Principles of Physical Development - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Principles of Physical Development
Description:
Title: No Slide Title Author: Computing Services Last modified by: Pamela Schuetze Created Date: 2/23/2001 4:53:27 PM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:31
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Principles of Physical Development
1
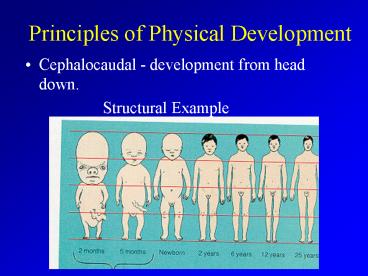
Principles of Physical Development
- Cephalocaudal - development from head down.
- Structural Example
2
Cephalocaudal DevelopmentFunctional Example
3
Principles of Physical Development
- Proximodistal development from inside out
- Mass-to-specific gross motor skills (large
muscles) develops first followed by fine motor
(small muscles) skills
4
Growth
- Newborn 20 inches long 7 1/2 pounds
- 1 inch per month
- ½ adult height by age 2
- double weight by 4 months, triple by 12 months
- Head Circumference
- Fontanels
- Ossification
5
Growth
- Adolescence
- Puberty growth spurt - age 9 for girls, 11 for
boys - Sexual maturation
6
Stages of Puberty
- Prepubescent Stage no longer a child but not
yet an adolescent. Secondary sex characteristics
begin to appear, but the reproductive organs are
not yet fully developed. - Pubescent Stage dividing line between
childhood and adolescence. Signs of sexual
maturity appear - the menstrual cycle in girls
and the first nocturnal emissions in boys.
Secondary sex characteristics continue to
develop. Gametes are produced (not in the
quantity/regularity of Fully mature sex organs). - Postpubescent Stage Secondary sex
characteristics become well developed and sex
organs begin to function in a mature manner.
7
Male Secondary Sex Characteristics
- Pubic hair appears about one year after the
testes and the penis have started to increase in
size - Facial/body hair appear when the pubic hair has
almost completed its growth. - Muscles increase markedly in size and strength.
- Voice changes begin after some pubic hair has
appeared. Voice breaks are common when maturing
is rapid. - Heightened Emotions Moodiness, sulkiness, temper
outbursts, anxiety and irritability. Testosterone
can also trigger a marked increase in aggressive
behavior.
8
Developmental Order - Males
9
Female Secondary Sex Characteristics
- Hips become wider and rounder due to enlargement
of the pelvic bone and development of
subcutaneous fat. - Breasts shortly after the hips start to
enlarge, the breasts begin to develop. - Hair pubic hair appears. Auxillary hair usually
begins to appear after the first menstrual cycle. - Voice becomes fuller and more melodious.
- Heightened Emotions Moodiness, sulkiness,
temper outbursts and a tendency to cry at the
slightest provocation These moods are especially
common during the premenstrual and early
menstrual periods.
10
Developmental Order - Females
11
Growth
- Early Adulthood
- height remains constant
- muscle tone/strength peaks in late teens/20s
12
Growth
- Middle Adulthood
- loss of fat and collagen in skin tissues
- aging spots
- thinner,graying hair
- lose 1/2 inch per decade in height, gain weight
- bone density begins decreasing
13
Menopause
- Peri-menopause transitional stage of two to ten
years before complete cessation of the menstrual
period (menopause). Age 35 to 50 years. - decreasing levels of estrogen
- irregular menstrual periods
- Menopause when a woman has gone through 12
months without menstruation (age 50) - hot flashes, headaches, dizziness, heart
palpitations, joint pain, osteoporosis
14
Growth
- Later Adulthood
- weight loss
- osteoporosis
- osteoarthritis
15
Brain Development
- Human brain most functional and best-organized
3 pounds of matter in universe. - Part of Central Nervous System
- Controls voluntary and involuntary activities
- 2 Hemispheres with 4 lobes
16
Development of Brain
17
Brain
18
Lobes
- Occipital lobe vision
- Temporal lobe speech/language and hearing
- Parietal lobe sensory motor processes
- Frontal lobe critical thinking
19
Nervous System Development
20
The Birth and Growth of Neurons
- Most neurons formed halfway through gestation
- Virtually no synaptic connections
- it is experience and interaction with the
environment that forms the synaptic connections - 83 of dendritic growth (connections between
synapses) occurs after birth
21
Photographs of Human Fetal Brain Development
Lateral view of the human brain shown at
one-third size at several stages of fetal
development. Note the gradual emergence of gyri
and sulci.
22
Childhood
- Synaptogenesis most occurs through 2nd year of
life - Myelination
- Lateralization
- Triples in weight by age 3
23
Use it or lose it Natural Selection of Brain
Wiring
- Exposure to enriched environments with extra
sensory and social stimulation enhances the
connectivity of the synapses - However, children and adolescents can lose up to
20 million per day when not stimulated
24
Adolescence
- Brain is full adult weight by age 16
- Continued myelination
25
Aging Brain
- Loss of neurons
- Diminished functioning in remaining neurons
- Changes in tissue surrounding neurons
- Declining levels of neurotransmitters
- Senile plaques
26
Brain Weight During Development and Aging
27
Chronic Brain Disorders
- Dementia general loss of intellectual abilities
- Alzheimer's brain atrophy neurofibrillary
tangles
28
Themes of Development
- Continuity vs. Discontinuity
- Early vs. Later Experiences
- Nature vs. Nurture
- Critical Periods






























![[PDF] Orthopedic Physical Assessment (Orthopedic Physical Assessment (Magee)) 6th Edition Full PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10084240.th0.jpg?_=20240723111)