Science Introduction and Expectations - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 58
Title: Science Introduction and Expectations
1
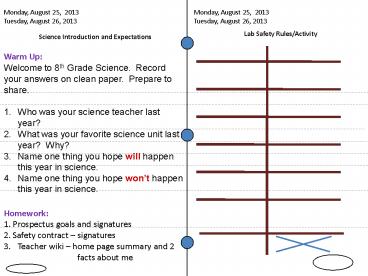
Monday, August 25, 2013 Tuesday, August 26, 2013
Monday, August 25, 2013 Tuesday, August 26, 2013
Lab Safety Rules/Activity
Science Introduction and Expectations
- Warm Up
- Welcome to 8th Grade Science. Record your
answers on clean paper. Prepare to share. - Who was your science teacher last year?
- What was your favorite science unit last year?
Why? - Name one thing you hope will happen this year in
science. - Name one thing you hope wont happen this year in
science.
- Homework
- 1. Prospectus goals and signatures
- 2. Safety contract signatures
- Teacher wiki home page summary and 2
facts about me
2
(No Transcript)
3
8th Grade Science Interactive Notebook Set-up
4
Page Set-Up Expectations
Date A-DayDate B-Day
Date A-DayDate B-Day
Classwork Titles Notes Diagrams Activities Hando
uts
Topic Title
Essential Question Write out questions Answer
to Essential Question Complete sentences Warm
Up Answer question in complete sentences
Homework Homework assignments should always be
written in your planner!
Page
Page
5
Date A-DayDate B-Day
Homework Title(s)
Warm Up Write out questions, charts, diagrams
AND your responses!!!
Inside Cover of Notebook
Keep This Page Blank!!!!
Homework Homework assignments should always be
written here, as the title AND in your agenda!
Page
6
Technology Cheat Sheet
Prospectus Page
Tape Technology Cheat Sheet Here
Tape 8th Grade Science Prospectus Here
7
Wednesday, August 27, 2014 Thursday, August 28,
2014
Wednesday, August 27, 2014 Thursday, August 28,
2014
Discovery Ed. Webquest
Science Introduction and Expectations
Fill in Technology Cheat Sheet and attach to
your notebook 1. Gaggle / Chromebook
login Username flastxxxx_at_cms.gaggle.net (first
initial last name last 4 of student
id) Password YYMMDD 2. Discovery Education
Science TechBook www.discoveryeducation.com User
ID/Login (student ID_cms) Password
(student ID ) 3. Powerschool
https//cms.powerschool.com/public Username
(middle set of numbers) Password (last set of
numbers)
Essential Question Using DE, what resources are
available to explore the rock cycle? How are
these resources useful? Warm Up Using the
following 10 words, sort the words into two
categories. Create a t-chart and label each
column.
Lithosphere Natural selection Cells Rock
layers Plate tectonics DNA Genetics Mantle Sedimen
tary Rock Organs
Homework Using DE Fossils and Studying
Earths Past choose one video, and summarize.
Write the main idea, 3 supporting details in your
paragraph.
Page 2
Page 1
8
SchoolNet Test ID
- FA2CY3QE
- 30 Question pre-assessment
- Read the question
- Select an answer for all questions
- Click the Next button
- When you finish, Log into Discovery Education
- Earths History 1st Unit
9
Discovery Education
- Interactive vocabulary - choose 3 words and write
a summary (1 video, 1 animation, and 1
definition) rock cycle, sedimentary rock,
superposition, igneous, convection, asthenosphere - Essential Questions - Locate 2 questions in the
orange question tab- copy and answer 1 question
you definitely know the answer, copy question you
have no idea the answer - Homework - Chose one video, and write summary.
Write main idea, 3 supporting details paragraph
10
Friday Aug 29, 2014 Tuesday, Sept 2, 2014
Friday Aug 29, 2014 Tuesday, Sept 2, 2014
Earths History Unit
Earth and the Rock Cycle
- Outline of Unit
- Earths Structure and Rock Cycle
- Relative and Absolute Dating
- Fossil Evidence of Earths Age
- Geologic Time Scale
- Evolution and Genetic Variation
- Natural Selection
11
Friday Aug 29, 2014 Tuesday, Sept 2, 2014
Friday Aug 29, 2014 Tuesday, Sept 2, 2014
Earths Structure and Rock Cycle
Earths Structure
Essential Question Explain the different
types of rocks found on Earths surface and some
physical results of geologic change on the
Earths surface? Give examples.
