Soil Formation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Soil Formation
Description:
Soil Formation Soil is formed when rock breaks down because of weathering, and mixes with other materials on the surface. Soil is a mixture of – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:378
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Soil Formation
1
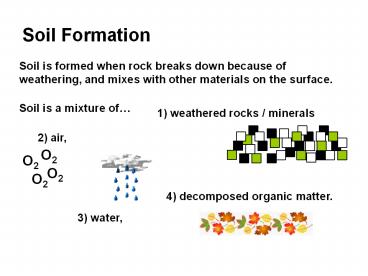
Soil Formation
Soil is formed when rock breaks down because of
weathering, and mixes with other materials on the
surface.
Soil is a mixture of
1) weathered rocks / minerals
2) air,
4) decomposed organic matter.
3) water,
2
Humus 4 - 5
Air 25
Weathered Rock 45
Water 25
3
Soil Formation
Decompose to break down living things into
smaller pieces, and
return nutrients to the soil.
Decomposers include
The F B I
Insects
Fungi
Bacteria
4
Soil Formation
LITTER Leaves and other plant material that
falls onto the surface of the Earth. Hasnt
decomposed yet.
5
Soil Formation
HUMUS Litter (from plants) and dead animals,
that have been decomposed
(broken down)..
6
Soil Formation
Organic living, or once living
(Technically, it means made of carbon atoms)
Humans
Animals
Plants
Dead Dinosaurs
Insects, Fungi, Bacteria
- All of these are living, or once living
- All of these are made of carbon atoms
- All of these are ORGANIC!!!
7
Soil Formation
Organic living, or once living
(Technically, it means made of carbon atoms)
Buildings
Cars
Televisions
Volcanoes
- All of these are NOT living!
- All of these are NOT made of carbon
- All of these are INORGANIC!!!
8
Soil Formation
Broken down rock particles are called
SEDIMENTS
SEDIMENTS
9
Soil Formation
Sediments come in three basic sizes
The size of the particles in soil is called
TEXTURE
10
Soil Formation
Sediments come in three basic sizes
Very large particles has large air spaces in
between, which dont hold water very well
SAND
Medium particles creates some space for air,
but also holds some water
SILT
Very small particles, close together allows no
space for air holds too much water
CLAY
11
Soil Formation
The type of soil in a certain region depends on
several factors
a FACTOR is something that contributes or
influences something else.
Some FACTORS of good grades are - studying -
participating - doing homework - learning
from mistakes
12
Soil Formation
The type of soil in a certain region depends on
several factors
a) the type of rock being weathered
13
Soil Formation
The type of soil in a particular area depends on
several factors
b) the type of weathering being done
by force
mechanical
The broken pieces have the same composition as
the originalrock.
14
Soil Formation
The type of soil in a particular area depends on
several factors
b) the type of weathering being done
by chemical change
The broken pieces have a different composition
from the original rock.
15
Soil Formation
The type of soil in a particular area depends on
several factors
c) Mostly it depends on the type of climate
in a region, which affects weathering.
Click here to see an animation on how soil forms
gradually, sometimes over hundreds of years.
16
Soil Formation
The more rain (water) there is, the more
weathering that takes place in the soil.
-- Wet areas have soils with different size
particles, which makes the soil healthy.
-- Too wet, and all the particles turn to
clay, which is too small. The
sediments are too closely packed, and
dont provide any space in between for air,
animals, or plant roots in the soil.
-- Too dry, and the soil doesnt get small
enough. The sandy soil has too much
space in between the particles, so
water drains right through.
17
Soil Formation
The more rain (water) there is, the more
weathering that takes place in the soil.
-- more water makes deeper layers (horizons)
than soils which have only a little rain.
-- deserts have shallow layers, because not
a lot of weathering takes place.
Therefore. bedrock is closer to the
surface.
-- rainforests have much deeper layers,
because the rock has weathered more.
The bedrock is much further down.
18
Soil Formation
The more rain (water) there is, the more
decomposition that takes place in the soil.
-- water helps make more humus.
