Electrolysis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 50
Title:
Electrolysis
Description:
Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Mark Last modified by: Mark Created Date: 6/1/2004 9:49:38 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Company – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:230
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Electrolysis
1
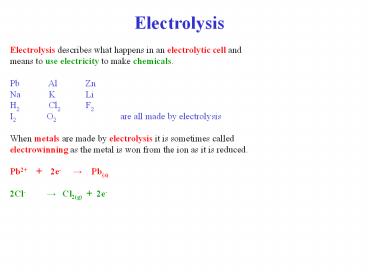
Electrolysis Electrolysis describes what
happens in an electrolytic cell and means to use
electricity to make chemicals. Pb Al Zn Na
K Li H2 Cl2 F2 I2 O2 are all made by
electrolysis When metals are made by
electrolysis it is sometimes called
electrowinning as the metal is won from the ion
as it is reduced. Pb2 2e- ?
Pb(s) 2Cl- ? Cl2(g) 2e-
2
Electrolysis of Aluminum Alcan Kitimat
B.C. Name of the Ore used Bauxite
Al2O3.3H2O Heating drives off the
water Al2O3.3H2O Heat ? Al2O3 3H2O Me
lting point of Bauxite is 2045 0C This is
too hot! Cryolite is added Lowers the melting
point to 1000 0C
3
DC Power -
C
C
Al2O3(l)
4
DC Power -
C
C
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
5
DC Power -
C
C
- reduction
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
6
DC Power -
C
C
- Reduction
Oxidation
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
7
DC Power -
C
C
- Reduction Cathode
Oxidation Anode
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
8
DC Power -
C
C
- Reduction Cathode
Oxidation Anode
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
9
DC Power -
C
C
- Reduction Cathode Al3 3e- ? Al(s)
Oxidation Anode
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
10
DC Power -
C
C
- Reduction Cathode Al3 3e- ? Al(s)
Oxidation Anode 2O2- ? O2 4e-
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
11
Liquid Al floats to the top and is removed.
DC Power -
C
C
- Reduction Cathode Al3 3e- ? Al(s)
Oxidation Anode 2O2- ? O2 4e-
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
12
Liquid Al floats to the top and is removed.
DC Power -
Oxygen gas
C
C
- Reduction Cathode Al3 3e- ? Al(s)
Oxidation Anode 2O2- ? O2 4e-
Al3 O2-
Al2O3(l)
13
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize.
K2SO4(aq)
14
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize. The Cathode will
stay inert because it already is reduced.
K2SO4(aq)
15
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize. The Cathode will
stay inert because it already is reduced.
DC Power -
Cu
Cu
2K SO42- H2O
K2SO4(aq)
16
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize. The Cathode will
stay inert because it already is reduced.
DC Power -
Cu
Cu
- Cathode Reduction
2K SO42- H2O
K2SO4(aq)
17
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize. The Cathode will
stay inert because it already is reduced.
DC Power -
Cu
Cu
- Cathode Reduction 2H2O 2e-?H2 2OH- -0.41 v
2K SO42- H2O
K2SO4(aq)
18
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize. The Cathode will
stay inert because it already is reduced.
DC Power -
Cu
Cu
- Cathode Reduction 2H2O 2e-?H2 2OH- -0.41 v
Anode Oxidation
2K SO42- H2O
K2SO4(aq)
19
You must look at the possible oxidation of H2O
SO42- Cu
Check out the reduction chart! S2O82- 2e-
? 2SO42- 2.01 v 1/2O2 2H(10-7M) ? H20
0.82 v Cu 1e- ? Cu(s) 0.52 v Cu2
2e- ? Cu(s) 0.34 v
Strongest Reducing Agent
20
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize. The Cathode will
stay inert because it already is reduced.
- Cathode Reduction 2H2O 2e-?H2 2OH- -0.41 v
Anode Oxidation Cu(s) ? Cu22e- -0.34 v
21
Non-Inert Electrodes You must understand that a
non-inert Anode might oxidize. The Cathode will
stay inert because it already is reduced.
- Cathode Reduction 2H2O 2e?H2(g)2OH- -0.41 v
Anode Oxidation Cu(s) ? Cu22e- -0.34 v
2H2O Cu(s) ? Cu2 H2 2OH- E0 -0.75 v
MTV 0.75 v
22
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
HCl(aq)
23
Analyze This Cell
Or it might look like this
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
Pourous membrane
HCl(aq)
24
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
25
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
Is this cell electrolytic or electrochemical?
26
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
Electrochemical- There is no power supply Cu
is higher and the cathode Zn is lower and the
anode.
27
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
Cathode Reduction No Cu2 to reduce!
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
Electrochemical- Cu is higher and the
cathode Zn is lower and the anode.
28
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
Cathode Reduction 2H 2e- ? H2(g) 0.00 v
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
Electrochemical- Cu is higher and the
cathode Zn is lower and the anode.
29
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
Cathode Reduction 2H 2e- ? H2(g) 0.00 v
Anode Oxidation What oxidizes? Zn H2O Cl-
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
Electrochemical- Cu is higher and the
cathode Zn is lower and the anode.
30
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
Cathode Reduction 2H 2e- ? H2(g) 0.00 v
Anode Oxidation Zn ? Zn2 2e- 0.76 v
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
Electrochemical- Cu is higher and the
cathode Zn is lower and the anode.
