire
- Beginning with Augustus, the Pax Romana meant
that people didnt have to worry about their
safety - Trade increased (throughout the known world!)
- Society building spread throughout the empire
3
Roman Literature
- Most influenced by Greek models.
- Most distinguished poet of the Augustan age was
Virgil.
"Omnia vincit amor " "Love conquers
all "Audentes fortuna iuvat" "Fortune favors
the bold
4
Art Architecture
- The Romans adopted many features of the Greek
style of art.
- The Romans excelled in architecture (columns and
curvilinear forms arch, vault, dome).
5
- 1st people in antiquity to develop and use
concrete on a massive scale.
6
Roman Architecture
7
Roman Aqueduct
8
Roman Bridges
9
All Roads Led To Rome
10
(No Transcript)
11
Roman Daily Life
- Rome was overcrowded, noisy, dangerous
- Insulae apartment blocks for the poor/ high
rent forced entire families to live in one room - Due to conditions (heat and odors), Romans spent
most of their time in the street
12
- Most citizens of Rome were unemployed as a result
of the Latifundia (plantation) system of farming - Entertainment gladiator contests-animals,
slaves, criminals would fight to death/ horse
and chariot races at Circus Maximus/ free food
(bread) and wine were given to the spectators as
a sort of unemployment solution - Magnificent public buildings baths, temples,
theaters, markets
Roman Colosseum
Gladiators
13
Circus Maximus
14
Economic life in the Empire
Self-sustaining individual networksthe Saharan
caravans, Arab and Chinese ships and most
famously the Silk Routes linked at key cities
such as Alexandria formed a truly
intercontinental trading system.
15
Roman Religion
- Augustus revived early Roman religious festivals
and ceremonies to bring back religion - Beginning with Augustus, emperors were often
declared gods and citizens asked to sacrifice to
them this guaranteed peace and prosperity
16
- Tolerance of all religions that werent harmful
to the state
- This includes the diefication of deceased
Emperors!
17
Judaism
- Judaea was a Roman province
- Unrest was common among the Jewish inhabitants
- Romans destroyed the temple in Jerusalem in 70 ad
and force many Jews from Jerusalem (Jewish
Diaspora)? - Jesus (Jew) began to teach during the midst of
the conflict
18
- Jesus as a profit of God (no room for Emperor
Gods - Message of love, hope and Heaven appealing to the
masses - Seen as a threat to Romes stability
19
- Denounced by Roman and Jewish leadership
- Tried and sentenced to death by the Prefect of
Judea Pontius Pilate
20
- By the order of Pontius Pilate Jesus is crucified
- Loyal followers believe that he overcomes death
21
- The gospel of Jesus spreads throughout the
Empire
- Christian communities are founded in Asia Minor
and along the Aegean Sea
22
- At first, persecution is sporadic
- In 303, Christians lost all legal rights
- Later laws called for execution for failure to
sacrifice to Roman Gods
The Christian Martyrs Last Prayer Jean-Leon
Gerome 1883
23
- Grows slowly at first, but begins to appeal to
the Romans for several reasons - salvation for all
- simple baptism
- could relate to Jesus suffering
- sense of belonging
- More personal relationship with god
24
- Constantine becomes the first emperor to convert
to Christianity
- Constantine issues the Edict of Milan in 313
(official tolerance of Christianity)
25
- On February 27th, 380, Emperor Theodosius makes
Christianity the official religion of the empire - hes also the last Emperor to rule both the
Eastern and Western halves of the Roman Empire
26
Upon Theodosius death, the empire is permanently
divided into eastern and western empires
27
Transformation of the Roman Empire
- The problem of barbarians
- Celts
- Germans
- Steppe peoples, especially Huns
- Huns upset balance of borders c. 370 C.E.
- Move of Goths into imperial territory to escape
Huns
28
(No Transcript)
29
Transformation of the Roman Empire
- Plague!
30
410 sack of Rome by the Visogoths
476 abdication of last western emperor
31
Fall of Rome
- Many Germanic kingdoms over the years replaced
the western empire
- Eastern Roman empire became known as the
Byzantine Empire and thrived around Constantinople
32
Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire)
- Resurgence under Justinian I (r. 527565 C.E.)
33
Justinian Code 529ce
The Emperor Justinian called on all of Romes
existing laws to be codified. (collected and
simplified into a clear and simple code of
laws.)
innocent until proven guilty
Many current legal systems around the world are
based on the Justinian Code
34
Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire)
- Religious Disputes
- Monophysites
- Iconoclasm
- Lasts until 1453!
- Nearly 1,000 years longer than the eastern half
35
What is the Legacy of the Roman Empire?
- Linguistic
- Legal
- Urban
- Transformation of Roman administration by
Christian church - ETC.what can you think of?
36
Contributions
- Roman Law
- all equal
- guaranteed legal protection
- Architecture
- roads, aqueducts, bridges
- arch, dome, concrete
- Latin
- Romance languages Spanish, French, Italian
- ½ of English words
37
The Fall of the Roman Empire
- any theories??
38
The Fall of The Roman Empire
- Political Causes
- inefficient and corrupt Government
- empire too big
- succession problems led to civil wars
39
SOCIAL CAUSES
- interested in luxury instead of patriotism
- sharp class distinctions
- Plague!
- Lead poisoning from water pipes caused mental
decline
40
ECONOMIC CAUSES
- small farmers abandoned land to big estates
(latifundia), less productive - economic decline due to large estates
self-sufficiency - heavy taxation destroyed peoples willingness to
work - slaves led to unemployment
41
MILITARY CAUSES
- Warlike spirit weakened by Christian teachings of
peace - Barbarian mercenaries in army
- armies set government policy
42
- and many more reasons.
- What reasons can you think of?
- Do you think it was a single reason or several?
43
(No Transcript)











![Download [PDF] Lucian and His Roman Voices: Cultural Exchanges and Confl PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10067570.th0.jpg?_=20240628026)
![Download [PDF] Lucian and His Roman Voices: Cultural Exchanges and Confl PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10060796.th0.jpg?_=202406211212)
![Download [PDF] Lucian and His Roman Voices: Cultural Exchanges and Confl PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10060444.th0.jpg?_=202406210511)
















