Songhai - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title: Songhai
1
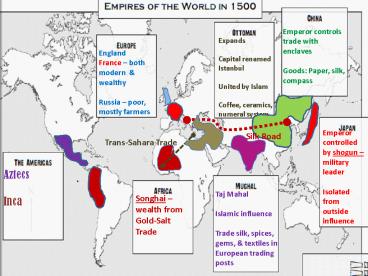
Emperor controls trade with enclaves Goods
Paper, silk, compass
Expands Capital renamed Istanbul United by
Islam Coffee, ceramics, numeral system
England France both modern wealthy Russia
poor, mostly farmers
Emperor controlled by shogun military
leader Isolated from outside influence
Silk Road
Trans-Sahara Trade
Aztecs Inca
Taj Mahal Islamic influence Trade silk, spices,
gems, textiles in European trading posts
Songhai wealth from Gold-Salt Trade
2
Mona Lisa by Leonardo da Vinci Renaissance man
Rebirth of classical knowledge
Begins in Italian city-states Spreads to
Northern Europe
Sistine Chapel By Michelangelo realist painter
sculptor
Humanism focus on human values and
accomplishments, learning
Shakespeare English playwright, poet of Northern
Renaissance Machiavelli The Prince
3
Martin Luther
Salvation by faith alone All humans equal before
God
Italians dominate Corruption and sale of
indulgences Huge wealth influence of merchants
Posts 95 Theses (problems) on church door Begins
Protestant movement
4
Henry VIII of England Pope in Rome
English church
property as his
Elizabeth I
Anglican Church Dissenters Spanish Armada
Colonies
John Calvin
Predestination What will happen to
you Protestant movement
5
Princes remains Catholic 30 Years
War
Edict of Nantes Calvinists in
France Makes 30 Years War political
John Wycliffe Jan Huss Council
of Trent
Society of Jesus (Jesuits)
Inquisition
individualism
secularism Religious toleration Printing
press Higher literacy, spreads new
ideas
6
Vasco da Gama Portugal Sails around
Africa to create trade route to
India Columbus Spain Reaches the New
World, decimates indigenous Americans
Magellan Spain His crew 1st to sail
around the world, he dies in Philippines Hernan
Cortes Spain Conquistador, conquered the
Aztecs in Central Mexico Francisco
Pizarro Spain Conquistador, conquered the
Inca in Peru Francis Drake England
Privateer, sailed around the world, defeated
Spanish Armada Jacques Cartier France
Reached Canada and claimed it for France
7
Europe Prince Henry of Portugal
pioneers exploration Demand for gold
Competition for colonies
Europeans Horses, cattle, diseases that kill
many Indians
Sugar rum
America Rigid class system Colonies imitate
mother country Christianity
Manufactured goods
lifestyles completely
leads to slavery Plantation economy and
environment
Slaves
Africa European trading ports
Slaves gold exported Christianity spreads
Western Hemisphere Native Americans Corn,
potatoes, tobacco
Economic practice, colonies benefit mother
country banking
system money for markets
8
Centralize Power take all of it for
themselves Rule by Divine Right Gods will
France
Builds palace of Versailles Spends to expand
royal power
Louis XIV
Russia
Westernizes Russia Builds St. Petersburg Takes
nobles power
Peter the Great
Ignores Parliament, raises taxes
Puritan military leader
9
Ignores Parliament, raises taxes
Puritan military leader
Grants rights and freedoms to Englishmen
Royal power Eventual democracy
Americas gov
Cromwell dies and Charles II
restores the monarchy to England
Peaceful, bloodless revolution William
Mary share power
equally with Parliament
Fights with Parliament Factions
modern political parties
10
Applies reason to human natural world,
stimulates religious tolerance and new government
Leviathan
Humans exist in nature Government protects us
John Locke
Government must protect our life, liberty,
property
The Spirit of Laws
Montesquieu
Government is a contract between people and ruler
Social Contract
11
Religious toleration, separation of church state
Voltaire
Thomas Jefferson
Declaration of Independence
Baroque composer
Concertos, fugues
Mozart
Symphonies, operas
Eugene Delacroix
Romantic painter
Miguel Cervantes
Don Quixote
12
Copernicus developed heliocentric
theory Kepler Discovered planetary motion
Isaac Newton Discovered laws of gravity
Galileo Used telescope to support heliocentric
theory
William Harvey Discovered blood circulation
Reason and observation lead to scientific method
13
Absolute monarchy Napoleon
Conquer Europe Napoleonic Code Congress of
Vienna
Power Map of Europe Political
philosophies (Liberal/Conservative)
Bastille starts the Revolution
Enlightenment Ideas on government
Terror takes power, uses
guillotine to execute
The success of the American Revolution
14
outposts of control for
Europe Catholicism
mother countries
Mining Viceroys
1823 President Monroe Latin
America is independent Threat to Americas peace
safety
Toussaint LOuvture France in
war slavery in Haiti (1st one)
Havana ?