31
Analyze This Cell
0.76 v
Voltmeter
Zn
Cu
Cathode Reduction 2H 2e- ? H2(g) 0.00 v
Anode Oxidation Zn(s) ? Zn2 2e- 0.76 v
H H2O Cl-
HCl(aq)
2H Zn(s) ? Zn2 H2(g) E0 0.76 v
32
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Electrolyte Must
contain the ion of the metal that plates Ni
plating a Cu penny Anode Cathode Ele
ctrolyte
DC Power
33
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Electrolyte Must
contain the ion of the metal that plates Ni
plating a Cu penny Anode Ni Cathode E
lectrolyte
DC Power
Ni
34
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Electrolyte Must
contain the ion of the metal that plates Ni
plating a Cu penny Anode Ni Cathode Cu
Electrolyte
DC Power
Ni
Cu
35
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Electrolyte Must
contain the ion of the metal that plates Ni
plating a Cu penny Anode Ni Cathode Cu
Electrolyte Ni(NO3)2
DC Power
Ni
Ni2 NO3-
Cu
36
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Electrolyte Must
contain the ion of the metal that plates Ni
plating a Cu penny Anode Ni Cathode Cu
Electrolyte Ni(NO3)2
DC Power -
Ni
Ni2 NO3-
Cu
37
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Electrolyte Must
contain the ion of the metal that plates Ni
plating a Cu penny Anode Ni Cathode Cu
Electrolyte Ni(NO3)2
DC Power -
Ni
- Reduction Cathode
Ni2 NO3-
Cu
38
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Must be
negative! Electrolyte Must contain the ion of
the metal that plates Ni plating a Cu
penny Anode Ni Cathode Cu Electrolyte
Ni(NO3)2
DC Power -
Ni
- Reduction Cathode Ni2 2e- ? Ni(s)
Ni2 NO3-
Cu
39
Electroplating Electroplating is the process of
reducing a metal on to the surface of
another. Anode Metal to be plated on top the
other metal Cathode The other metal to be
covered with the new metal Electrolyte Must
contain the ion of the metal that plates Ni
plating a Cu penny Anode Ni Cathode Cu
Electrolyte Ni(NO3)2
e-
DC Power -
Ni
- Reduction Cathode Ni2 2e- ? Ni(s)
Oxidation Anode Ni(s) ? Ni2 2e-
Ni2 NO3-
Cu
40
Silver plating a Loonie Anode Cathode E
lectrolyte
41
Silver plating a Loonie Anode Ag Cathode
Electrolyte
Ag
42
Silver plating a Loonie Anode Ag Cathode
Loonie Electrolyte
Ag
Loonie
43
Silver plating a Loonie Anode Ag Cathode
Loonie Electrolyte AgNO3
Ag
Loonie
Ag NO3-
44
Silver plating a Loonie Anode Ag Cathode
Loonie Electrolyte AgNO3
e-
e-
Ag
Loonie
- Reduction Cathode Ag 1e- ? Ag(s)
Oxidation Anode Ag(s) ? Ag 1e-
Ag NO3-
45
Electrorefining Electrorefining is the process
of purifying a metal by electrolysis. Impure
metal is oxidized at the anode and pure metal is
reduced at the cathode. This is the same as
electroplating. The Electrorefinning of
Lead Cominco Trail, B.C. Cathode
Anode Electrolyte
DC Power -
46
Electrorefining Electrorefining is the process
of purifying a metal by electrolysis. Impure
metal is oxidized at the anode and pure metal is
reduced at the cathode. This is the same as
electroplating. The Electrorefinning of
Lead Cominco Trail, B.C. Cathode
Pure Pb Anode Electrol
yte
DC Power -
47
Electrorefining Electrorefining is the process
of purifying a metal by electrolysis. Impure
metal is oxidized at the anode and pure metal is
reduced at the cathode. This is the same as
electroplating. The Electrorefinning of
Lead Cominco Trail, B.C. Cathode
Pure Pb Anode Impure Pb Ele
ctrolyte
DC Power -
48
Electrorefining Electrorefining is the process
of purifying a metal by electrolysis. Impure
metal is oxidized at the anode and pure metal is
reduced at the cathode. This is the same as
electroplating. The Electrorefinning of
Lead Cominco Trail, B.C. Cathode
Pure Pb Anode Impure Pb Ele
ctrolyte Pb(NO3)2
DC Power -
Pb2 NO3-
49
Electrorefining Electrorefining is the process
of purifying a metal by electrolysis. Impure
metal is oxidized at the anode and pure metal is
reduced at the cathode. This is the same as
electroplating. The Electrorefinning of
Lead Cominco Trail, B.C. Cathode
Pure Pb Anode Impure Pb Ele
ctrolyte Pb(NO3)2
DC Power -
Pb2 NO3-
- Reduction Cathode Pb2 2e- ? Pb(s)
50
Electrorefining Electrorefining is the process
of purifying a metal by electrolysis. Impure
metal is oxidized at the anode and pure metal is
reduced at the cathode. This is the same as
electroplating. The Electrorefinning of
Lead Cominco Trail, B.C. Cathode
Pure Pb Anode Impure Pb
Electrolyte Pb(NO3)2
DC Power -
Zn2Pb2 NO3-
- Reduction Cathode Pb2 2e- ? Pb(s)
Oxidation Anode Pb(s) ? Pb2 2e-
Au Cu