Diffusion - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Diffusion
Description:
Diffusion Movement of atoms in a material Thermal Energy = Atom Movement Eliminates concentration differences Important for material processing (heat treating ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:149
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Diffusion
1
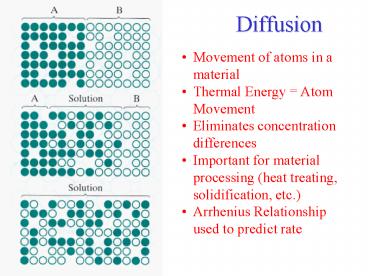
Diffusion
- Movement of atoms in a material
- Thermal Energy Atom Movement
- Eliminates concentration differences
- Important for material processing (heat treating,
solidification, etc.) - Arrhenius Relationship used to predict rate
2
Predicting Diffusion
- Ficks first Law
- J -D (DC/Dx)
- Where
- J Flux
- D Diffusion Coefficient
- DC/Dx Concentration Gradient
- Diffusion Coefficient
- D D0 exp (-Q/(RT))
- Where
- D diffusion coefficient
- Q Activation Energy
- R Gas Constant (1.987 cal/mol.K)
- T Absolute Temp, K (C 273)
- D0 Constant for diffusion system
3
Imperfections in the Crystal Lattice
4
Mechanisms of Diffusion
- Self Diffusion (pure metals)
- Vacancy Diffusion
- Interstitial Diffusion
5
Types of Diffusion
- Volume Diffusion
- Grain Boundary Diffusion
- Surface Diffusion
6
Volume Diffusion
- Diffusion through VOLUME of crystal
- Highest packing eff.
- Least amount of defects
- SLOWEST!!
7
Grain Boundary Diffusion
- Diffusion along the GRAIN BOUNDARY
- More room
- More defects
- FASTER!
8
Surface diffusion
- Diffusion along a material SURFACE
- Lots of room
- Lots of defects
- FASTEST!!!
9
Types of Diffusion
- Volume Diffusion
- Grain Boundary Diffusion
- Surface Diffusion
10
Factors Affecting Diffusion
- Diffusion Mechanism
- Type of Diffusion
- Crystal Structure
- Bonding
- Temperature
- Ionic Materials
- Polymers
11
Compare and Contrast
- Slip
- Diffusion
- Movement of DISLOCATIONS through a crystalline
material - Responsible for plastic deformation
- Affected by
- Crystal structure
- Bonding
- Temperature (since it affects bonding)
- Movement of ATOMS in a material (can be
crystalline or amorphous) - Eliminates concentration differences
- Affected by
- Mechanism and type
- Temperature
- Bonding
- Material structure (crystal or amorphous)
12
Creep
- Tensile specimen is subjected to constant load
at elevated temp - Specimen will elongate continuously until failure
- Applied stress below yield strength of that
material
13
Creep and Dislocation Climb
- Movement of dislocation perpendicular to its slip
plane by diffusion of atoms to or from the
dislocation line - Vacancies must move to or from dislocations to
cause plastic strain - Dislocations escape from lattice imperfections,
continue to slip and causes additional
deformation of specimen even at low applied
stress - Diffusion controlled phenomenon
- Arrhenius Relationship
- creep rate K s n exp (Q c / R T)
- R gas constant
- T temp, K
- c, K, n material constants
- Q Activation energy related to self diffusion
when dislocation climb is important
14
Diffusion and Materials Processing
- Surface Treating
- Grain Growth
- Diffusion Bonding
- Sintering