Machine studies during beam commissioning - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Machine studies during beam commissioning
Description:
Title: Slide 1 Author: meddahi Last modified by: Christine Petit-Jean-Genaz Created Date: 6/14/2004 12:48:45 PM Document presentation format: A3 Paper (297x420 mm) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:16
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Machine studies during beam commissioning
1
Machine studies during beam commissioning of the
SPS-to-LHC transfer lines
M. Meddahi, I. Agapov, K. Fuchsberger, B.
Goddard, W. Herr, V. Kain, V. Mertens, D.
Missiaen, T. Risselada, J. Uythoven, J.
Wenninger, CERN, and E. Gianfelice, Fermilab.
TH6PFP040
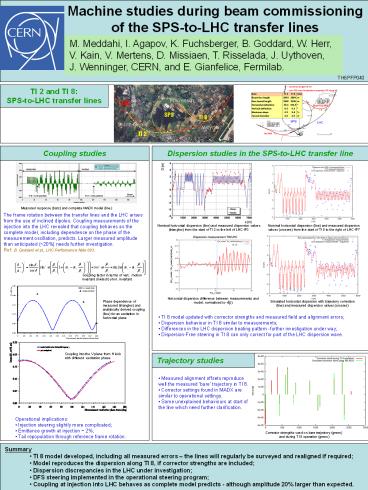
TI 2 and TI 8 SPS-to-LHC transfer lines
Dispersion studies in the SPS-to-LHC transfer
line
Coupling studies
Measured response (bars) and complete MADX model
(line)
The frame rotation between the transfer lines and
the LHC arises from the use of inclined dipoles.
Coupling measurements of the injection into the
LHC revealed that coupling behaves as the
complete model, including dependence on the phase
of the measurement oscillation, predicts. Larger
measured amplitude than anticipated (20) needs
further investigation. Ref B. Goddard et al.,
LHC Performance Note 003.
Nominal horizontal dispersion (line) and measured
dispersion values (triangles) from the start of
TI 2 to the left of LHC-IP3
Nominal horizontal dispersion (line) and measured
dispersion values (crosses) from the start of TI
8 to the right of LHC-IP7
Coupling factor in terms of vert. motion
invariant divided by hor. invariant
Horizontal dispersion difference between
measurements and model, normalised to v(b)
Simulated horizontal dispersion with trajectory
correction (line) and measured dispersion values
(crosses)
Phase dependence of measured (triangles) and
analytically derived coupling (line) for an
excitation in horizontal plane
- TI 8 model updated with corrector strengths and
measured field and alignment errors - Dispersion behaviour in TI 8 similar to
measurements - Differences in the LHC dispersion beating
pattern -further investigation under way - Dispersion-Free steering in TI 8 can only
correct for part of the LHC dispersion wave.
Coupling into the V plane from H kick with
different excitation phase
Trajectory studies
- Measured alignment offsets reproduce well the
measured bare trajectory in TI 8. - Corrector settings found in MADX are similar to
operational settings. - Some unexplained behaviours at start of the line
which need further clarification.
- Operational implications
- Injection steering slightly more complicated
- Emittance growth at injection 2
- Tail repopulation through reference frame
rotation.
Corrector strengths used on bare trajectory
(green) and during TI 8 operation (green)
- Summary
- TI 8 model developed, including all measured
errors the lines will regularly be surveyed and
realigned if required - Model reproduces the dispersion along TI 8, if
corrector strengths are included - Dispersion discrepancies in the LHC under
investigation - DFS steering implemented in the operational
steering program - Coupling at injection into LHC behaves as
complete model predicts - although amplitude 20
larger than expected.