Qualitative Research - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Qualitative Research
Description:
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Last modified by: Dr.C Created Date: 1/1/1601 12:00:00 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Other titles – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:72
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Qualitative Research
1
Qualitative Research
2
Case Study 1 IS 2008-9
How to Create an Immersive Environment for
Primary Literacy.
- Production of a Demonstrator and presented to
teachers. Discussion. Voice recording made. - Production of Prototype 1 and presented to
teachers. Discussion. Voice recording made.
Questionnaire administered (Open and Closed). - Production of Prototype 2 and presented to
teachers. Voice recording made. Questionnaire
administered (Open and Closed). - Deployment with Children, Observations made.
- Data analysis, Hypothesis formation.
3
Case Study 2 IS 2009-10
Visual Semiotics in Games How does visual
content influence players movement and choices
- Questionnaire Administered
- Observations
- Player played 2 x 2 minutes of Unreal. Video
recording. Researcher made notes. - Movie replayed and researcher asked player to
explain choices and movement. Audio Recording. - Next .. Data analysis
4
The Data generated in both Case Studies.
- Text response to open questionnaire items
- Text written by researcher during observations
- Video recordings
The Role of the Researcher.
- Present in the generation of data
- Can influence the generation of data
- Is involved in the subjects activities
5
Aims of Qualitative Research
- Understand the phenomena from the point of view
of the research participants - Interpret experiences and meanings of people
- Discover themes and relationships and key words
to formulate closed questions.
6
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
- Participants selected purposefully not randomly
- Involves behaviour of people, opinions and
feelings - Uses details of individual cases in gaining
understanding - Researcher is a participant observer
7
When to use Qualitative Methods
- Concepts need to be developed (little previous
research) - Phenomena cannot be reduced to numerical
variables - Need for novel researcher-devised framework
8
Data, Sampling and Analysis
- Data Types Text response to questionnaire,
transcripts of observations, screen-shots video
recordings - Purposive sampling to maximize variation
- Snowball Sampling Select a sample and ask them
to recommend next sample - Data processing summary, simplification,
abstraction - Data display tables, charts, networks
9
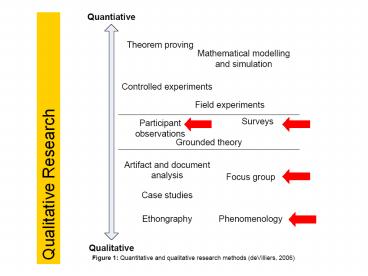
Qualitative vs. Quantitative.
Meanings derived from numbers. Meanings expressed through words.
Numerical data. Rich, interesting, data.
Analysis conducted through the use of diagrams and statistics. Analysis conducted through categorisation into themes
10
Analysing Qualitative Data Case Study 1
Example. Researchers analysis of her own
observation notes/transcripts.
- First reading of transcripts Look for themes
emerging. - Second reading Look for occurrences of each
theme in each transcript. Identify concepts. - Look for relationships between themes.
11
Analysing Qualitative Data Case Study 1
Themes from the researchers Observation
Transcripts
(Item) Theme Comments
(24) used quit clock
(2) understood how to select a lesson
(8) use of floor target
(66) expressed enjoyment
(9) engaged with spellings
(10) completed spellings
(14) read static instruction
(17) used F2
12
Analysing Qualitative Data Case Study 1
Relationships between Concepts abstracted from
players.
Fun learning Control Exciting Adventure
Fun 10 9 3
Learning 7 5 6
Control 2 4
Exciting 6
Adventure
13
Mixed Mode Research
Uses both Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches
- Numbers can add precision to words and narrative
- Words and images can add meaning to numbers
E.G. Qualitative research is used to create a
theory. Quantitative research is used to test
that theory
E.G. Quantitative research could be used to
classify behaviour, then qualitative research
could investigate the intentions of the people
who showed that behaviour.
14
The Questionnaire
- Cost Effective
- Familiar to Most People
- Reduce Bias
- Low response rate
- Cannot probe responses
- Respondent is unknown
-
15
General Guidance
- Clarify Goals How will you use the data?
- Justify the purpose of each individual question
- Keep it short (two pages?)
- Begin with light and interesting items
- Place the most important items in the first half
- Try it out on a small sample of the target
population
16
Case Study 1 Justification of Questions
Design of Questionnaire presented to the Teachers.
1. I use Computer Software as an aid to delivering literacy in class It is important to understand how many teacher do not use software because it would affect the reliability and therefore the validity of the results
5 The proposed ideas for this EIE is relevant to teaching literacy at KS2 Are the ideas about content relevant for the target audience?
11 The EIE theme is gender neutral It is important that neither sex are disadvantaged by the chosen theme which would affect the learning outcomes.
17
Workflow
- Define Research Aims
- Identify Population and Sample
- How to collect replies?
- Questionnaire Design (including Pilot Survey)
- Main survey
- Analysis
18
Questionnaire Design
- Ask Open Ended Questions to generate key words
- Consider your mind map
- Consider your analysis approach t-test,
chi-squared - Write your closed questions (types will follow).
19
Question Types Open vs. Closed
What do you think are the reasons for football
hooliganism?
Do you think football hooliganism is caused by
(tick if appropriate) Lack of discipline at home
Players behaviour on pitch Family breakdown
Youth unemployment Poor schooling Violence on
T.V. Other (please specify)
20
Single vs. Multiple Response
Which of the following means do you use to travel
to college? Bus Car Bike
What is your most usual means of travelling to
college? (Tick one box only) Bus Car Bike
21
Ranked Response
Place in order of importance to you the following
features of a camping holiday (Indicate by
numbering from 1-5 in order where 1 is the most
important) Open air Mobility Cost People
Atmosphere
22
Rated Response
(Circle the number under the initials that
applies. VIVery important IImportant
NNeutral UUnimportant VUVery Unimportant).
Indicate your view of the following aspects of a
camping holiday
VI I N U VU
Community Life 5 4 3 2 1
Low Cost 5 4 3 2 1
Outdoor Life 5 4 3 2 1
23
Question Wording
Some general rules can be stated on question
wording Be concise and unambiguous Avoid
double questions Avoid questions involving
negatives Ask for precise answers Avoid
leading questions
24
Precise Answers
Ask for precise answers if you think the
information is available and there are no other
constraints (e.g. too intrusive on privacy). For
example Give your age on lst September 2001
years is preferable to Are you Under
18 . 18-65 ... Over 65
25
Question Wording
- Evokes the truth. Questions must be
non-threatening. - Asks for an answer on only
one dimension. - Can accommodate all possible
answers. What brand of computer do you own?
A. IBM PC B. Apple -
Has mutually exclusive options. Where did you
grow up? A. country
B. farm C. city - Produces
variability of responses Are you against drug
abuse? (circle Yes or No)
26
Question Wording
- Follows comfortably from the previous question.
- Does not presuppose a certain state of affairs
Are you satisfied with your current auto
insurance? (Yes or No) - Does not imply a
desired answer. (Leading Question) - Does not use
emotionally loaded or vaguely defined words.
(e.g., most, least, majority) - Does not use
unfamiliar words or abbreviations. (CPU, GPU) -
Is not dependent on responses to previous
questions. Avoid Branching 1. Do you currently
have a life insurance policy ? (Yes or No) If
no, go to question 3 2. How much is your annual
life insurance premium ? - Does not ask the
respondent to order or rank a series of more than
five items