Side-Channel Attacks on Smart Cards - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Side-Channel Attacks on Smart Cards
Description:
Lavina Thong Last modified by: Lavina Thong Created Date: 3/7/2006 2:29:08 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Company: Universal Avionics Systems Corporation – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:161
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Side-Channel Attacks on Smart Cards
1
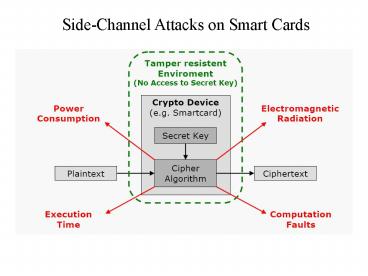
Side-Channel Attacks on Smart Cards
2
- Timing Analysis
- Cryptosystems take different amount of time to
process - different inputs.
- Performance optimisations in software
- Branching/condiational statements
- Caching in RAM
- Variable length instructions (multiply,divide)
- Timing measurements taken with various input data
can be - used to deduce internal workings.
3
Timing Analysis Example Repeated Square and
multiply of modular exponentiation
Input M, N, d (dn-1dn-2...d1d0)2 Output S
Md mod N S 1 for j n-1...0 do S S2 mod N
if (dj 1) then S SM mod N return S
4
Timing Analysis Counter-measure
Input M, N, d (dn-1dn-2...d1d0)2 Output S
Md mod N S 1 for j n-1...0 do S S2 mod N
T SM mod N if (dj 1) then S
T return S
5
- Timing Analysis
- Counter measures
- Implementing constant timing for all operations
- Add noise to the execution time.
- Prevent an attacker from learning the inputs to a
- vulnerable operation.
- Previous example
- S Md mod N (Can sign multiple Ms to
deduce d) - M Re. M mod N gt S M mod N
- (M is hidden from attacker)
- R-1S R-1RedMd R-1RMd Md mod N S
6
- Computational Fault Analysis
- Induce faults on computation by
- power supply
- clock frequency and duty cycle,
- working temparature
- UV lights
- microwaves
- ion beam
7
- Computational Fault Analysis
- Fault induced in CRT used to speed up RSA
signature - S Md mod N
- Sp Mdp mod p and Sq Mdq mod q
- dp d mod (p-1), dq d mod (q-1)
- S upSp uqSq mod N
- 2 signatures on same message, 1 good, 1 faulty
can - be used to factor N when exactly one of Sp or Sq
- is faulty.
- Sq Mdq mod q. Signature S will be invalid.
- p gcd(N,M- Se )
8
- Computational Fault Analysis
- Coutermeasure
- Results could be verified before exposed.
- Randomization by padding messages.
9
Power Analysis Simple Power Analysis (SPA)
Information about the operation is deduced
directly from tracing the global consumption
power of the chip Eg. DES key rotation Eg. RSA
exponentiation Differential Power Analysis
(DPA) Statistical analysis on power consumption
over several executions of the same algorithm
with different inputs Idea The average traces
on power consumption reduces noise and reveals
otherwise obscured small biases.
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
Conclusion Smart cards crypto is constrained by
the physical limitation of the microprocessor.
Implementation needs to take into account of
possible attacks. Counter measures taken for
attacks need to take into account the efficiency
of the implementation in practice.