-- not enough water means the dead things
dont add to the soil as quickly.
-- too much water means the soil may become
leached of nutrients.
19
Soil Formation
A drawback of more water is that it leaches
thesoil of nutrients much faster.
-- leach means to dissolve and remove.
-- a coffee maker drips water through solid
particles. The water leaches away the
flavor and pulls it down into the pot.
-- leaching removes the nutrients from the
topsoil and carries them down to the
C horizon where plants cant reach
them.
20
Soil Formation
Heat also contributes to soil formation. More
heat speeds up chemical weathering of soil
-- in warm, wet areas the rocks break down
faster and smaller because heat speeds
up chemical reactions.
-- warm, wet areas heat speeds up the rate of
decomposition, mixing dead things into
the soil more
-- cold slows down chemical reactions, but
does add to mechanical weathering by
contributing to ice-wedging in really
cold places.
21
Soil Formation
It is a combination of hot or cold temperatures,
and a combination of wet or dry factors, which
contribute to soil formation.
Hot and dry produces sandy soils, like a desert
22
Soil Formation
It is a combination of hot or cold temperatures,
and a combination of wet or dry factors, which
contribute to soil formation.
Hot and dry produces sandy soils, like a desert
Hot and wet produces leached soils, like in a
rainforest.
23
Soil Formation
It is a combination of hot or cold temperatures,
and a combination of wet or dry factors, which
contribute to soil formation.
Hot and wet produces leached soils, like in a
rainforest.
Warm and wet makesMediterranean climate,or
southern forests.
24
Soil Formation
It is a combination of hot or cold temperatures,
and a combination of wet or dry factors, which
contribute to soil formation.
Cool and wet producesa northern forest climate.
Warm and wet makesMediterranean climate,or
southern forests.
25
Soil Formation
It is a combination of hot or cold temperatures,
and a combination of wet or dry factors, which
contribute to soil formation.
Cool and wet producesa northern forest climate.
Cool and dry producesa prairie /
grasslandclimate.
26
Insects
Soil Importance
Why is soil so important?
ANIMALS NEED SOIL.
Fungi and bacteria
Soil provides a home for thousands of different
types of animals
Burrowing mammals
Worms
27
Soil Importance
Why is soil so important?
PLANTS NEED SOIL.
Soil provides plants all the things they need to
survive and grow
Minerals
Water
Space
28
Soil Importance
Plants remove CO2, and make oxygen.
Why is soil so important?
HUMANS NEED PLANTS. PLANTS NEED SOIL.
Plants give us food, or they are food for our
food (cows eat grass?)
Plants make most of the energy for the world.
29
Soil Importance
Why is soil so important?
Without plants storing the energy of the sun in
their bodies, there would be no energy on the
planet.
-- There would be no food to eat.
-- There would be no electricity, gas for
engines, plastic materials, heat for houses,
etc.
30
Soil Importance
Why is soil so important?
SOIL STORES WATER.
Even though water covers 75 of the planet, only
1 is fresh water the rest is too salty
31
Soil Importance
Why is soil so important?
SOIL STORES WATER.
Out of that 1, only 1 is liquid the rest is
frozen as glaciers and icebergs.
32
Soil Importance
Why is soil so important?
SOIL STORES WATER.
Out of that 1, only 1 is drinkable the rest
is polluted in lakes and rivers.
33
Soil Importance
Why is soil so important?
SOIL STORES WATER.
The remaining 1 is in the soil
it is called GROUNDWATER
34
Soil Conservation
Conserve means to save for later
EROSION
The process of carrying sediments (soil) from one
location to another
Erosion destroys or removes soil.
35
Soil Conservation
Conserve means to save for later
EROSION
We need to prevent erosion as best we can, to
conserve this important resource.
36
Soil Conservation
Conserve means to save for later
COVER PLANTS or CROPS
Plant roots hold down soil and prevent erosion.
- Dont walk off trails it kills plants,
exposing soil
- Dont pull weeds - if you pull, replace with
seeds for
new plants
37
Soil Conservation
Conserve means to save for later
TERRACING