Mexico City ?
15
Miguel Hidalgo 1810-1821
Lima ?
Enlightenment
liberated northern Creole
from Venezuela Class
system (Creoles, Mestizos, Natives)
? Sao Paulo
BuenosAires ?
16
National pride in your countrys interests
Leads the Red Shirts in joining Northern
Southern Italy
Uses nationalism to unify Northern Italy
Germans Italy unhappy with result Congress of
Vienna
In Rome are the last to join and unify the
country of Italy
Unsuccessful revolutions in 1848
Great Britain expands political rights
17
Nationalism
Realpolitik
Franco-Prussian War
Otto Von Bismarck
18
England
Natural resources (coal, iron), stable
government, steam engine
Increased education Better standard of
living Better transportation Urbanization - more
cities
Harsh working conditions Factory system ends
cottage industries Pollution poor
housing Enclosure movement
19
James Watt
Steam Engine
Spinning jenny used in Englands textile
factories
James Hargreaves
Eli Whitney
Cotton Gin demand for labor leads to slavery
Henry Bessemer
Process for making strong, cheap steel
Smallpox vaccine
Edward Jenner
Discovers bacteria cause of sickness
Louis Pasteur
20
European conflicts brought to colonies Dutch
British set up trading ports in India Christian
missionaries convert natives to Christianity
Directly ruled by foreign power
(America 13 colonies) Country protected
by another 1 (Hawaii) Region where 1 country gets
trading rights (China)
Nationalism competition for power
wealth Industrial Revolution demand for natural
resources and markets
Matthew Perry 1854
America East India Company
Built in Egypt to cut travel time to
India, England controls it
Held in 1884, European Powers divide
up Africa for themselves
21
Matthew Perry 1854
America East India Company
Spheres of Influence
Built in Egypt to cut travel time to
India, England controls it
Held in 1884, European Powers divide
up Africa for themselves
Great Britain Indian National Congress
pushes for independence
Foreigners Boxer
Boxers attack US merchants
22
mperialism
lliances
ationalism
ilitarism
Competition for colonies, resources, and markets
Europe divided into competing groups Central
Germany Allies England, France, Russia
Balkan Peninsula powder keg of ethnic
tension Many diplomatic failures
Armistice signed Treaty of Versailles ends the
war
Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand of Austria
starts the war
Zimmerman Note makes America join on Allied side
Russian Revolution forces Russia to leave the
war sign treaty
23
Woodrow Wilson Americas president Wanted to stay
out of WWI Created 14 Points plan for peace
Kaiser Wilhelm II Germanys leader Loses empire
after the war to the Allies
League of Nations
Alliance
Forces Germany to accept guilt for war Puts limit
on Germanys military
Independence for helping Europeans fight in WWI
future wars
Ottoman Empire Middle east
America
England
weakness
France
24
Japan
Bolsheviks
New Economic Policy
Vladimir Lenin
Landless peasants
Stalin
Tsar Nicholas
Communist
5 Year Plans
WWI
Soviet Union
Secret police
farms
Great Purge
25
German reparations High protective
tariffs Americans using credit 1929 Stock
Market Crash
unemployment
banks
prices
inflation
political
26
Joseph Stalin Leads Soviet Union Communist Signs
non-aggressionpact withHitlernot to fight
Benito Mussolini Leads Fascist Party Wants to
return Italy to glory of Rome Invades Ethiopia
in show of force
Adolf Hitler Anti-semitism National Socialism
Nazi Party Invades Occupies neighboring
countries
Hideki Tojo Hirohito Militarism Industrial
izes Japan Invade Korea, Manchuria, China for raw
materials
27
Hideki Tojo Hirohito Militarism Industrial
izes Japan Invade Korea, Manchuria, China for raw
materials
Giving in to avoid war at the Munich Conference
Poland
France Nazis
Americas president at
the start of WWII
Britain air
England over Nazis
President when FDR dies,
orders a-bomb dropped
Germany Soviet Union
non-aggression pact
Englands prime minister
who stands up to Nazis
Supreme Allied commander
