Figure 28.1 The duration of sleep - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 42
Title:
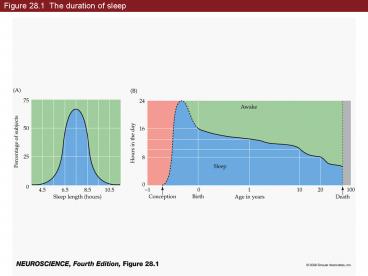
Figure 28.1 The duration of sleep
Description:
Title: Neuroscience, 4e Last modified by: Sinauer Created Date: 10/16/2000 7:08:56 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Company: Sinauer Associates, Inc. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:65
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Figure 28.1 The duration of sleep
1
Figure 28.1 The duration of sleep
2
Figure 28.1 The duration of sleep (Part 1)
3
Figure 28.1 The duration of sleep (Part 2)
4
Figure 28.2 Circadian rhythmicity of core body
temperature and growth hormone cortisol levels
5
Box 28A Sleep Styles in Different Species
6
Box 28A Sleep Styles in Different Species (Part
1)
7
Box 28A Sleep Styles in Different Species (Part
2)
8
Figure 28.3 Consequences of total sleep
deprivation in rats
9
Figure 28.3 Consequences of total sleep
deprivation in rats (Part 1)
10
Figure 28.3 Consequences of total sleep
deprivation in rats (Part 2)
11
Figure 28.4 Rhythm of waking and sleeping in
isolation, with and without daynight cycle cues
12
Figure 28.5 Photoreceptors responsible for
signaling circadian light changes
13
Figure 28.5 Photoreceptors responsible for
signaling circadian light changes (Part 1)
14
Figure 28.5 Photoreceptors responsible for
signaling circadian light changes (Part 2)
15
Figure 28.5 Photoreceptors responsible for
signaling circadian light changes (Part 3)
16
Box 28B Molecular Mechanisms of Biological Clocks
17
Box 28B Molecular Mechanisms of Biological Clocks
18
Figure 28.6 EEG recordings during the first hour
of sleep
19
Box 28C(1) Electroencephalography
20
Box 28C(2) Electroencephalography
21
Box 28C(3) Electroencephalography
22
Figure 28.7 Physiological changes during the
various sleep states
23
Figure 28.7 Physiological changes during the
various sleep states (Part 1)
24
Figure 28.7 Physiological changes during the
various sleep states (Part 2)
25
Figure 28.7 Physiological changes during the
various sleep states (Part 3)
26
Figure 28.8 Circuitry involved in decreased
sensation and muscle paralysis during REM sleep
27
Figure 28.8 Circuitry involved in decreased
sensation and muscle paralysis during REM sleep
28
Figure 28.9 Activation of specific neural
circuits triggers sleep and wakefulness
29
Figure 28.10 Cortical regions whose activity
changes during REM sleep
30
Figure 28.11 Important nuclei in regulation of
the sleepwake cycle
31
Figure 28.11 Important nuclei in regulation of
the sleepwake cycle (Part 1)
32
Figure 28.11 Important nuclei in regulation of
the sleepwake cycle (Part 2)
33
Figure 28.11 Important nuclei in regulation of
the sleepwake cycle (Part 3)
34
Figure 28.11 Important nuclei in regulation of
the sleepwake cycle (Part 4)
35
Box 28E Drugs and Sleep
36
Figure 28.12 Thalamocortical neuron activity in
sleep and awake states
37
Figure 28.13 Thalamocortical feedback loop and
the generation of sleep spindles
38
Figure 28.13 Thalamocortical feedback loop and
the generation of sleep spindles (Part 1)
39
Figure 28.13 Thalamocortical feedback loop and
the generation of sleep spindles (Part 2)
40
Figure 28.14 Summary scheme of sleepwake states
41
Figure 28.15 Sleep pattern of a patient with
obstructive sleep apnea
42
(No Transcript)