Disease and Immunity
1 / 33
Title: Disease and Immunity
1
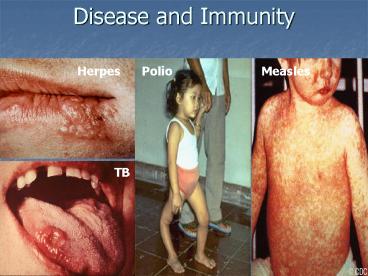
Disease and Immunity
Herpes
Polio
Measles
TB
2
Pathogens
- Any foreign invader that enters the body and
causes disease - Pathogens include
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- protists
- A disease that can spread to others is called
- Infectious
- Contagious
- communicable
3
The Bodys Reactions
- The first defense is our skin and mucous
membranes - Sweat and oil is toxic to some bacteria
- Mucus will trap invaders
- Fever an elevated body temperature will
suppress bacterial growth and speed up our immune
response - Normal 98.6 degree F / 37 degrees C
4
The Bodys Reactions to a localized (small)
infection
- Inflammatory response
- Injured cells release chemical alarm signals
- Capillaries respond by swelling and leaking fluid
and white blood cells - Swelled area is warm
- White blood cells arrive to attack
- Pus in wounds is dead pathogens
5
Bacteria
- Can be pathogenic
6
Characteristics of Bacteria
- How they eat
- Heterotrophic
- Eat other things
- Autotrophic
- Make their own food like plants
- Oxygen requirements
- Anaerobic
- Undergo fermentation (no oxygen)
- Aerobic
- Use oxygen
7
Bacteria Classification
- Two Kingdoms
- Eubacteria most common bacterial forms
- All pathogenic bacteria
- Archaebacteria Most primitive bacterial forms
that live in extreme environments
8
Kingdom Eubacteria
- Most common
- 3 basic shapes
- Rod
- Sphere
- Spiral
- Prefix strep Chains
- Prefix staphlo Clusters
9
Gram staining
- Bacteria can also be classified by whether or not
they retain color when stained by a certain
chemical. - Whether or not they retain the color is based on
the components of their outer membrane - Gram-positive bacteria retain the color (violet)
- Gram-negative bacteria do not retain the color
and are dyed with a secondary dye which turns
them pink.
10
- Different types of antibiotics are needed to
treat infections based on whether the bacteria is
Gram-negative or Gram-positive - Some antibiotics kill bacteria by damaging their
peptidoglycan cell wall - Which bacteria would be resistant to an
antibiotic that worked in this fashion?
11
Bacterial diseases
- Tetanus
- Bubonic plague (The Black Death)
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Sinus infection
- Strep throat
- Tuberculosis (TB)
12
Antibiotics and Bacteria
- Antibiotics only work against bacteria!
- Some antibiotics are made from chemicals that
bacteria and fungi produce naturally - Penicillin is made is from a type of fungus
- Other antibiotics have been created in medical
laboratories - Amoxicillin, Zithromax, Tetracycline, Vancomycin
13
Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria
- Remember evolution
- 1) Bacteria have different characteristics due to
mutations. - 2) Some of these mutations help the bacteria to
survive an attack by antibiotics. - 3) The stronger (more resistant) bacteria survive
and infect a new person (host).
14
Tuberculosis
- Certain types of this pathogenic bacteria can no
longer be treated by antibiotics - How can you help to
- stop the spread of
- antibiotic resistant
- bacteria?
15
Useful Bacteria
- Breakdown organic matter and recycle carbon and
nitrogen - Help with the production of food
- Clean up environmental disasters
Intestinal Bacteria
16
Protists
- Single or multicelled organisms that live in
water - Plant like or
- animal like
17
Three representative protists
flagella
eyespot
Pseudopod false foot
- Euglena
paramecium
amoeba
cilia
18
Protist (protozoan) disease
- Malaria
- Anopheles mosquito
- plasmodium
- African Sleeping sickness
- Tsetse fly
- Trypanosoma
19
African Sleeping Sickness
20
(No Transcript)
21
VirusesA paothgen that is unable to grow or
reproduce outside of a host cell. It is
considered non-living
The Common Cold
- Virology is the study of viruses
22
Virus Structure
Capsid/
- Viruses are extremely small
- They have a
- Nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
- Capsid - A protein coat that protects the virus
- Protein tail -used to infect host
23
Structure of Influenza Virus
Used to attach to host cell
Glycoprotein
RNA
Capsid
Protein
Protein
Envelope
24
Family Virus Disease
Adenovirus Common cold Common cold
Flavivirus Hepatitis C (non-A, non-B)Yellow fever HepatitisHepatitis, hemorrhage
Hepadnavirus Hepatitis B virus (HBV) Hepatitis, liver carcinoma
Herpesvirus Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)Herpes simplex type 1Herpes simplex type 2Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8) Mononucleosis, nasopharyngeal carcinomaCold soresGenital lesionsChicken pox, shingles
Papovavirus Human papillomavirus (HPV) Warts, cervical carcinoma
Paramyxovirus MeaslesMumpsParainfluenza MeaslesMumpsCommon cold, ear infections
Poxvirus Orthopoxvirus Smallpox (eradicated)
Retrovirus Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)Adult T-cell leukemia, lymphoma, neurologic disease
Rhabdovirus Rabies Rabies
25
Viruses and Their Hosts
- When a virus meets a host cell, it can insert its
genetic material into its host, taking over the
host's functions - The infected cell stops producing its own
proteins and starts to make new viruses! - Basically, it hijacks the cell!
26
Viral Phases
- Lysogenic phase - viruses are dormant inside host
cells for long periods. - The host is not sick.
- Lytic phase - The virus is stimulated
- new viruses are formed, self-assemble, and burst
out of the host cell, killing the cell and going
on to infect other cells. - The host is now sick with a viral infection
27
(No Transcript)
28
Viral Mutations
- Viruses are able to rapidly mutate
- Flu
- HIV
- Attacks white blood cells the cells that
protect our bodies from germs and infections - HIV is latent until another infection triggers
the lytic stage - Kills white blood cells
- HIV has a high rate of replication and mutation
which has made it difficult to make a vaccine
29
Two Ways to Control Viruses
- Vaccination An injection of a harmless version
of a virus which causes an immune response. - The body begins to produces antibodies against
that virus - Antiviral Drugs Drugs that slow down or stop a
viral infection - Tamiflu
30
Acquired Immunity An immunity that develops
after exposure
- 2 kinds
- Active Immunity When your body makes its own
antibodies - Getting sick
- vaccines
- Passive Immunity
- Antibodies are given to the person
- Mothers milk
31
White Blood Cells (WBC)
- These are your immune cells
- Most are made in your bone marrow
- There are many types
- Lymphocytes
- Leucocytes
- Neutrophils
- B cells, T cells
32
WBC that you need to know
- T cells
- Killer cells
- Made in bone marrow
- Attacks a specific pathogen
- B cells
- Made in bone marrow
- Attack a specific pathogen by making antibodies
- They stick to the surface of a pathogen and so it
cannot infect any other cells
33
Memory Cells
- T cells and B cells that remain in the body after
an infection has been destroyed. - They provide the body with active immunity in the
future against that disease - Your body made memory cells against chicken pox
when you had it as a kid. You now have life long
immunity to chicken pox! - Why cant we get life long immunity to the flu or
a cold?