The Nervous System
1 / 30
Title:
The Nervous System
Description:
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System the center of all thought, learning and memory Functions of the Nervous System the center of all thought, learning ... –
Number of Views:48
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Nervous System
1
The Nervous System
2
Functions of the Nervous System
- the center of all thought, learning and memory
3
Functions of the Nervous System
- the center of all
- thought, learning and
- memory
- regulates and
- maintains
- homeostasis (a state of balance)
- examples body temperature, heart rate,
respiration, digestion
4
Functions of the Nervous System
- the center of all
- thought, learning and
- memory
- regulates and
- maintains homeostasis
- (a state of balance)
- examples body
- temperature, heart rate, respiration, digestion
- keeps us in touch with our internal and external
environment
5
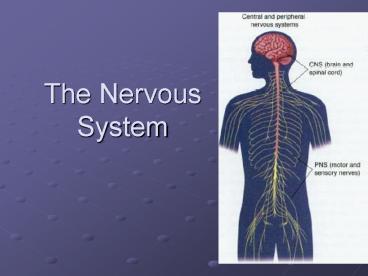
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous
- System- brain and
- spinal cord
6
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System- brain and spinal cord
- Three Main Parts of Brain
- Cerebrum-
- interprets input from
- senses and controls
- voluntary muscles
7
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System- brain and spinal cord
- Three Main Parts of Brain
- Cerebrum- interprets
- input from senses and
- controls voluntary
- muscles
- Cerebellum- coordinates
- actions of muscles and
- helps keep your balance
8
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System- brain and spinal cord
- Three Main Parts of Brain
- Cerebrum- interprets
- input from senses and
- controls voluntary muscles
- Cerebellum- coordinates
- actions of muscles and
- helps keep your balance
- Brainstem- controls
- homeostasis and
- coordinates involuntary
- muscles
9
What is this part of the brain called?
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Brain stem
- Spinal cord
1 2 3 4 5
10
What is the function of the brain stem?
- Controls homeostasis voluntary muscles
- Controls senses voluntary muscles
- Controls balance coordinates muscles
- Controls homeostasis involuntary muscles
1 2 3 4 5
11
When you feel hungry, what function is your
nervous system trying to carry out?
- Maintaining homeostasis
- Moving your body
- Sensing your environment
- Keeping your balance
1 2 3 4 5
12
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous
- System- connects the
- Central Nervous System
- to the rest of the body
13
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System- connects the Central
Nervous System to the rest of the body - Two Groups
- Somatic nervous system-
- controls voluntary actions
- and input from senses
- (sound, sight, touch, etc.)
14
Two Divisions of the Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System- connects the Central
Nervous System to the rest of the body - Two Groups
- Somatic nervous system-
- controls voluntary actions and
- input from senses (sound,
- sight, touch, etc.)
- Autonomic nervous system-
- controls homeostasis by
- regulating the heart, breathing,
- and digestion without
- conscious thought
15
Which division of the nervous system is made up
of the brain spinal cord?
- Autonomic nervous system
- Somatic nervous system
- Central nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
1 2 3 4 5
16
Which part of the Peripheral Nervous System
controls processes that maintain homeostasis
without you even thinking about it?
- Autonomic nervous system
- Somatic nervous system
- Central nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
1 2 3 4 5
17
Nerve cells are called neurons
- Impulse- a message carried by a neuron
18
Nerve cells are called neurons
- Impulse- a message carried by a neuron
- Synapse- the small space that an impulse jumps
between neurons
19
Types of Neurons
- Sensory neurons in the skin, muscles, joints,
and organs that can sense pressure, temperature,
and pain
20
Types of Neurons
- Sensory neurons in the skin, muscles, joints,
and organs that can sense pressure, temperature,
and pain - neurons in nose tongue sense tastes and smells
- neurons in inner ear
- sense sounds
- rods and cones in eye
- sense sight
21
Types of Neurons
- Motor neurons stimulate muscle cells throughout
the body
22
Types of Neurons
- Motor neurons stimulate muscle cells throughout
the body - includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm,
intestines, and bladder
23
What is an impulse?
- A nerve cell
- A message carried by neurons
- The space between two neurons
- A reflex
1 2 3 4 5
24
What is this structure called?
- Axon
- Synaptic terminal
- Nucleus
- Dendrite
1 2 3 4 5
25
What does a motor neuron stimulate?
- Brain cells
- Sensory organs
- Muscle cells
- Sensory neurons
1 2 3 4 5
26
Types of Neurons
- Interneurons connect other neurons
27
Types of Neurons
- Interneurons connect other neurons
- all neurons in the central nervous system (brain,
spinal cord) are interneurons
28
Reflex
- Reflex- an involuntary
- response to a stimulus
- (change in environment)
- that allows the body to
- respond quickly without
- thinking about it.
29
What is a change in the environment that your
body responds to called?
- Stimulus
- Response
- Reflex
- Sense
1 2 3 4 5
30
Which is not true about a reflex?
- It is a quick response.
- It is voluntary.
- It does not require conscious thought.
- It is a response to an external stimulus.
1 2 3 4 5