Heat vs Temperature - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Heat vs Temperature
Description:
Heat vs Temperature Heat: The energy that transfers from one object to another because of a temperature difference between them. a higher-temperature object to a ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:55
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Heat vs Temperature
1
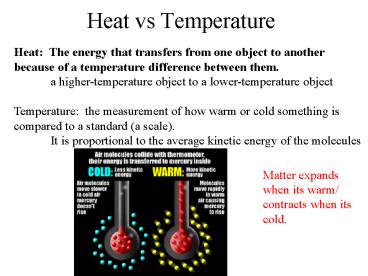
Heat vs Temperature
Heat The energy that transfers from one object
to another because of a temperature difference
between them. a higher-temperature object to a
lower-temperature object Temperature the
measurement of how warm or cold something is
compared to a standard (a scale). It is
proportional to the average kinetic energy of the
molecules
Matter expands when its warm/ contracts when its
cold.
2
Measuring Heat
calorie - the most common unit of heat The
amount of heat required to raise the temperature
of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. 1000
calories 1 kilocalorie The SI unit of heat
and all forms of energy is joules 1 calorie
4.184 Joules
3
Thermal Expansion
- Many substances expand when heated
- When heated, the particles (atoms or molecules)
in a substance vibrate more. This means they
need more space. So the substance expands
The particles in a substance do not expand
themselves!
4
Expansion joints in bridges
5
Compensations for Thermal Expansion
gap
rail track
oval hole for nut and bolt to slide along
Railways tracks are laid in sections with gaps
between them. The railways sections are held
together by fish-plate and fastened by bolts
and nuts through oval holes.
6
Compensations for thermal expansion
Expansion Joint
Pipelines carry very hot gases (such as steam),
therefore need expansion joint (in ring form) to
avoid damages given by expansion.
7
Contraction can be a problem too!
Overhead power lines and telephone wires
In summer and winter, the overhead power lines
and telephone wires will expands and contracts
due to the changing weather.
8
Expansion of various Solids
Different materials expands by different amount
when heated through the same increase in
temperature.
Materials Increase in length (mm)
per m
aluminium 0.25 brass
0.19 iron
0.12 steel
0.11 glass
0.09 invar
0.01
9
Bimetallic Strip
A bimetallic strips is made up of two strips of
different metals.
Brass expands more than iron when hot, and
contracts more too. Ex. Thermostats, oven
thermometers.
10
Heat Transfer
- Heat always moves from a warmer place to a cooler
place. - Hot objects in a cooler room will cool to room
temperature. - Cold objects in a warmer room will heat up to
room temperature.
11
Heat Transfer
- 3 ways to transfer heat
- Conduction
- Radiation
- Convection
Bill Nye Heat - http//www.youtube.com/watch?vsvq
ieBM2ijs
12
Conduction
- Conduction transfer of heat by direct
contact. - Conductors materials that transfer heat well
- Insulators materials that delay the transfer
of heat.
13
Why does metal feel colder than wood, if they are
both at the same temperature?
Metal is a conductor, wood is an insulator. Metal
conducts the heat away from your hands. Wood does
not conduct the heat away from your hands as well
as the metal, so the wood feels warmer than the
metal.
14
Convection
- Convection Heat is transferred by currents in a
liquid or a gas. When heated molecules move from
one place to another, taking the heat with them. - Warm molecules rise and cool molecules sink
15
Radiation
- Radiation transfer of heat by means of
electromagnetic waves - energy is carried by electromagnetic waves and
does not involve the movement or the interaction
of matter. - can occur through matter or through a vacuum.
16
Four containers were placed equidistant from a
heater. Which container would have the warmest
water after ten minutes?
The __________ container would be the warmest
after ten minutes because its surface absorbs
heat _______ the best. The _________ container
would be the coolest because it is the poorest at
__________ heat radiation.
dull black
radiation
shiny metal
absorbing
17
Four containers were filled with warm water.
Which container would have the warmest water
after ten minutes?
shiny metal
The __________ container would be the warmest
after ten minutes because its shiny surface
reflects heat _______ back into the container so
less is lost. The ________ container would be the
coolest because it is the best at _______ heat
radiation.
radiation
dull black
emitting
18
1st Law of Thermodynamics
The energy of the universe is constant. Energy
can be neither created nor destroyed, so while
energy can be converted to another form, the
total energy remains constant.
Any Isolated System
Energy In
Energy Out
AKA Law of Conservation of Energy.
19
Heat added
increase in internal energy
external work done by the system.
- 30. If 10 J of energy is added to a system that
does no external work, by how much will the
internal energy of that system be raised? 10J - 31. If 10J of energy is added to a system that
does 4J of external work, by how much will the
internal energy of that system be raised? 6J - 32. 100J of heat is added to a system that does
60J of external work. The internal energy change
of the system is? 40J
20
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Heat will always flow from an object of higher
temperature to an object of lower temperature
or natural systems tend to proceed toward a state
of greater disorder. aka entropy
21
Entropy
A measure of the disorder of a system.
x
Systems tend to change from a state of low
entropy to a state of higher entropy. That is to
say, if left to themselves, systems tend to
increase their entropy.
22
Increasing Entropy
Solids Liquids Solutions Gases
Fewer Particles More Particles