- Warm Up Using textbook p.9-10. Answer the
following questions in complete sentences - Explain how Earth is made up of materials with
different densities. - How can scientists explore the Earths interior
without seeing it?
Homework Answer the essential questions on
pages 1 of your notebook.
Page 3
Page 4
12
- Rock Group Jigsaw Instruction Sheet Rubric
- Goal Present the required information in
approximately 4 minutes. - READ ALL RESOURCES. TAKE NOTES AND DETERMINE THE
IMPORTANT DETAILS TO TEACH TO THE CLASS - Characteristics- clear description, diagrams,
labeled, color - Change over time - how it changes (rock or
structure of the Earth) - Supporting Details - fossils, crystals, remains
of organisms, energy (radioactivity from Earths
core) - Key Vocabulary (suggested to use) cementation,
minerals, crystallization, fossils, heat,
pressure, melting, temperature, core, crust,
mantle, asthenosphere, layer, erosion, sediment,
change over time, deposition, lava, magma,
tectonic plate
13
Wednesday, September 3, 2014 Thursday, September
4, 2014
Wednesday, September 3, 2014 Thursday, September
4, 2014
Earth Structure and Changes
Earth Structure
Essential Question What is earths structure
and some physical results of geologic change on
the Earths surface? Give examples.
- Notes from group presentations
- Layers of Earth
- Rock Cycle
- Igneous
- Metamorphic
- Sedimentary
- Theory of Uniformitarianism (320)
- Five Ways Earth Changes (1100)
- DE Video Clips Notes
Warm Up The stem GEO- means Earth. Make a list
of as many words that you can think of that
involve the stem GEO-.
Homework 1. Bring in at least one picture
representing at least one geologic change. I.D.
when, where, how (Weathering, Erosion, land mass
motion, volcanic eruption, Earth crust
movement) 2. Answer the essential question
from page 3 of your NB
Page 6
Page 5
14
Think-pair-share What do you think youre
looking at? What kind of rock is in the picture?
What happened that may have caused this to
happen?
15
Check for understanding
- How is the structure of the earth similar to a
boiled egg?
- How are rocks recycled over time? Discuss three
rock types. - How does the earth change over time?
16
Friday, September 5, 2014 Monday, September 8,
2014
Friday, September 5, 2014 Monday, September 8,
2014
Forces that Build and Destroy
Mining Earths Changes Evidences for the Theory
of Uniformitarianism
- Essential Questions (leave space to answer)
- How does the sun affect the formation of
sedimentary rocks? - How do magma and lava differ?
- How does the formation of intrusive and extrusive
rocks differ? - How does increasing pressure and temperature
affect a rock?
What? When? Where? How did it happen?
Crustal Movement
Volcanic Eruption
Weathering
Erosion
Land Mass Motion
- Warm Up
- How does the Theory of Uniformitarianism help us
understand earths history? (Use your video notes
from last class.) - What evidence do scientists use to study earths
history?
Homework Answer all essential questions.
Page 8
Page 7
17
Constructive And Destructive Forces Web-quest
Resources
- http//iweb.jackson.k12.ga.us/cstewart/geology/Des
tructive.html - http//hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/geophys
/intrus.html - http//www.rocksandminerals4u.com/metamorphic_rock
s.html - http//education.nationalgeographic.com/education/
encyclopedia/magma/?ar_a1 - http//www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/
content/investigations/es0602/es0602page02.cfm - http//www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/environm
ent_earth_universe/rock_cycle/revision/4/ - http//www.learner.org/interactives/rockcycle/
- www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content
/investigations/es0602/es0602page02.cfm
- Task Evaluate online resources and create an
informational brochure - Use the organizer provided by teacher
- Maximum group size 3
- Use selected resources
- Carefully complete each section
- Self assess your use of essential vocabulary and
your level of understanding.
18
Tuesday, September 9, 2014 Wednesday, September
10, 2014
Tuesday, September 9, 2014 Wednesday, September
10, 2014
Classify
- Rock Classification Lab
- Problem What properties can be used to classify
rocks? - Data
- Essential Questions (leave space to answer)
- What properties can be analyzed to classify rocks?
Sample Number Visible Properties Rock Type
1
2
3
4
6
8
9
11
14
15
- Warm Up
- Why are the names intrusive and extrusive
appropriate for two types of igneous rock? - What is their main difference?
