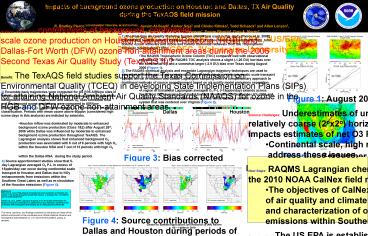
Figure 1: August 2006 RAQMS and Observed TOC - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Figure 1: August 2006 RAQMS and Observed TOC
Description:
Impacts of background ozone production on Houston and Dallas, TX Air Quality during the TexAQS field mission R. Bradley Pierce1 (GOVERNMENT PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:45
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Figure 1: August 2006 RAQMS and Observed TOC
1
Impacts of background ozone production on Houston
and Dallas, TX Air Quality during the TexAQS
field mission
R. Bradley Pierce1 (GOVERNMENT PRINCIPAL
INVESTIGATOR) Jassim Al-Saadi2, Amber Soja2 and
Chieko Kittaka2, Todd Schaack3 and Allen Lenzen3,
Kevin Bowman4, Jim Szykman5, Tom Ryerson6, Anne
M. Thompson7, Pawan Bhartia8, Gary A. Morris9
1NOAA/NESDIS, 2NASA/LaRC, 3UW /SSEC, 4NASA/JPL,
5US/EPA, 6NOAA/ESRL, 7PSU, 8NASA/GSFC,
9Valparaiso University
Requirement Provide information to air quality
decision makers and improve NOAAs national air
quality forecast capability Science What were
the contributions of background, continental
scale ozone production on Houston-Galveston-Brazo
ria (HGB) and Dallas-Fort Worth (DFW) ozone
non-attainment areas during the 2006 Second
Texas Air Quality Study (TexAQS II)? Benefit
The TexAQS field studies support the Texas
Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) in
developing State Implementation Plans (SIPs) for
attaining National Ambient Air Quality Standards
(NAAQS) for ozone in the HGB and DFW ozone
non-attainment areas.
- 1) The Real-time Air Quality Modeling System
(RAQMS) is used in this study Pierce et al,
2009. The RAQMS TexAQS analysis includes
assimilation of Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI)
total column ozone retrievals and ozone and
carbon monoxide retrievals from the Tropospheric
Emission Spectrometer (TES). - The RAQMS Tropospheric Ozone Column (TOC)
compares well with observational estimates of TOC
. The RAQMS TOC analysis shows a slight (-1.26
DU) low bias over the continental US and a
somewhat larger (-2.9 DU) bias over Texas during
August 2006 (Figure 1).
- 2) The RAQMS chemical analysis and ensemble
Lagrangian trajectory techniques are used to
characterize the amount of net ozone production
(P-L) that occurs during synoptic scale transport
prior to arrival in Houston and Dallas.
Lagrangian sampling offers a complimentary
approach to traditional methods of source
apportionment based on air quality model
emissions separation. - A region of Enhanced Lagrangian averaged O3 P-L
(gt15ppbv/day) extends across Texas from the
Louisiana Gulf Coast towards New Mexico on
September 2nd, 2006 and is associated with
north-northwesterly surface winds behind a
surface low pressure system that was centered
over Virginia (Figure 2).
Figure 1 August 2006 RAQMS and Observed TOC
- 3) Ensemble back trajectories were computed for
US EPA AIRNow sites in the Houston and Dallas
Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSA) to determine
background influences on Houston and Dallas O3.
Bias corrected MSA and Background ozone
predictions were compared to AIRNow observations
(Figure 3). Lagrangian averaged O3 P-L was used
for daily classification. Periods with mean ozone
above 60ppbv (considered high ozone days in this
analysis) are indicted by asterisks. - Houston inflow was dominated by moderate to
enhanced background ozone production (Class 12)
after August 28th, 2006 while Dallas was
influenced by moderate to enhanced background
ozone production throughout TexAQS. The
Lagrangian analysis shows that enhanced
background O3 production was associated with 6
out of 9 periods with high O3 within the Houston
MSA and 7 out of 15 periods with high O3 within
the Dallas MSA during the study period.
Dallas
Houston
Figure 2 September 2nd, 2006 Lagrangian averaged
O3 P-L
Figure 3 Bias corrected RAQMS MSA and Background
mean O3 vs AIRNow observations
- Science Challenges Underestimates of urban
photochemistry due to the - relatively coarse (2ox2o) horizontal resolution
of the RAQMS chemical analysis - impacts estimates of net O3 P-L within the urban
source regions. - Continental scale, high resolution modeling
studies should be conducted to - address these issues.
- Next Steps RAQMS Lagrangian chemical analyses
will be conducted during - the 2010 NOAA CalNex field mission.
- The objectives of CalNex are to address key
science questions at the Nexus - of air quality and climate change regarding
influences of long-range transport, - and characterization of ozone and aerosol
precursors and greenhouse gas - emissions within Southern California.
- Transition Path The US EPA is establishing a
system to allow air quality - planners to produce and access equivalent results
for locations of their choice. - Lagrangian photochemical sampling of CMAQ has
been developed and applied - to Baltimore, MD air quality studies Fairlie et
al, 2009.
4) Source apportionment studies show that 5-day
Lagrangian averaged O3 P-L in excess of
15ppbv/day can occur during continental scale
transport to Houston and Dallas due to NOy
enhancements from emissions within the Southern
Great Lakes as well as re-circulation of the
Houston emissions (Figure 4).
References Pierce, R. B., et al, (2009), Impacts
of background ozone production on Houston and
Dallas, TX Air Quality during the TexAQS field
mission, J. Geophys. Res., 114, D00F09,
doi10.1029/2008JD011337 Fairlie, T.D., et al.,
(2009), Lagrangian Sampling of 3-d Air Quality
Model Results for Regional Transport
Contributions to Sulfate Aerosol Concentrations
at Baltimore, MD, in Summer 2004, Atmospheric
Environment, doi10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.02.026
The views, opinions, and findings contained in
this study are those of the authors and should
not be construed as an official National Oceanic
and Atmospheric Administration or U.S. Government
position, policy, or decision.
Figure 4 Source contributions to Dallas and
Houston during periods of enhanced (Class 1)
background O3 P-L