Numerical Integration - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Numerical Integration
Numerical Integration In general, a numerical integration is the approximation of a definite integration by a weighted sum of function values at discretized ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Title: Numerical Integration
1
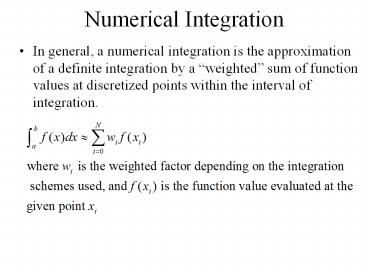
Numerical Integration
- In general, a numerical integration is the
approximation of a definite integration by a
weighted sum of function values at discretized
points within the interval of integration.
2
Rectangular Rule
f(x)
heightf(xn)
heightf(x1)
x
xa
xb
xx1
xxn
3
Trapezoidal Rule
f(x)
The rectangular rule can be made more accurate by
using trapezoids to replace the rectangles as
shown. A linear approximation of the function
locally sometimes work much better than using the
averaged value like the rectangular rule does.
xa
xb
x
xx1
xxn-1
4
Simpsons Rule
Still, the more accurate integration formula can
be achieved by approximating the local curve by a
higher order function, such as a quadratic
polynomial. This leads to the Simpsons rule and
the formula is given as
It is to be noted that the total number of
subdivisions has to be an even number in order
for the Simpsons formula to work properly.
5
Examples
i xi f(xi)
1 1.125 1.42
2 1.375 2.60
3 1.625 4.29
4 1.875 6.59
6
Trapezoidal Rule
i xi f(xi)
1 1
1 1.25 1.95
2 1.5 3.38
3 1.75 5.36
2 8
Simpsons Rule
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.