Lewis and Clark Expedition - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
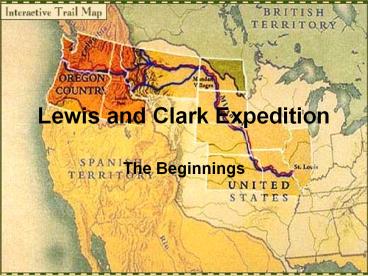
Lewis and Clark Expedition
Description:
Lewis and Clark Expedition The Beginnings – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:250
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lewis and Clark Expedition
1
Lewis and Clark Expedition
- The Beginnings
2
Thomas Jefferson
- Jefferson took office in 1801 and during the time
most of the United States lived 50 miles from the
Atlantic Ocean - Americans only knew about the West from fur
trappers and British and Spanish Explorers - Jefferson decided to form an expedition on a
budget of 2,500 to explore the West - In order to form the expedition he needed to get
permission from Congress and January 18, 1803 he
sent a confidential letter to congress requesting
the expedition to be formed. - Congress granted his request and the idea for the
expedition was formed.
3
Reasons for Exploring
- Jefferson wanted to find a water route that lead
to the Pacific Ocean. - He hope to establish relationships with Indian
tribes of the West in hopes establish trade - Jefferson also wanted to see what could be
learned about the geography of the West, the
lives and languages of Native Americans, the
plants and animals, the soil, the rock, the
weather, and how they differed from those in the
East.
4
Louisiana Purchase
- The expedition was founded before the Louisiana
Purchase was bought and Jefferson was going
explore the land even though the French owned it. - Jefferson wanted the territory but mainly he
wanted control over the port town of New Orleans. - The land was purchased from France who was being
ruled at the time by Napoleon Bonaparte. - They agreed to purchase the Louisiana Territory
which included New Orleans. In the end the
acquired more land that they had originally hoped
for. - The purchase from France cost 15 million and was
827,000 square miles of land. - The new territory gained doubled the size of the
United States.
5
(No Transcript)
6
Meriwether Lewis
- Meriwether Lewis was one of Thomas Jeffersons
childhood friend. - He served six years in the Frontier army and rose
to the level of a Captain. - In 1801 Lewis was appointed as Thomas Jeffersons
personal secretary and aid. - Lewis was named the commander of the expedition
created to explore the lands gained during the
Louisiana Purchase. - He was given the task of finding a co-commander
to help him lead the expedition.
7
William Clark
- Clark was a Virginia native just like Meriwether
Lewis. - All of Clarks brothers were Revolutionary War
veterans and he started his military career at
the age of 19 by joining the Virginia Militia. - He reached the status of a lieutenant in the
regular army and later moved up to the position
of a Captain. - Twice Clark was used to spy on the Spanish to
monitor their building of forts and explorations.
8
Reasons the leaders were chosen
- Meriwether Lewis
- Brave, practical and careful
- Familiar with the woods
- Knowledgeable with Indian manners and character
- In great physical condition
- Took courses in astronomy as well as cartography.
- Sharp eye for details about plants and animals
- William Clark
- Learned how to build forts
- Knew how to draw maps
- Could lead pack trains through enemy country
- Had fought the Indians on their ground.
9
The beginning of the Expedition
- Lewis and Clark were responsible for choosing the
men to accompany them on their journey. - They started preparing and gathering people and
supplies to take with them on the trip. - The men had an keel boat crafted so that they
could travel up the river. - The keel boat was useful because it could be
rowed, sailed, poled like a raft, or towed from
the riverbank. - Two wooden Pirogues were taken along as well to
hold men and supplies.
10
Types of Supplies Brought
- Mathematical instruments
- Camp supplies
- Presents for Indians
- Clothing
- Arms and Ammunition
- Medicine and medical supplies
- Books and resources
11
Mathematical Instruments
- Surveyors compass
- Hand compass
- Quadrants
- Telescopes
- Thermometers
- Sextants
- Plotting instruments
- Chronometer
12
Camp Supplies
- 150 yards of cloth to be oiled and sewn into
tents and sheets - Pliers
- Chisels
- Steels for striking fire
- Hatchets
- Mosquito curtains
- Fishing hooks and line
- Soap
- Portable soup
- Salt
- Writing ink , paper and crayons
13
Presents for Indians
- Pocket mirrors
- Sewing needles
- Scissors
- Sewing Thread
- Ribbons
- Combs
- Handkerchiefs
- Tobacco
- Tomahawks that served as pipes
- Knives
- Kettles
- Beads
14
Clothing and Ammunition
- Flannel shirts
- Coats
- Frocks
- Shoes
- Woolen pants
- Blankets
- Knapsacks
- Stockings
- 15 .54 Caliber riffles
- Knives
- 420 pounds of sheet lead for bullets
- 176 pounds of gunpowder
- 500 rifle flints
- 1 compressed air rifle
15
Medical Supplies
- 50 dozen of Rushs pills
- Lancets
- Forceps
- Syringes
- Tourniquets
- Doses for physic, emetic, diaphoretic
- Other drugs for blistering, salivation, and
increased kidney output
16
Library Resources
- Bartons Elements of Botany
- Antoine Simon Le Page du Pratzs History of
Louisiana - Richard Kirwans Elements of Mineralogy
- A Practical Introduction to Spherics and Nautical
Astronomy - The Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris
- a four-volume dictionary
- a two-volume edition of Linnaeus (the founder of
the Latin classification of plants) - tables for finding longitude and latitude
- map of the Great Bend of the Missouri River
17
Corps of Discovery
- The Corps of Discovery was the name given to
Lewis and Clark and the members of their
expedition. - The corps consisted of many different types of
people and it was Lewis and Clarks job to decide
what types of men they needed for the job and who
was best suited.