- Homework
- Make sure all E.Q.s have been answered.
- Test Mon (A) and Tues(B)
- Earths Layers,
- Rock Cycle,
- 3 Types of Rock
- Uniformitarianism
- Forces of Change
Answer analysis questions 1-2 and 1-3 completely.
Page 9
Page 10
19
Thursday, September 11, 2014 Friday, September
12, 2014
Thursday, September 11, 2014 Friday, September
12, 2014
Complete Labs (1st ½ of class)
Test Review (2nd ½ of class)
- Essential Questions (leave space to answer)
- How are rocks distributed in earths crust?
- 1. Complete Rock Activities 2 and
- Attach your work to page 10
- 2. Review sheet
- Warm Up
- 1. How is the structure of the earth similar to
a boiled egg? - How does the earth change over time?
- How are rocks recycled over time?
- What role does the sun play in rock formation?
- Homework
- Make sure all E.Q.s have been answered.
- Test Mon (A) and Tues(B)
- Earths Layers,
- Rock Cycle,
- 3 Types of Rock
- Uniformitarianism
- Forces of Change
Page 11
Page 12
20
Rocks Activities 2 and 3
- 2. A Crust Full of Rocks
- 3. Mystery Rocks
- Study the graphs
- Answer 1-7 in complete sentences
- Problem What properties can be used to classify
rocks? - Data
- Analyze and Conclude Questions 1-6
Sample Color Texture Foliated or Banded Rock Group
A 1
B4
C6
D11
E14
F15
21
Monday, September 15, 2014 Tuesday, September 16,
2014
Monday, September 15, 2014 Tuesday, September 16,
2014
Law of Superposition and Relative Age of Rocks
Rock Cycle and Uniformitarianism Test
- Essential Questions (leave space to answer)
- How are rocks used to construct earths
chronological history?
- Relative Age the age of an object in relation
to another object - If undisturbed, oldest on the bottom and youngest
on the top - Law of Superposition - layers (strata) that are
younger will be deposited on top of layers that
are older - View
- DE Interactive
- Superposition
Warm Up Think about the word recrystallization
. What do you think happens during this
process? What type of rock does the word allude
to?
- Homework
- 1. Determining Which is Older handout
- color code rocks and identify which is older
- 2. Answer todays E.Q.
Page 13
Page 14
22
Forces that Disturb Chronologycontinued
- Movement of Tectonic plates
- Can bend layers like a taco (oldest layer may be
bent until its on the top. - Faults a break in earths crust where rock
slips past another - Intrusion magma (igneous rock forms) that has
forced its way through existing rock layers
23
Sometimes Rock History Erodes Away
- Unconformity - a buried erosion surface
separating two rock masses or strata of different
ages (a missing rock layer due to erosion)
24
(No Transcript)
25
Homework
26
Wednesday, September 17, 2014 Thursday, September
18, 2014
Wednesday, September 17, 2014 Thursday, September
18, 2014
Exploring Geologic Changes
Exploring Geologic Changes
Essential Questions (leave space to answer) 1.
How are rocks used to construct earths
chronological history? 2. How do geologic
changes impact earths geologic chronology?
Check for Understanding Forming and
Unconformity Activit
y Exploring Geologic Changes in Rock Layers
(25 min) Group roles chief investigator,
materials manager, timekeeper, problem solver
Materials - 3 foam blocks, 2 cardboard blocks,
one textbook Answer summary questions on clean
paper
Warm Up Using the reading sheet Earths Crust
in Motion Write main vocabulary words and
definitions in your notebook Copy main ideas
Think about How do stress forces
affect rock? Why do faults form and where do they
occur? How does movement along faults change
Earths surface?
Homework Create your own diagrams. Draw, label,
and color and example of a rock formation Include
the following strata, intrusion, fault,
unconformity, relative age from oldest to
youngest
Page 15
Page 16
27
(No Transcript)
28
Answer Garden
- Youre class access code is _______________.
- Question What are the key words from the last
two lessons? - Watch your answers grow!!!!
29
Friday, September 19, 2014 Monday, September 22,
2014
Friday, September 19, 2014 Monday, September 22,
2014
Absolute Age / Radioactive Dating
Absolute Age / Radioactive Dating
Essential Questions (leave space to
answer) Essential Questions How can the amount
of parent material in a rock sample be determined
by using half-lives? How does the amount of
parent material in a sample change as time
increases?
