Brain Anatomy - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
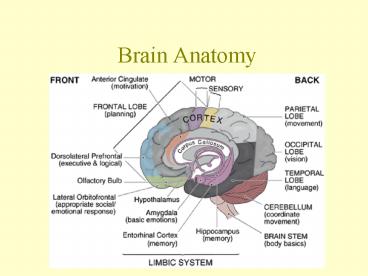
Brain Anatomy
Description:
Brain Anatomy Dura Mater Superficial Fuses brain to skull Arachnoid Reduces friction Filled with CSF; shock absorber Pia Mater Very Vascular; needs a lot of oxygen ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:259
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Brain Anatomy
1
Brain Anatomy
2
Meninges - 3 layers
- Dura Mater
- Superficial
- Fuses brain to skull
- Arachnoid
- Reduces friction
- Filled with CSF shock absorber
- Pia Mater
- Very Vascular needs a lot of oxygen due to high
metabolic rate of neurons
3
- Cerebrum
- Diencephalon
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla Oblongata
- Cerebellum
Gross Anatomy 6 Regions
4
Precentral gyrus Motor Strip Postcentral gyrus
Sensory Strip Central Sulcus separates
frontal from parietal lobe
Gyri elevated ridges Sulci furrows
5
(No Transcript)
6
Corpus Callosum
- Bridge between Right and Left Hemispheres
- Enables Right and Left sides to communicate with
each other - Problems
- Split Brain Syndrome
7
- Functions
- Cognition and Memory
- Prefrontal Area involved with intellect,
complex learning abilities and personality plays
a role in mood feelings of frustration and
anxiety are formed here - Gatekeeper Judgment, critical thinking and
reasoning skills - Problems
- Relationships between events, memory loss,
behavior disorders, Inappropriate social and/or
sexual behavior - Prefrontal lobotomy 1950s
Cerebrum Frontal Lobe
8
Motor Areas
- Function
- Motor Strip Control voluntary motor function
- Premotor Cortex skill area controls learned
motor skills
Precentral gyrus
- Brocas area
- Left hemisphere
- Directs the muscles of tongue, throat and lips
when speaking - Becomes active as we plan to speak
- Syntax and grammar rules are remembered
9
Try This!!
Yes the bick. I would say tha the vick daysis
nosis or chipickers. Represents problems with
Brocas area!! Only found in the left hemisphere
of the frontal lobe Problems will affect our
ability to pronounce words, form sentences,
speaking becomes a problem
10
Sensory Areas
Located in parietal, temporal and occipital lobes
11
Parietal Lobe
- Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- Spatial Discrimination ability to identify the
body region being stimulated - Area is identified by receiving information from
skin sensory receptors and proprioceptors in
skeletal muscles. - Try This!!
- Problems
- Inability to locate and recognize body parts
disorientation - Cant discriminate between different sensory
stimuli
12
- Located posterior to Primary Somatosensory Cortex
- Major function to analyze different sensory
stimuli (temp, pressure - Evaluate what the body is feeling
- Try this!!
- Different senses are distributed through all lobes
Somatosensory Area
13
- Auditory Areas sound waves are interpreted
- Gustatory cortex perception of taste
- Olfactory Cortex interprets chemical odors
- Language
- Wernickes area called the speech area
- Language comprehension
- Understanding jokes
- Reading unfamiliar sounds
- Problems
- Hearing problems
- Aphasia inability to speak
Temporal Lobe
14
Occipital Lobe
- Visual Areas
- Receives stimuli from eyes
- Interprets information from past experiences
- Problems
- Loss of vision or seeing stars
- Cant recognize the object you see
15
Posterior Association Area
- Large region including parietal, temporal and
occipital lobes - Plays a role in recognizing faces, patterns, and
identifying surroundings - Also includes Wernickes area
16
Diencephalon
- Connects to cerebrum
- Includes
- Thalamus,
- Hypothalamus,
- Limbic system
- Pineal gland (epithalamus)
- Pituitary gland
17
Thalamus
Greek for Inner room
- Contains relay and processing centers
- Relay Station involved in memory process
- Sorts out information, edits
- Gateway to cerebrum
18
Hypothalamus
- Controls Body Homeostasis
- Autonomic Nervous System
- Influences BP
- HR (force and rate)
- Digestive tract motility
- Emotions
- Pleasure, fear, rage
- Sex Drive
- Body temperature regulation
- Food intake hunger
- Thirst (water balance)
- No blood-brain barrier
- Circadian rhythms
- Control of Endocrine
- (secrete ADH, oxytocin)
19
Hypothalamus and Pineal Gland
- Problems with hypothalamus
- Pineal Gland
- Problems
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Hypothermia
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sleep Disturbances
- Dehydration
- Part of epithalamus
- Secretes hormone melatonin
- Helps regulate Sleep-Wake Cycle
20
- Hypothalamus is heart of Limbic System Emotional
Brain - Contains Amygdala
- Recognizes angry or fearful facial expressions
- Contains Hippocampus
- Involved with learning, long-term memory and
storage - Problems
- H.M. Case Study STM to LTM
- Had difficulty remembering anything after his
surgery - Was able to learn new motor skills, despite not
being able to remember learning them
Limbic System
Ring
21
- Link between NS and Endocrine system
- Produces GH and TSH
- Posterior part of gland is a hormone storage area
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland -gt
22
Brain Stem Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata
- Primitive Brain
- Pathway between lower brain and spinal cord and
lower brain and higher brain functions
23
- Contains 2 pairs of sensory nuclei (Colliculi)
Auditory and Visual Reflex Centers I.e. rxns to
flashlight or loud noises - Motor nuclei for 2 cranial nerves (III, IV)
involved in eye movements - III Oculomotor eye movement
- IV Trochlear rotates eye up and down
- Cerebral Peduncles descending bundles of motor
nerve fibers connect to cerebellum - RAS center begins here Filters out repetitive
sensory stimuli. (99 of all stimuli is
ignored)
Midbrain
24
Colliculi of Midbrain
- Corpus Quadrigemini
- Superior Colliculi
- Visual Reflex Centers
- Follow movement with eye
- Associated with Cranial nerve III
- Inferior Colliculi
- Auditory Reflex
- Startle Reflex
Midbrain
25
Bridge Connects cerebellum to brain stem
cerebrum and S. cord Relay Center Cranial Nerves
(V-VIII) are attached here Respiratory Center
Involuntary Control of pace and depth of
breathing Problems Hyperventilation
Pons
Bridge
26
Connects Brain to S. cord relays info to
Thalamus Contains major centers for Autonomic
Regulation such as HR, Bp, respiration and
digestive activities Cardiac Center adjusts
force and rate of heart beat Vasomotor Center
regulates BP Respiratory Center controls rate
and depth of breathing with N. Fdbk loop in
pons. Controls other pleasant body Activities
vomit, hiccupps, cough, sneeze, swallow, and
gag Again no blood-brain barrier!
Medulla Oblongata
27
- Coordination fine tunes voluntary and
involuntary movement (Sports) - Receives stimuli from proprioceptors evaluate
body position - Maintains balance and posture
- Imbalances
- Ataxia Lack of coordination
- Tremors
- Alcohol affects motor skills reaction time
- Easily passes through blood-brain barrier
Cerebellum