18
Translators
- Lewis and Clark needed translators of many Indian
languages to help them along their journey. - They often hired men who spoke multiple languages
and help them with many Indian tribes. - Some translators did not know English and Lewis
and Clark had to go through a line of many
translators just to communicate. - Verbal Indian language, while useful was not the
only form of communication the explorers needed
to use. Sign language was an important aspect in
Native American culture, so Lewis and Clark
brought translators along who could sign as well.
- They also needed translators who were familiar
with the unknown territories of the west.
19
Toussaint Charbonneau
- Charbonneau was a French fur trader who lived
amongst the Hidatsa and Mandan Indians. - He spoke French as well as Hidatsa and was chosen
to be a translator and to also bring his one of
his wifes Sacagawea along on the trip. - At first Charbonneau rejected the offer because
he did not want to have to perform regular duties
of other men on the trip, but he apologized and
the Captains signed him onto the trip.
20
George Drouillard
- Drouillard was helpful to Lewis and Clark because
he knew the Indian character and sign language. - He had a French Canadian father and a Shawnee
Indian mother. - He was one of the only non-military men to
complete the trip from camp Dubois to the Pacific
and back
21
- Sacagawea was a Shoshone Indian girl who was
taken from her people by the Hidatsa Indians. - She was then sold to Toussaint Charbonneau as a
slave who then later took her as one of his
wives. - Charbonneau and Sacagawea were a translating team
because she knew how to speak Shoshone as well as
Hidatsa. - She remembered trails from when she was a child
and proved to be very valuable on the trip
22
Jean Baptiste
- Sacagewea was the only woman on the expedition
and she was also pregnant at the time. - She had a baby boy and named him Jean Baptist
Charbonneau. - Clark too great favoritism to the little boy and
foundly referred to him as little pompy or pomp. - This nickname was created because he was a little
boy who was always showing off and dancing. - Clark carved his name into a tower of sandstone
in a river bend and called it Pompys tower.
Today you can still see the name and it is the
only evidence of the explorers that is still left
on the trail.
23
York
- York was Captain Clarks slave and he is the only
other non-military man besides Drouillard to
complete the whole trip. - He helped the explorers wherever needed and was
said to be a hunter and also concerned with the
safety of the camp. - The Indians often took interest in York because
he was the first black man that they had ever
seen.
24
Seaman
- Lewis brought along his Newfoundland dog on the
trip with him. - The dogs name was originally thought to be
Scannon do to historians misreading the journals
written by the men on the trip. - Seaman was a great companion and would often help
the explorers by barking and warning them of up
coming dangers.
25
Military Officers
- Lewis and Clark took many military officers with
them along the trip. They were used as protection
as well as man power to maneuver the boats and
supplies. - The men ranged in rank from captains to sergeants
and privates.
26
Charles Floyd
- Floyd was a sergeant on the trip.
- He wrote journals along the way that were later
published along with another Corps member. - He died unexpectedly on the trip and was the only
reported causality. - Medical professionals believe that he died of a
ruptured appendix.
27
Francois Labiche
- Labiche was a private on the trip, but he became
very useful to Lewis and Clark. - He was useful in the train of translation because
he could speak French which enabled him to talk
to Charbonneau who could speak to Sacagewea. - Labiche was also a skilled boatman and frontier
trader and knew several lower Missouri Indian
languages.

























![READ [PDF] Mountain Man: John Colter, the Lewis & Clark Expedition, and the Call of the PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10107554.th0.jpg?_=20240824102)
![READ [PDF] Mountain Man: John Colter, the Lewis & Clark Expedition, and the Call of the PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10108884.th0.jpg?_=20240825062)
![READ [PDF] Mountain Man: John Colter, the Lewis & Clark Expedition, and the Call of the PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10110288.th0.jpg?_=20240826058)
![READ [PDF] The Journals Of Lewis And Clark (Lewis & Clark Ex PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10115928.th0.jpg?_=20240901098)

![READ [PDF] Mountain Man: John Colter, the Lewis & Clark Expedition, and the Call of the PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10134714.th0.jpg?_=20240921016)