- 3 minute Check Up
- When studying an undisturbed rock core, how do
you know which is the oldest and youngest rock
layer? - When might the youngest layer in sedimentary rock
not be on the top? - Can you determine the exact age of rock by
studying layer positions? - Write your own definition for relative age.
- Warm Up
- worksheet - Relative Ages of Rocks
- Homework
- Bring in plain MMs or Skittles for a sweet
lab! - Test Autopsy.
Page 17
Page 18
30
DE KIM Cards
- radioactive dating
- absolute age
- Radioactivity
- index fossils
- half-life
- Use DE for definitions and animations of the
words red. Use your technology to research the
words in black
31
Tuesday, September 23, 2014 Wednesday, September
24, 2014
Tuesday, September 23, 2014 Wednesday, September
24, 2014
Determining Absolute Age
Absolute Age / Radioactive Dating
Essential Questions (leave space to answer) 1.
How do rocks provide evidence of earths absolute
age?
- Absolute Age assigns a quantitative estimate of
the number of years ago an event occurred. - Determining Absolute Age
- Radioactive Dating using radioactive particles
found in a rock to determine the actual age of
the rock - Radioactivity Radioactivity is a process in
which subatomic particles escape from the nuclei
of unstable atoms releasing energy. - See diagram atom
Warm Up What is radioactive dating? How is that
different from relative dating?
- Homework
- Bring in plain MMs or Skittles for a sweet
lab! - Choose an element from the half- life chart and
create a graph representing the daughter and
parent element over time. - Test October 1 and 2
Page 19
Page 20
32
Which rocks do geologist use?
- -Igneous rocks are most useful due to unique
chemical makeup. Radioactive materials are
unchanged. - Sedimentary rock is not as reliable because its
made of many different rock particles - Metamorphic dating usually results in the age of
the change, not the original rock
33
(No Transcript)
34
Determining Absolute Age
- Use an elements Half-life The time it takes for
an element to decay. - Examples
- Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years.
- Always found in LIVING organisms
- Potassium-40 has a half-life of 1.3 billion years
- Half Life You Tube
- Using a specific calculation can help you
determine the absolute age using half-lives
35
Visuals Help with Radioactive DecaySee page 57A
in textbook.
36
Practice Time!!!Copy this chart
Element Z is found in an igneous rock and we are
trying to determine the rocks age. We know Zs
half life is approximately 3,000 years and that
the rock is currently 25 radioactive. How old
is the rock?
Element Y is found in an igneous rock and we are
trying to determine the rocks age. We know Ys
half life is approximately 3,000 years and that
the rock is currently 6.25 radioactive. How old
is the rock?
Element X is found in an igneous rock and we are
trying to determine the rocks age. We know Xs
half life is approximately 3,000 years and that
the rock is currently 50 radioactive. How old
is the rock?
Percentage of Radioactive Material in Rock Number of Half Lives
100 0
50 1
25 2
12.5 3
6.25 4
3.126 5
100 Radioactive Igneous Rock
94 decayed
87.5 decayed
50 decayed
50 Radio- active
75 decayed
25 r-a
12.5
6
Three Half Lives
Four Half Lives
One Half Life
Two Half Lives
37
Graph Examples
38
Graph Example
39
(No Transcript)
40
LAST PRACTICE ITEM FOR TODAY!!!
- Closure - Venn Diagram Relative and Absolute Age
41
Thursday, September 25, 2014 Friday, September
26, 2014
Thursday, September 25, 2014 Friday, September
26, 2014
MM Lab and Article Review
MM Lab and Article Review
Essential Questions (leave space to answer) How
can two sided objects be used as a model for
radioactive decay?
- Now its time for a sweet model !!
- Two person TEAMS
- 1 chief investigator and communicator
- A organized, sometimes organized, disorganized
- B Clear, almost clear, confusing
- Materials Manager and Timekeeper
- A organized, sometimes organized, disorganized
- B Clear, almost clear, confusing
- Materials (per pair)
- 4 cups (2 original and 2 decayed)
- 25 candies (MMs or Skittles) EACH
- 2paper towel
- 25 minutes of time
- USE THE RUBRIC when making the graph
Warm Up 1. Grade your HW using the rubric 2.