of all allied forces
Japan America
US general in charge of
the battle in Asia/Pacific
D-Day
Hiroshima Nagasaki
28
Jews, non-Aryans, disabled
Adolf Hitlers Final Solution
1930s-1940s
Political enemies, intellectuals
Joseph Stalin secret police
Soviet Union
Rwanda
Hutu militia
1994
Artists, enemies, intellectuals
Cambodia
1970s
29
Marshall Plan
US occupies under Gen. MacArthur
Tokyo
Nuremburg
Japanese war criminals (Tojo)
Japan now a powerful, wealthy ally
Nazis
US gives to democracies to prevent communism
Universal Declaration of Human Rights UN
statement of basic rights all humans deserve
Superpowers the Soviet Union
America Soviet Union
Democracy free market capitalism Communism
state control
NATO military alliance of democracies Warsaw
Pact military alliance
Support West Germany Berlin
Take over East Germany, wall off Berlin
30
Yalta Conference
England, Soviet Union America
Eastern Europe as satellite nations
Iron Curtain
Trumans Doctrine
Deterrent to war
Mao Zedong
communist
Chiang Kai Shek nationalists
Taiwan
31
Communist democratic
China USA NATO
Divided in 2 today
France
Ho Chi Minh
Contain Vietnam is all communist
Economic military
Nationalism
NATO military alliance
Berlin Wall
Union Estonia
Latvia
32
Indian Subcontinent
Middle East
Africa
Led non-violent protest against
British rule
Israeli Prime Minister led Israel in
Yom Kippur War
led violent struggle against
English rule in Kenya
became 1st prime minister
after Gandhis assassination
Egypts president,
nationalized Suez Canal, built Aswan Dam allied
with Soviets
First black president of
South Africa, fought against apartheid
Developed nuclear program and
allied with Soviets
33
Group led by
Gandhi that fought for independence
Gives power of self-determination to African
colonies
After WWI used to control territories in Mideast
prohibited discrimination
(caste system)
Mandate power in Syria Lebanon
imperial rule by Europeans
economic exploitation
Mandate power in Jordan Palestine
England divided India by religion
with Muslims in Pakistan
Fights for independence from France
Created after WWII out of Palestine
today the worlds largest
democracy
peaceful transitions to
independence
Differences create conflicts in
Palestine, Israel, etc
federal system gives most
power to states in India
violent fight for independence
has eased
financial problems
long struggle against
apartheid (Segregation)
34
- High Literacy rate
- Low fertility rate (babies per mother)
- Slow or no population growth
- Freemarket economies
- Large middle class
- Political freedom
- High Birth rates rapid growth
- Low literacy rates
- Little access to health care
- Poverty
- Poor health
Ethnic religious conflict
Climate change
illiteracy Pollution rapid growth
Terrorism
35
Refugees countries
Guest workers temporary
- Munich Olympics
- 9/11 attacks
- Car bombings
- Suicide bombers
- Airline hijackers
Global peace keeping
organization
lends money to
developing nations at a cost
Surveillance Review of privacy rights Security
at ports and airports Identification badges and
photos
free trade agreement between US,
Canada, Mexico
Global
organization promoting free trade
- common currency and easier
borders in Europe
36
North South America, Europe Billions New
Testament
Israel, America Millions Torah written
record of Hebrew beliefs
India South Asia Billion Vedas
China, India, Asia Millions 4 Noble Truths
Middle East Africa Billions Koran (Quran)
37
Catholics Protestants in N. Ireland Jesus as
son of God Councils agree on Church doctrine
India Pakistan Karma knowledge that all
thoughts actions have consequences Reincarnatio
n rebirth based on karma
China freedom of religion Enlightenment
spiritual happiness 8 Fold Path steps you
take to reach Enlightenment
Arab Israeli conflict Yom Kippur War over
Israel 10 Commandments Guide moral religious
conduct
Arab-Israeli conflict Middle East 5 Pillars
basic acts of faith for all Muslims Mecca
Medina holy sites Muslims should pilgrimage to