?. Results and discussion
1 / 1
Title: ?. Results and discussion
1
W incorporated carbon nanocomposite films
prepared by hybrid ion beam deposition
Ai-Ying Wanga ,(aywang_at_kist.re.kr), Hyo-Shin
Ahna, Kwang-Ryeol Leea, Jae-Pyoung Ahnb aFuture
Technology Research Division, Korea Institute of
Science and Technology, Seoul, 130-650, South
Korea bNano-Materials Research Center, KIST,
South Korea
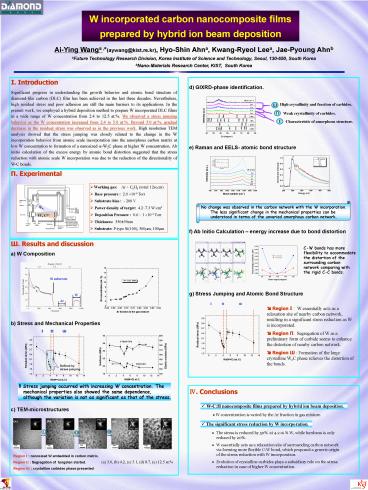
?. Introduction Significant progress in
understanding the growth behavior and atomic bond
structure of diamond-like carbon (DLC) film has
been achieved in the last three decades.
Nevertheless, high residual stress and poor
adhesion are still the main barriers to its
applications. In the present work, we employed a
hybrid deposition method to prepare W
incorporated DLC films in a wide range of W
concentration from 2.4 to 12.5 at.. We observed
a stress jumping behavior as the W concentration
increased from 2.4 to 5.0 at.. Beyond 5.0 at.,
gradual decrease in the residual stress was
observed as in the previous work. High resolution
TEM analysis showed that the stress jumping was
closely related to the change in the W
incorporation behavior from atomic scale
incorporation into the amorphous carbon matrix at
low W concentration to formation of a nanosized
?-W2C phase at higher W concentration. Ab initio
calculation of the excess energy by atomic bond
distortion suggested that the stress reduction
with atomic scale W incorporation was due to the
reduction of the directionality of W-C bonds.
- d) GIXRD-phase identification.
- e) Raman and EELS- atomic bond structure
?
Weak crystallinity of carbides.
?
Characteristic of amorphous structure.
?. Experimental
- ? Working gas Ar C6H6 (total 12sccm)
- ? Base pressure 2.0 ?10-6 Torr
- ? Substrate bias - 200 V
- ? Power density of target 4.27.3 W/cm2
- ? Deposition Pressure 0.6 1 ?10-4 Torr
- ? Thickness 35050nm
- ? Substrate P-type Si(100), 500?m, 100?m
No change was observed in the carbon network with
the W incorporation. The less significant change
in the mechanical properties can be understood
in terms of the unvaried amorphous carbon network.
- ?. Results and discussion
- W Composition
- b) Stress and Mechanical Properties
C-W bonds has more flexibility to accommodate the
distortion of the surrounding carbon network
comparing with the rigid C-C bonds.
Si substrate
C
W
Ar
? Region ? W essentially acts as a relaxation
site of nearby carbon network, resulting in a
significant stress reduction as W is
incorporated. ? Region ? Segregation of W as a
preliminary form of carbide seems to enhance the
distortion of nearby carbon network. ? Region ?
Formation of the large crystalline W2C phase
relieves the distortion of the bonds.
Defined by stress jumping
!! Stress jumping occurred with increasing W
concentration. The mechanical properties also
showed the same dependence, although the
variation is not as significant as that of the
stress.
?
?
?
Region ? nanosized W embedded in carbon matrix.
Region ? Segregation of tungsten
started. Region ? crystalline carbides phase
presented
(a) 3.0, (b) 4.2, (c) 5.1, (d) 8.7, (e) 12.5 at.