Pennies have two sides. Each time you flip a
coin, what is the probability of getting heads or
tails? ______ 3. If given 10 coins, how could
you demonstrate the half-life of elements?
Propose an experiment using 2 sided coins.
(________)
- Homework
- Make sure all Essential Questions between pages
13 and 21 are answered thoroughly. - Relative and Absolute Age Test next Wed / Thurs
Page 21
Page 22
42
SchoolNet Quizhttps//cms.powerschool.com/public
__CY8WA7JE7_
- 10 Question open notebook quiz
- Read questions carefully
- Use a calculator if needed
- Select an answer for all questions
- After the quiz, go to Ms. Youngs wiki to access
the enrichment activity.
43
Wrapping up
- A - How did todays activity model radioactive
decay of material? - B - Explain the similarities between the graph
created today and the graph you created for
homework. - C - Argue that radioactive dating is more
effective at determining the actual age of a rock
than the Law of Superposition.
44
Check Out
- How did todays activity model radioactive decay
of material? - Communicate to your partner one thing they did
well and one area for improvement from the rubric.
45
Monday, September 29, 2014 Tuesday, September 30,
2014
Monday, September 29, 2014 Tuesday, September 30,
2014
Test Review Study Guide
Test Review Study Guide
Essential Questions (leave space to
answer) Describe how rocks are used to study
earths past.
- Group A
- Read 2 short radioactive dating articles and
respond to text using text codes in your notebook
(small handout) - View DE Video The Geology of the Grand Canyon
406 - Respond to text using text codes in your notebook
(small handout) - Group B
- Read 1 Relative Age article and respond to text
using text codes in your notebook (small handout) - View DE Video The Geology of the Grand Canyon
406 - Respond to text using text codes in your notebook
(small handout)
Warm Up Venn diagram comparing and contrasting
relative and absolute age
Homework Study for your test. Test next class.
Study Notebook and activities between pages
17-24
Page 23
Page 24
46
- 3-2-1 Article SummaryResponses must be based on
the article.
- Lodge McCammon Songs Radioactive Dating
- Song in DE
- Listen once 309
- Complete guide second time
- 3 elements used for radioactive dating
- 2 objects commonly dated using radioactive dating
- 1 thing that helped you learn this concept the
best
47
Wednesday, October 1, 2014Thursday, October 2,
2014
Wednesday, October 1, 2014Thursday, October 2,
2014
Fossils
Rock Cycle, Relative and Absolute Age Test
- Background
- provide evidence that life on Earth has changed
over time. - (Learning from Fossils clip 110)
- (The Wooly Mammoth clip 425)
- Fossils evidence indicate changes in Earths
environment - Example -Tropical plant fossils found in polar
regions indicate that polar regions were once
much warmer than they are today. - Fossils Notes Organizer
- Textbook Section 2.1 A
- Pages 45A 51A
- Article Old Timers
- Use text codes to interact with the text
- Essential Question
- How does the location of an index fossil help
determine the age of rocks around it.
- Warm Up
- Radioactive Dating Song
School Net Test ID https//cms.powerschool.com/pub
lic PE7KU8DA
Homework 1. Finding Clues to Rock Layers
handout
Page 26
Page 25
48
Friday, October 3, 2014Monday, October 6, 2014
Friday, October 3, 2014Monday, October 6, 2014
Fossils and Geologic Time Scale
Geologic Time Scale
- Essential Questions
- How does the geological scale help scientists
learn about earths past life forms, land forms,
and climate.
- As geologists and paleontologists studied rock
and fossil records, they found evidence of major
changes in life and land forms at certain time. - Rocks records indicate that earth is about 4.6
billion years old - Evidence shows the moon formed around the same
time so the moon is about____ years old. - Major changes relate or correlate to geologic
time units - Geologic Time Scale is a timeline based on major
events in the history of earth and/or life on
earth
- Warm Up
- You have gone through some major events as you
have developed. When . - a. Were you born? ______________
- Start going to school? ________________
- Large enough to sit in the front seat of a
car?_____ - Learn to tie your shoes? _______________
Homework Discovery Ed Video Historical
Geology A Glimpse of Earths Past 30 minutes
Page 28
Page 27
49
Literacy - Geologic Time Scale Article
- Two ways to relate the order of geologic
events.. - Relatively Placing events in a sequence
- Chronologically s of years ago
- DE Video Discovery Ed Video
- Historical Geology A Glimpse of Earths Past
30 minutes - You need a Interactivity Worksheet yours to
write on - Read the instructions for the Interactivity
Worksheet. Complete notes handout while viewing
the program.
