Momentum - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Momentum
Description:
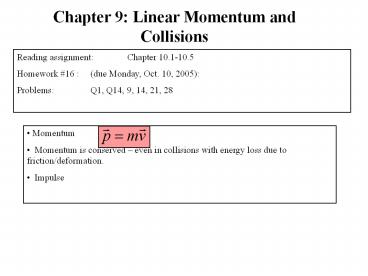
Chapter 9: Linear Momentum and Collisions Reading assignment: Chapter 10.1-10.5 Homework #16 : (due Monday, Oct. 10, 2005): Problems: Q1, Q14, 9, 14, 21, 28 – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:60
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Momentum
1
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
Reading assignment Chapter 10.1-10.5 Homework
16 (due Monday, Oct. 10, 2005) Problems Q1,
Q14, 9, 14, 21, 28
- Momentum
- Momentum is conserved even in collisions with
energy loss due to friction/deformation. - Impulse
2
Black board example 9.3
- You (100kg) and your skinny friend (50.0 kg)
stand face-to-face on a frictionless, frozen
pond. You push off each other. You move
backwards with a speed of 5.00 m/s. - What is the total momentum of the
you-and-your-friend system? - What is your momentum after you pushed off?
- What is your friends speed after you pushed off?
3
(No Transcript)
4
Impulse (change in _________________)
A change in _________ is called impulse
During a collision, a force F acts on an object,
thus causing a change in momentum of the object
For a constant (average) force
Think of hitting a soccer ball A force F acting
over a time Dt causes a change Dp in the momentum
(velocity) of the ball.
5
Black board example 10.1
- A soccer player hits a ball (mass m 440 g)
coming at him with a velocity of 20 m/s. After it
was hit, the ball travels in the opposite
direction with a velocity of 30 m/s. - What impulse acts on the ball while it is in
contact with the foot? - The impact time is 0.1s. What is the acting on
the ball?
6
Elastic and inelastic collisions in one dimension
________________ is conserved in any collision,
elastic and inelastic. ___________________ is
only conserved in elastic collisions.
Perfectly inelastic collision After colliding,
particles __________________. There is a loss of
kinetic energy (deformation). Inelastic
collisions Particles _________________ with
some loss of kinetic energy. Perfectly elastic
collision Particles __________________ without
loss of kinetic energy.
7
Perfectly _____________ collision of two
particles (Particles stick together)
Notice that p and v are vectors and, thus have a
direction (/-)
There is a loss in kinetic energy, Eloss
8
Perfectly _________ collision of two
particles (Particles bounce off each other
without loss of energy.
Momentum is ____________
Energy is _____________
9
For elastic collisions in
Suppose we know the initial masses and
velocities. Then
(10.38) (10.30)
(10.39) (10.31)
10
Black board example 9.2
- Two carts collide elastically on a frictionless
track. The first cart (m1 1kg) has a velocity
in the positive x-direction of 2 m/s the other
cart (m 0.5 kg) has velocity in the negative
x-direction of 5 m/s. - Find the speed of both carts after the collision.
- What is the speed if the collision is inelastic?
- How much energy is lost in the inelastic
collision?
11
Black board example 9.5
Ballistic Pendulum
- In a ballistic pendulum a bullet (0.005 kg) is
fired into a block (1.0 kg) that is suspended
from a light string. The block (with the bullet
stuck in it) is lifted up by 0.05 m. - What is the speed of the combined bullet/pendulum
right after the collision? - Find the initial speed of the bullet?
- Find the loss in mechanical energy due to the
collision
12
_______________ collisions (Two particles)
Conservation of momentum
Split into components
If the collision is ____________, we can also use
conservation of energy.
13
Black board example 9.3
Accident investigation. Two automobiles of equal
mass approach an intersection. One vehicle is
traveling towards the east with 29 mi/h (13.0
m/s) and the other is traveling north with
unknown speed. The vehicles collide in the
intersection and stick together, leaving skid
marks at an angle of 55º north of east. The
second driver claims he was driving below the
speed limit of 35 mi/h (15.6 m/s).
13.0 m/s
??? m/s
Is he telling the truth? What is the speed of the
combined vehicles right after the
collision? How long are the skid marks (mk 0.5)