50
Tuesday, October 7, 2014Wednesday, October 8,
2014
Tuesday, October 7, 2014Wednesday, October 8,
2014
Change Over Time Project
Change Over Time Project
Essential Question 1. How do fossils show how
organisms and environments have evolved over
time? 2. How are fossil and geologic records
used to show Earths history ?
- Change Over Time Brochure
- Use the template to organize the following
topics Research and describe the theory of
continental drift and past continental, fossil
evidence supports continental drift, organisms
change over time. - Use the QR codes for selected research sites.
- Creativity note add image representative of the
content - Make sure to use the rubric to self-assess your
brochure
Warm Up Read the Geologic Time Scale reading
sheet. Answer the following questions. 1. Why
is the geologic time scale used to show Earths
history? 2. What methods did geologists use when
they first developed the geologic time scale? 3.
How did geologists decide where one division of
the geologic time scale ends and the next begins?
4. What are the different units of the geologic
time scale?
Homework 1. Finish the brochure
Page 30
Page 29
51
Thursday, October 9, 2014Friday, October 10, 2014
Thursday, October 9, 2014Friday, October 10, 2014
Geologic Time Scale Wrap Up
Geologic Time Scale Wrap Up
Essential Question 1. How do fossils show how
organisms and environments have evolved over
time? 2. How are fossil and geologic records
used to show Earths history ?
- B day
- Paleontology review
- Go over fossil notes sheet
- Summarize Patterns Historical Geology A
Glimpse of Earths past - Are you ready for some Football!
Warm Up Using your fossil notes sheet and the
Old timers article. 1. How do fossils provide
evidence of environmental changes that occurred
in the past? 2. An ancient tropical fossil was
found in the polar region. What do you think a
paleontologist would suggest based on this
finding? Explain why. 3. List the 5
characteristics of index fossils.
- A day
- Review Geologic Time Scale video notes
- Activity 1 Mapping geologic time scale
- Activity 2 DE Explore Tab Evidence of Evolution
- Homework
- Online Quiz Informal (double weight)
- Code_LY2TE3_
Page 32
Page 31
52
Closure
- How does the Geological Time Scale help
scientists to learn about Earths past life
forms, land forms, and climate?
53
Monday, October 13, 2014Tuesday, October 14, 2014
Monday, October 13, 2014Tuesday, October 14, 2014
Evidence of Climate Change
Evidence of Climate Change
Essential Question 1. How do ice cores change
over time? 2. How do ice cores tell scientists
about Earths changing atmospheric makeup?
- Carbon Dioxide Graphing Activity
- Students analyze the link between atmospheric
temperatures and carbon dioxide (CO2)
concentrations by looking at ice core data
spanning hundreds of thousands of years. - Understand the link between temperatures and CO2
concentrations in the atmosphere - Learn how to analyze patterns from the past and
present - Learn how past patterns can help to predict
future scenarios
Warm Up Using textbook, pg A 51- Read Ice Cores
(2 paragraphs) -Create a KIM card for the vocab
word ice core -Answer the question How does an
ice core provide information about Earths
history?
- Homework
- Finish Graphs
- CO2 Over Time
- Temperature Over Time
Page 34
Page 33
54
ICE CORES
- Each layer records the concentration of gases and
tiny particles in the atmosphere during the time
the ice was formed. - Antarctica Ice core was drilled that measured 3
km. or 1.86 miles long! - Contained air bubbles that showed climate changes
for the last 740,000 years. - During that time, Earth had 8 Ice Ages
55
(No Transcript)
56
(No Transcript)
57
Vocabulary Word Web
- Carbon
- Carbon cycle
- Carbon dioxide
- Fossil fuel
- Greenhouse effect
- Greenhouse gas
- Ice core
- Temperature anomaly
1.
2.
Climate Change Over Time
3.
4.
58
Closure
- A
- B
C
- What is an ice core?
- How do ice cores change over time?
- How do ice cores change over time?
- How do ice cores tell scientists about Earths
changing atmospheric makeup?
- Explain how ice core and tree ring data provide
evidence of climate change over time. - Provide examples (determines how levels of carbon
dioxide have changed over time.)